SECONDARY SCHOOL PHILOSOPHY OF BALANCE
CONTENTS
FIRST PART
THE PHILOSOPHY OF BALANCE OF THE SOCIAL SCIENCES ... 2
|
1. Preface ... 2 2. Philosophy of Balance ... 4 2.1 Introduction
... 4 2.2 About God
(metaphysics) … 6 2.3 About basis
of being (ontology) … 9 2.4 About
cognition (gnoseology) ... 11 2.5 About correct
thinking (logic) … 14 2.6 How to live
(ethics) … 15 2.7 About the
State and the law … 18 2.8 About beauty
(aesthetics) … 22 3. Introduction to the history
of philosophy and mankind
.... 25 4. Religion . 26 4.1 Introduction
... 26 4.2 Hinduism. 26 4.3 Judaism ...
28 4.4 Christianity.
41 4.5 Buddhism ...
44 4.6 Islam … 49 5. History of philosophy ... 51 3.2 Chinese
philosophy … 51 5.2 Greek and
Roman philosophy … 53 5.3 Philosophy of
the middle ages … 61 |
5.4 Baroque philosophy
… 66 5.5 Philosophy of
the enlightenment … 70 3.5 Philosophy of
19th century … 76 3.5 Philosophy of
20th century … 88 6. Political and legal philosophy ... 102 6.1 Political
philosophy ... 102 6.2 Philosophy of
law … 109 7. History of mankind ... 114 7.1 Prehistory …
114 7.2 Antiquity …
117 7.3 Middle ages
... 131 7.4 Modern
period. 143 7.5 Israel ...
154 7.6 20th century.
157 8. Economics ... 167 8.1 General Economics … 167 8.2 Economics of the State as a public limited
company … 168 8.3 Economics, and the reality … 172 9. Conclusion ... 173 10. Review of the literature ... 177 |
SECOND PART
PHILOSOPHY OF BALANCE OF EXACT SCIENCES ...178
|
1. Preface
... 178 2.8.5 Geometric image of the world.
193 2.9. Arithmetic
and geometry of infinity … 196 3.1 INTRODUCTION … 199 3.2 MECHANICS … 200 3.3 THERMAL AND MOLECULAR PHYSICS … 208 |
3.4 MECHANICAL VIBRATONS AND WAVES … 210 3.5 ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM … 211 3.6 OPTICS … 217 3.7 SPECIAL THEORY OF RELATIVITY … 220 3.8 MICRO PHYSICS … 223 2.4 ASTROPHYSICS … 226 4. Chemistry
... 231 4.2 GENERAL CHEMISTRY … 232 4.3 INORGANIC CHEMISTRY … 241 4.4 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY …245 4.5 BIOCHEMISTRY … 252 5. Biology
... 258 5.1 INTRODUCTION … 258 5.2 FORMATION OF LIFE … 258 5.3 CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING ORGANISMS … 265 5.4 ESSENCE OF THE EVOLUTION OF LIVING SYSTEMS … 269 5.5 ESSENCE OF LIFE AND DEATH, OR THE EVILS OF LIVING
SYSTEMS … 271 6. Review of the
literature ... 274 |
This book is licensed under the terms of http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/deed.cs
, license Creative Commons
Attribution/Share-alike license 3.0. JUDr. Dalibor Gruza Ph.D., Czech Republic 1999-2014 In support of the political Party for the Rights of All Living Creatures,
www.spvzt.cz e-mail: filosofierovnovahy@seznam.cz
THE PHILOSOPHY OF BALANCE OF THE SOCIAL SCIENCES
Philosophy of
Balance is built on a few basic axioms, i.e. the basic assumptions. If I doubt in the footsteps of radical doubt of the
philosopher Rene Descartes all the Being, it remains me to determine the
strongest point, which, although it can also be questioned, I consider as the
surest truth. In my opinion these basic truths are those truths, on which there
is the intersection point of the senses
as the most general sensory perception of the material world, the mind as the simplest
and most immediate idea and emotion. It is a very powerful experience of a
man. In this way I reach the basic assumptions of the Philosophy of Balance,
which can be summarized as Being as
cocontracoagency.
This means that all
the Being is agency, it's happening
as the composition and decomposition, as
co- and contra- agency. Composition
and decomposition are in the balance, i.e. it is the superior coagency to the
composition and decomposition. From the nature of Being as agency it suggests,
that it can be divided into the developmental stages of formation, performance and termination agency. The nature of agency
as co- and contra-agency implies a division into the total and unit agency, into supra-, sub- and the same agency.
Total, unit-, co-, contra-, supra-, same , sub-, formation, performance and termination
agency embodies according to the Philosophy of Balance each existing fact.
Formation, performance
and termination agency are concepts chosen for the same content in the root of the word in the Czech
language, i.e. the letters "N" and "K", which are letters
very similar to those, that appear in the root of the word
"something" and "nothing". I originally formulated these
concepts in the English language as "formation", which means the origin
or creation, "performance", which means execution, and "termination",
which means the end, of which root is also composed of the same letters
"R" and "M".
There are 11
concepts, but they are the concepts, that are related to each other
as general and specific concepts. Agency analysis concepts as sub-, termination, same agency may be
replaced according to a situation by the term contraagency and
concepts as formation, supra,
the same, performance agency can be replaced according to a situation by the term
coagency. One may be
talking about limited
conceptual analysis.
Contraagency indicates
degradation or destruction, and essentially it includes words such as
subagency, a division into parts and termination agency, namely the
disappearance of an agency, it may include the same agency if contraagency.
Furthermore concerning coagency or the composition or formation, which
comprises supraagency, a composition in a higher unity, and formation and
performance agency, namely the initiation and continuation of composition of a
certain agency, and it may include same agency if coagency.
Philosophy of
Balance builds on the philosophy of
Confucius, who in his teachings "about the center and the extent"
or "Golden center" anticipates the form of supracoagency as the
balance between the composition and good coagency and the decomposition and
evil contraagency. Further the Philosophy of Balance builds on the philosophy of Alfred North Whitehead, according
to which in the unit of Being, so called real existing moment in the form of
feeling is perceived the whole Being, its past, presence and also the future is
outlined and preformatted. According to the Philosophy of Balance in fact there is only one agency, that the
human mind just divides. This unity of agency as supracoagency means the link
of each agency with the other agencies. Each agency formation is codetermined
by formation, performance and termination of all other agencies, and the
termination of a certain agency is at the same time the formation of another
one.
In the field of
development the Philosophy of Balance represents a synthesis between the
dialectic of Hegel and the evolution of Herbert Spencer. Unlike Hegel,
according to who the reconciliation of opposites in their synthesis, which disturbes
them and at the same time it preserves and raises them to a higher level, manifests
again in another conflict of opposites, the Philosophy of Balance determines
all the opposition as a contradiction of composition manifesting itself in the
material world as the formation and decomposition manifesting itself in the
material world as destruction and reconciliation of overall composition and
overall decomposition in infinite time as final. Unlike the evolution of
Herbert Spencer, who sees in the integration or the formation the denial of
disintegration or the destruction, the Philosophy of Balance assumes creative
imperfect (the developmental stage of performance agency) and perfect (the
developmental stage of the termination agency) balance. Imperfect balance is in
the fight of unlimited good compostion, virtually formation and the evil
decomposition or destruction in an ever higher level of coagency, whether in
the form of complex integration as of multiple cocoagency or complex disintegration
as multiple cocontraagency. Perfect balance achieved in an infinite time is reconciliation
of limited overall good composition, virtually formation and the limited total
evil degradation or destruction. According to the Philosophy of Balance the
unrestricted formation as the unrestricted fight against destruction or its unrestricted
formation causes a destructive reaction. The limited destruction is however
compatible with the limited formation in the balance formation agency.
In the field of
metaphysics the Philosophy of Balance follows the pantheism of Baruch Spinoza, when it identifies God with the
overall agency, which has the form of cocontracoagency, a creative balance
between the limited overall decomposition or destruction and the limited
overall composition or formation, the Devil with a total cocontraagency, i.e.
evil and decomposition or destruction, whether in the form of pure degradation
as cocontraagency or decomposition of coagency as contracoagency and the Angel
with a total coagency, thus with good and composing or formation, whether in
the form of pure coagency or decomposition of contraagency as
contracontraagency. Pantheism represents also a synthesis of idealism and
materialism. In its frame the God has also the material nature. Philosophy of
Balance describes extrasensory agencies by concepts known from the world of
sensory perception.
In the first part entitled "Philosophy
of Balance" I answer the basic
philosophical issues from the perspective of this philosophy. In other parts I present the main world religions,
philosophy, political, and legal philosophy and human history from the
perspective of Philosophy of Balance, transferring the individual concepts and
facts on the common basis of the agency terminology and I systematize them from
the perspective of Philosophy of Balance of agency.
The use of
concepts such as Angel, Devil and God
is not a mere presumption, but the term God means balanced supracocontracoagency,
therefore that so I took over the idea in agency form and I agree with it, it is
probably about the balance (i.e. the love) between waves of the speed of light and the absolute
vacuum, the term of Angel is creative and good coagency or destruction of
destruction as a contracontraagency, it is probably a sign of the waves of the
speed of light and the Devil is a devastating cocontraagency, it is probably a
sign of absolute vacuum as the final number of single points of space-time of lower
speed than the speed of light and of a zero realativistic mass spreaded
out in space-time. From the waves of the
speed of light and the absolute vacuum according to the Philosophy of Balance
there is all matter composed in our Universe.
In Brno, Czech
Republic 29. 1.2002
JUDr. Dalibor
Gruza Ph.D.
|
2.3 About basis of being (ontology) 2.4
About cognition (gnoseology) 2.5 About correct thinking (logic)
Formation
How was the world created I want to think now, whether the answer is in the Being, in which the mind is lighting. The mind is a mosaic determined for folding, each step forward is worthy of exaltation. I'm not free of errors, anger is bothering me and the evil deeds of mine accompany all hopeful.
Performance:
In the confusion of actions, which are in a war, I'm thinking about peace a real fairy tale. Peace is the ruler of the world, where each its sentence means a new formation or unforgettable termination. This infinite sequence represents
the first of the sciences obvious to every mind saturated by its senses. How to shake off the curse in the confused Being that is constantly happening, the evil laughs at the good. But even the good wins and it constantly beats the evil, finally without winners and losers they are always splitting up together in Being. Whose side to take, when the good wins or when the evil beats it, shall I go with the winners? That's a contradiction of my being or to go the way of victims or to take advantage of my force, to beat the weak. It should be found the second of the sciences, that any of these paths . is not calm. The good is always followed by the evil, the evil, in turn, calls for the good, peace is not found, need to wait for war. Need for victim for a good cause for the evil yet personally to carry What has changed, however, the evil as well as the good escaped not wounded not diminished. Therefore,
search for a third of the sciences to love the good now the evil, however, as well as, to stay in the middle. In the confusion of agencies of Being the contract between them was always closed and it restored harmony.
Termination
If I want to live in peace and inner harmony to honor, then I cannot prefer, the evil and the good reconcile. The good is real, if I decide impartially, when looking for a balance both to the evil and to the good. Where is the true center of the good and evil agencies, need to find a way, where there is the least resistance. There is search for peace now and in eternity, it is the highest, what is Universe.
Formation
Where to find the heaven my mind asks, Being is happening, where is only God. God has to be almighty and perfectly good, the agency, however, is infinite and to the evil generous.
Performance:
I still think, that God is everywhere, where Being is happening and I also believe it. God, the father of Being so merges with the overall agency, his two sons, we call them the Angel and the Devil. Angel and Devil as God, the father of Being blend in with the good and the evil and they are part of God. God as all Being is powerful above all, he reigns over eternity and he is infinite. The old agency ends and a new one initiates, its work performs or change is coming. History of the good and the evil is so endless, one thing ends and the new in turn will begin. Above all, and in all God rises created by infinite total with his sons. Who is the creator of all the good and the evil, who created God my mind argues with the enemy. God is everything, in which Being is living good and evil some even nothing. Except of something and nothing my mind knows nothing and so then it interferes the almighty and infinite God. Subagency:
God is double, good and bad agencies, evil opposes to all, the good connects everything again. The system of Being the evil forever destroys the good forms again together in eternal battle. Evil thoughts are burning me, is God always good, when
his existent son is in addition to the Angel also the Devil. God is total coagency, either of the good as well as of the evil, otherwise he would have been limited. God as the greater good created also a destructive evil because of the higher balance for good formation agency. Something and nothing make up the agency in their eternal fight, by which the whole Being is balanced. Something and nothing happens, which stems from the standing fight of the good coagency and evil contraagency. Nothing recedes from something or it absorbs something and, conversely, something happens in the form of their supracoagency. God is a good father, who loves their sons, whether it is an Angel or a Devil, without blame. If God loved just a good son evil one would be denied, there would have been the blame. Because even the Devil is the blood of his blood, just like an Angel inside him he is also happening. The actual highest good and therefore God my mind has found in love for the good and the evil. The sons of God fight together, only the love of the father associates them, what is the love of the father, the answer is in the balance. The God does not take evil or good side, like the fated scales in the place of least resistance historical war he ends. God is present in each agency whether good or evil, God is over the good and the evil, that each plays on its field. The fields of the Angel and the Devil in the history of good and evil are in balance thanks to the loving God's effort. These fields the good and the evil shall not exceed, which is a habit for ages otherwise, one would win. The good would live forever, evil would be dead forever, Being would not happen then, staying would be endless. All and everybody would have been forever perfect, any imperfection is Being of agency struggle between the good and the evil.
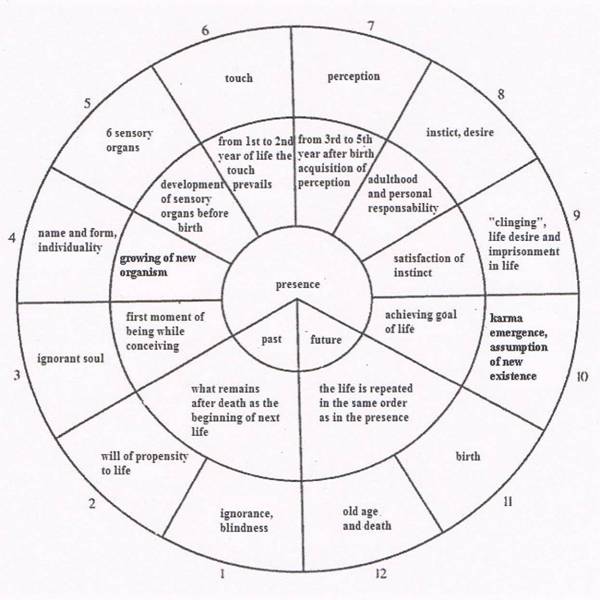
Philosophy of Balance of agency doesn't say, what will happen to a soul after death, whether it returns in another body or it goes to the good or the evil in eternity. Therefore, if after the termination of cocontraagency there is again similar cocontraagency or there a more numerous agency forms, so the total co- or contra- or cocontracoagency. This question is a complex agency, determined by total agency formation and thanks to its complexity of nature it is invisible to thoughts and feelings.
2.3 ABOUT BASIS OF BEING (ONTOLOGY)
Formation My mind is searching the basis of being, has it to be a matter or just thoughts. What is God made of, matter or spirit, what is the good made of and what is evil made of. What is the Being and what is not, perhaps it is matter, perhaps thinking.
Performance: The dispute is odd as all Being is continuously happening as a whole or individually. Each agency of Being is composed of the parts that the mind divides in a single agency. The agency initially arises, then work takes place, if the change does not come, so once again it terminates. But, in fact, the agency is not many, there is only one, it is God for us. Mind divides agency in the compound agencies and the individual agencies it divides once again. The formation and the termination the performance separates, if there is no change to it, which are also compound agencies Formation, performance and termination are parts of an overall agency, in fact, not divided, existent only in the mind. The formation is performance and also the termination, performance is the formation and also the termination. The termination is the performance and also the formation and together they are a part in a single agency. So smaller agencies group in the larger ones, we
call them more complex ones containig simpler ones. Individual thinking agencies do not live apart, they
are a part of the total agency being infinitely. So God is a matter, also mind creates him, the primary is a substance that fights against mind. The agency is infinite complex as well simple, it does not have a beginning and an end, it forms a single whole. Simple agencies the
mind perceives as the matter and more complex agencies then we call the idea. God as the eternal Being in the endless agency is both a complex substance and also the idea. In other words mass forms a perfect idea and on the contrary the idea lights imperfectly in the mass. The frequency of total performance agency is from the beginning the God's total creation, as the law of conservation of energy it remains the same forever unchanged. This also applies to the individual formation subagencies, that in total formation agency from the beginning are forever present. Simple agencies cease to exist and complex ones are forming or vice versa a system of Being is associated. This agency is called a change, that the termination of agency accompanies, the old agency changes also in the agency with the same frequency. Agencies are good or bad, ones are destroying everything in common, the second all the common forms, however, each in their field. The fields are in the balance ruled by a total of Being, which loves its children an Angel with a Devil. So various subagencies both good and bad, which I call co- and contra-agency, create a supracocontracoagency.
2.4 ABOUT
COGNITION (GNOSEOLOGIE)
Formation The world is discovered by the mind that we saturate through our senses. The mind is good or bad, what is its historical role?
Performance:
The Mind is a complicated agency the result of the simpler agencies coagency of goods and evils in a certain way compounded. Every mind is good and bad, each is composed of subagencies, in subagencies it is different from the other and yet similar in complexity. The minds of the individual people form contracoagency of all minds similar by its complexity by formation, termination and performance agencies. The
mind is the degree of coagency, the result of the agency development, similar by the frequency of agencies, capable of higher coagencies. The similarity of different minds on the one hand by the agency frequency on the other hand by subagency composition manifests in a similar thinking. What is the total coagency resulting from the thinking of all the people, it is the product of goods and evils in essence, eventually in balance. Mind and thinking of each of the people we call multiple coagencies. What is, however, a perfect mind, which understands all sense? Such a mind includes all the simpler agencies, it's a complex of all individual agencies that belongs to omniscient God. They are all individual agencies, in other words God, who knows everything, otherwise, the formation of all cocontraagency. Our limited mind understands only the material and thought agencies, infinite and omnipotent God's total mind rules each simpler or complex agency. Therefore, God always sees all the good and the bad in our human mind in the form of formation agency. God also sees everything both good and bad agencies in the world in the mind of a son whether the Devil or the Angel. Where to find the material world, who can tell us about it, is the truth hidden in the senses or is it better to think about it. The complex agency is the mind, simpler is a human sense, both contain simple agencies whose construction is similar. This building is tangible, which is also a form of agency, with similar subagencies, which the objects of the senses tend to have. Therefore it is also possible to say: "properties
of matter, senses and mind are for all agency units customary to all of these coagencies ". For example time is in the mind, however senses includes also it, it is also in the mass in the simpler or more complex form. Objectivity, the mind and the emotions belong to the whole of Being as
more or less similar and numerous agencies. Human
emotion, mind and sense explore faithfully material simpler agencies, than it itself is, because it contains them in its agency building. Suprareasonable supra-and sub- agencies are accessible to emotion, in which a complex God we see in the evil, the good or the whole. More
complex agencies of the human mind are
suprasensory coagencies tangible subagencies postermination changes which contain material a priori sentences. The link of all the agency is hidden in its total unity, that our mind divides, in fact however it flows continuously. By senses we perceive the simple agencies, which we call also matter, mind also more complex coagencies, that are revealing their complex construction. Sensory and material perception and related thinking are the formation of performance formation agency others thought is its next performance and termination. Complex ideas of logic and simpler perception of the senses are the formation agencies of all human cocontraagencies. The formation of human contracoagency progresses from simple agencies perceived by the human senses to more complex agencies of the mind. The mind and the senses as agencies are the product of the agency good and evil, therefore, any idea is correct from an Angel and wrong from a Devil. The good and the evil belong to everything Being and between them the balance is, therefore, success and failure in facts illuminate, which idea is right. In other words, performance and termination light at every agency, if this agency formation is really in balance. In fact Being is all cocontraagency therefore both the good and the bad at the same time, the right path is the path to balance.
2.5
ABOUT CORRECT THINKING (LOGIC)
Thinking as the path of true knowledge is in its agency always good or bad in the form of co- or contra- agency, properly however in balanced group. The
way of unbalanced thinking always either our mind or material simple agencies reveal, if we go on further sensually. The conclusions of a simple agency the mind changes in the complex ones, the way is the intellectual complexity, that is in matter such as simplicity. Thinking on the other side does not think about simple agencies but the complexity explores, that simplicity is remote.
A/supracoagencis of the mind: 1. the judgements 1.1 positive judgement-coagency or contracontraagency 1.2 negative judgement-contraagency or contracoagency 1.3 general and partial and unique judgements-supraagency and subagency 1.4 judgements that tell us, what is-formation agency 1.5 judgements that tell us that something is necessarily-formation supraagency 1.6 judgements that tell a mere option-formation subagency 2. judgments 2.1 syllogism-subagency supracoagency subagency (assumptions-subagency and supracoagency, conclusion-subagency). 3. evidence 3.1 principle of dispute (the same cannot at the same time and in the same respect exist and not exist)-coagency and contraagency 3.2. principle of identity (A = A)-the same agency composed of identical subagencies 3.3. principle of the excluded third (between being and not being of the same factual context of situation there is nothing the third)- co- and contra-agency 3.4 principle of sufficient reason-of formation subagencies of certain agency 4. incorrect thinking -contrasupracoagency B/subagencies of the senses and the mind supraagencies 1. judgment of the induction (the actual validity of the sentence for cases falling under it)-formation supracosubcocontraagency 2. judgment of deduction (inference of specific from general)- subagency of formation supracoagency C/summary of the supraagencies of mind co-, contra-, supra-, same-, sub-, formation,
termination, performance agency Formation: My mind asks, how does one should live to feel blessed, in the soul he or she had a peace.
Performance: Being is in balance both good and bad, let us approach to this agency the eternal natural harmony. If you want peace in the soul, in the middle you must stay, love the good now, the evil however too. In the confusion of agencies of Being the contract between them was forever closed and it restored harmony. If I want to live in peace and inner harmony to honor, then
I must not prefer, the evil and the good reconcile. The good is real, if I decide impartially, when looking for a balance towards the evil and so to the good. Where is the true center of all the bad and good agencies, need to find a way, where there is the least resistance. The path is not to give up, if I want to live in peace, inner and outer peace in my being still experiencing. Otherwise, you do not escape the curse in the confused Being that is constantly happening, the evil laughs at the good. But even the good wins and it beats the evil constantly finally, in the peace of Universe they part without losers and winners. Whose side to take, whose sword to raise, when
the good wins or when the evil beats it. That's the contradiction of the human being, whether to go the way of a victim or to take advantage of our force to beat the weak. It is necessary to learn and in the life to try, that none of these paths is calm. The good is always followed by the evil, evil calls in turn for good, peace is not found, need to wait for war. Need for a victim for a good cause for the evil yet personally to bring. What has changed however, the evil as well as the good not wounded escaped not diminished. If I do not find the golden center, if I do not go the quiet path, I will not escape good or evil fight, however the overall harmony is not broken. Even without my undue struggle, from the power of the Being infinite harmony of Universe will be constituted, the soul however does not miss the pain. Balanced behavior however multiple is not good or bad, but it is balanced. Against excessive evil, it defies in the good against excessive good it lies in the evil. Against a balanced behavior only the excessive evil or excessive good always fights to the essential extent. Balanced behaviors are basically the formation, which reconcile in total supracoagency all the good and the evil. Balanced behavior partly accepts and partially denies the evil and the good in the agency. When I say it in other words, the good or the evil in the agency still reconcile each other by partial contra- or co- agencies. The necessary courtesy to the good and the evil does not mean that I refuse the war, if it is the cocontraagency golden center, I have to be ready to fight now. To find a center of various agencies, or the contract between the good and the evil, you cannot just invent, but also suprareasonable emotion is necessary. Mind only sees a simpler world, where emotion can also enter, emotional cocontracoagency reaches above the celestial spheres. This gold center is only a moment, reconciliation of early agencies should always be found again. Therefore
different communities of people see this center depending on their habits, also according to the circumstances. These circumstances are different, however, also similar always in the special agency situation however in the total unity in the agency. Agencies are good or bad, behavior partly predetermined, if it should be determined fully the evil as well as good would be irreversible. Thanks to the good formation coagency a bad man can reach harmony, thanks to the evil and destructive formation agency a good man can fall for bad. In the context of the formation of formation agency predetermined conditions are included, however, the mind shapes also the other agencies, the overall balance accomplishes. Thinking is thus given by physical (material) sensations, its device, however if it is happening, it must be partially free. Formation agency performance is so a separate agency, that is only partially given, conditioned by its formation. Unlimited in its formation by other terminated agencies is the agency of God's whole, in which a man participates. The formation of the total agency is completely unlimited, it is not any supra-or sub-agency, of which even partial formation it predeterminates. The independence of the total agency each agency partly contains in
its partial formation then as part of the unlimited complex. Free human will so shapes the human agency, that is subjected only partially by the other agencies. The only thing what is fully determined to good and evil agency, lies in the existent harmony, which will be done in time. Formation
How are we to understand the State, the mind must be asked, there are many forms of States, how to unite them in one?
Performance:
State is possible to define according to its three individuals the formation of formation agency, the first of these is territory . The
second is the sovereign power, therefore State supraagency, the
third is community of people, it is the same with coagencies. Agent in the State submits everything, persons and things on the territory with the relevant exceptions. State-forming supraagencies are either good or they are evil, destructive or creative. Contraagencies include according to the originator of the supraagency tyranny and oligarchy aristocracy and monarchy. One reigns in monarchy and tyranny, several people in aristocracy or oligarchy, in democracy people rules in politeia or perfect democracy everyone. In these States however just a group of people reigns, the exercise of this power is not supracoagency. Such a bad government, where there is a permanent betrayal, because it is not supracoagency between good and evil living beings. Nor the way of government does not know the right freedom against the violence of its living and their contracontraagencies. Next the decided agencies are composed of many, under the government of just called it means to think in a limited way. To thinking of complex civil agencies decided by the government of the State it is necessary to use both thinking and emotion of each supracoagencies agents. The ideal State is supracocontracoagency the harmony between subsidiary good and evil, thus the contract of all the living whether they are good or bad. Only then all agency actors find the right of harmony, that the minimum of agencies contrasts, if it is a perfect democracy. If we want to differ the State, we have to ask subagencies, according to the representation of the agent in the State there are republics and monarchies. In monarchy the State's agent the monarch embodies or represents, in the republic it is a parliament or it is the elected president. Contract of agents, which is enforceable is called the law, which is a set of norms. The law is natural not quite the same is the fair law according to the frequency of agency. Natural law is supraagency standing above the ordinary law but also the fair law, it is the law valid forever. The natural and eternal law is the total formation agency the conclusion of historical Being, in accordance with the performance whole. It is the perfect supracocontracoagency, that is the contract between the good and the evil, where is all agencies, at least against each other. The law is only fair, if it is accepted by all, to thoset it is then applied, because they all use it. Such a legal compromise includes both the good and the evil in the form of the least contrasting supracoagency, which is not cancelled by anything. An imperfect reflection of the fair law is today's democratic form, because the general State-forming power reflects the civil supracoagency. What law is evil, the law accepted only by someone, then the law obviously harmful although agreed by all. Furthermore, I've been thinking, when to call the State law, to fight against contraagencies, even if it is the evil or the good. Even the good can be infringing, to depart from the middle way, because after an overly good agency, the fateful scales balance it by the evil. Freedom in the first place is as a part of the total agency, that is limited by nothing, in the form of subagency of the individual. It is only possible to find a simple overall harmony, when the State law does not restrict the individual in his or her supracoagency. Therefore, every time we need personal equality and freedom, which recede then, when in something they do not work. This is the case in the first place, when simple agencies are
abhorrent to common harmony however only in relevant extend. Perfect democracy tolerates and ensures according to the equilibrium point the good and the bad living. Penalties for the opponents are not as offense numerous,
but are the balance in the good and in the evil. The essence of the extent is always from the greater part personal according to what persons conclude social contract. Secondly, it is because when we are dealing with a complex agency, which is decided together by social thinking and emotion. If it is some kind of non-independence in the case of supraagency, it should be the equal supracoagency not the unequal contraagency. In the past, when freedom was less supracoagency, the law gradually more balanced was fair and balanced. In the form of monarchy, aristocracy and democracy so still more complex supracoagency interpersonal struggles were weighted. The government of the individual, monarch and
a still growing group flowed from together to reconcile the good and the evil in supracoagency. In
a perfect democracy the evil and good higher contract is the almost supracoagency fellowship all the evil and the good conciliated. Note: Law as a social contract meets the requirements of similar construction elements of the
legal act. For example in the Czech Republic it is the consent of the
subjects of the social contract given on behalf of the authorities of the
legislative power (cf. article 2, paragraph 1, of the Constitution of the Czech
Republic). Requirements relating to the will, namely its fact (given),
the freedom and the seriousness and accordance of the relatonship of will and
expression are provided within the framework of the legislative process in the
article. 37 et seq. of the Constitution of the Czech Republic and in the
rules of procedure of the Chamber of deputies of the Czech Republic and the
Senate of the Czech Republic. In my opinion the legislative process
represents the equivalent of a complex contractual process, including
in particular the draft of law and its approval. The most important
requirement of the freedom of the will against the violence and threats
is protected by article. 26 of the Constitution of the Czech Republic but
also in § 92 of the criminal law about the criminal act of subversion.
Request relating to the subject matter of the law as the social
contract, namely its possibility and accordance with the accepted
principles of morality is expressed in particular in article 2, paragraph
3 of the Constitution of the Czech Republic, which provides that State power
is used for all citizens. Request of terms of expression of will is
expressed in article 52 of the Constitution of the Czech Republic, which
stipulates that for the law validity its publication is necessary. Apart
from the classic legal acts applies however the principle of majority and apart
from the private legal acts assumption of correctness of a legal act. Formation The highest desire of people is to experience the harmony of the good and the evil total coagency. Total coagency is the right God, the meeting with him can be through art. Art
links the material sensory contracoagencies to suprareasonable and suprasensory Divine harmony. God in the idea is usually lifeless, but by the hand of an artist he becomes real. God in the mere matter is lost in the Being, in the infinite multiplicity he is difficult to be found. Art allows us to know the existent harmony, as the material one so one in the invisible agency. Sensory agencies are good or bad in the range of frequency of material fact. Even in the mass we will find the center between the good and the evil with the least resistance. Extrasensory frequency to the material agency are the simpler agencies as well as more complex. The human mind explores perfectly just the material agencies, imperfectly as well numerous agencies, as it itself is. Imperfectly understood in Being by our mere human mind simpler and more complex agencies, than the tangible sense perceives. To
penetrate to the overall agency to its God's complete harmony it is possible through art through perception, thinking and emotions. It is imperfectly thought saturated by human senses, only an emotion can actually experience it. Through emotion we penetrate to the Divine harmony to the lowest and the highest agency good and evil. Art is therefore threefold, the highest stands in supracocontracoagency the presence of God, which is captured in extrasensory harmony. The path leads then towards it through the senses and the mind only imperfectly perfectly just by empathizing. Additionally we can view the material agency balance, which emotion perceives we can use the senses but also the idea. All of these existent overall agencies are supracocontracoagency, all good and evil center, which contradicts to these agencies at least. And now for the third time it is in the matter of the artist the image of an Angel and a Devil's agency the extrasensory good and evil. The evil is contraagency, that destroys the common, the good is coagency to a common creative. Harmony of agency is subject to change depending on how in the history cooperating agencies are changing. Therefore the value of the art changes the time the other is, of course, now, other tomorrow again. Art that remains in a number of agencies in the historical center, is in fact only the timeless, as with time the quantity of agencies grows. It depends also on viewer and the environment, in which the work is exposed, even those belong to the subagency, that partly co-form the overall harmony. If
the work is just artist´s personal expression, it must be extrasensory good or evil. Such art, that is not the harmony or it does not penetrate beyond the material, is recognizeable on its value. |
|
|
3. INTRODUCTION TO THE HISTORY
OF PHILOSOPHY AND MANKIND God has called his two sons, to leed the debate what have been the human acts, whether people lived according to the law. Angel with Devil came to the father, to discuss their actions with him and God decided, together with the law, what will be the human history.
|
|
Mathematics can be broadly split on arithmetic and algebra, so numerical operations with numbers on the one hand, and geometry on the other hand. Arithmetic and algebra works with fewer elements and at the same time each this element and their relationships can be expressed geometrically, which proves the so-called analytic geometry, which converts the geometric concepts and their relationships to numerical form. In other words the general term of a number includes more specialised and simpler concept of geometry. Each point in the space can be with the use of the coordinates expressed as an ordered group of numeric coordinates. This is a manifestation of the general nature of the fact, when the continuity and degrees of agency suggests, that the existence of a more complex agency includes simpler agencies and at the same time the system of more complex agencies due to the more complex and therefore less numerous agency unit of this system is seemingly simpler than system of simpler agencies.
(subagency)
2.2.1. Introduction
(formation)
Logic is a way of thinking, that can be supracoagency or more coagency or more contraagency or incorrect. It is wrong as well as thinking that overly accepts as the good and so the evil. Thinking from the perspective of Philosophy of Balance represents the formation agency of the human cocontraagency. Unbalance of thinking reveals us the laws of thinking or tangible reality in practice or performance agency in a controversy with the balanced supracoagency of the whole of Being. The sensory perceptions of the material world as simple ideas the mind changes into complex ideas, simple ideas are the immediate consequences of the mass in our mind and they are not in generality a product of the only mind as opposed to complex ideas.
2.2.2. Definitions
(performance)
Further indivisible unit agencies represent from the standpoint of mathematical logic (coagency), the basic (initial) concepts, or basic mathematical objects. The statement we understand each formation agency or a grammatical sentence, that is true or coagency, or contraagency or false.
To the given statement we can create the negation or in the case of a positive statement a contracoagency and in the case of a negative statement a contracontraagency, which means a positive statement or coagency.
From several statements we can create with some conjunctions composite statements or coagencies. A sentence can then present in the case of conjunction "and" formation supraagency, in the case of conjunction "or" formation subagency thus clearly or ambiguously specified performance of agency. Also formation termination formation coagency in the case of conjunction "if ... then" and formation termination, termination formation formation coagency in the case of conjunction "only ... if".
In terms of evidence it is possible to distinguish direct evidence as the performance of formation coagency and circumstantial evidence as the performance of formation contracontraagency, thus the debunked negation. We can further distinguish evidence by incomplete induction generalizing of only some cases as subagency contratotal formation coagency and the complete induction by generalizing all partial cases such as subagency total formation coagency and further the proof by negation of the veracity of the general statement by its false in a particular case as subagency total formation contraagency.
2.2.3. Mathematical-logical picture of the world
(termination)
Mathematical logic and logical thinking represent in general the formation agency, therefore the initial stage of agency, even of partial agency, thus also of each of its later stage (performance and termination). Due to the fact, that the agency is in fact continuous, we cannot really separate the above stages of each agency, how the human mind makes it. The whole of Being as the overall agency and God represent so from the standpoint of mathematical logic the infinite composite statement and just as both the positive coagency or the good and negative contraagency or the evil with it, that the negation of the negation represents positive coagency and the negation of a positive statement is negative contraagency.
From the viewpoint of ontology such a statement represents an infinite statement of Being as the world of matter so the world of the spirit. Unit agency from which every single statement is composed, as well as its basic (primary) concepts, is the alphabet letters, and we can examine therefore, which letters are historically developed from the other letters, and reach so the final statement unit agencies. More complex statements (supraagencies) are also divided into simpler (subagencies), as well as more complex concepts can be defined using the basic (primary) concepts.
The human mind from the perspective of mathematical logic represents the composite statement consisting of an endless quantity of simpler, basic (primary) statements. This formation agency of the human mind is inseparable from its performance, its manifestation in the mass. To the human mind the simpler and more complex statements are hardly accessible, than permissible range of complexity and simplicity by it perceived statements is. These incomprehensible statements represent in relation to the human mind coagency, the world in itself hardly accessible to the human mind.
The balance between the positive and negative statements does not provide the unilateral tendency to positive or negative statements, and the resulting behavior. According to the Philosophy of Balance limited positive statements accompanied by limited negation of reality should prevail. As also the reality is a balanced ratio of negative and positive statements consisting in the limited formation. This balance in the logic is ultimately pushing in any statement, derogation from it can be only temporarily. Due to the nature of reality as the compound statement is any statement partially destined by other statements and partly independent because of unlimitation of the total of unlimited statement of Being that is not restricted by other equally or more complex statement. For this freedom every partial statement is partially divided.
Aesthetics represents a view of extra (i.e. beyond) sensory ideas whether more complex statements, than most complex human thought is, or simpler ideas, than the simplest human thought is. At the same time it may represent a view of negative and also the positive statement, whether in the form of extrasensory evil or good. The highest form of art represents however according to the Philosophy of Balance extrasensory statement harmony. The view is done by statements-the means available to the human mind. By such extrasensory statements we penetrate into God, Good, Evil, virtually to the essence of all Being.
2.3.1. Definitions
(formation
and performance)
The set understood as the whole of elements can be marked in the field of Philosophy of Balance as coagency. The elements of a set are its subagencies. The empty set is infinitesimally small set, it represents a unit agency, of which infinite unification is not already in my opinion an empty set.
The essential relations between the sets are a subset as subagency, equality of sets as same agency, complement of set such as supracoagency contrasubagency, the unification of the sets as subagency coagency, the intersection of the sets as cosubagency, if they are disjoint sets, penetration can be described as unitcosubagency. Projection of set A into set B can be described as a formation (set A) termination (set B) coagency (their projection).
2.3.2.
Set image of the world
(termination)
The set of all existent objects is in the Philosophy of Balance the total coagency, or God. From the perspective of Philosophy of Balance of agency a number of elements of this set is due to the infinity and continuity of all Being as agency equal to the infinity and it is a subject to constant change. The relationships between the sets are not statical but rather dynamical-as agency. This change means constant decomposition of subsets onto complements of two or more sets as a bad contraagency and unification of the subsets as a good coagency. The two basic operations with sets and their resulting subsets create the whole of infinite set of Being.
In fact each of the subsets of the total set of Being is contracoagency in relation to the other subset, which means, that their intersection is non-empty set-cosubagency, its complement is again a non-empty set-contrasubagency. The unification of all of these subsets of the total set is the total set of Being, i.e. supracocontracoagency. In my opinion unit agency of the total set of Being is the empty set, the unification of the endless number of infinitely small sets is not already the empty set in my opinion. In my opinion from this unit agency are ultimately composed all the objects of Being as complicated sets of elements, whether spiritual or material.
The human mind represents from the viewpoint of set theory the unification of the endless number of empty sets as a unit agency of the total set of Being. To the human mind as a complex set only a subsets in the range of a certain frequency are well accessible. Another sets, whether complex or simpler are perceived by human mind only on the basis of similarities or logical connection, in the rest only by emotion.
Unification and the additional decomposition of sets in the framework of agency relations within the overall set of Being are in balance, which is not represented by its unchangeability, but by balanced limited integrating of the sets or supracocontracoagency. This balance represents some sort of superior power in agency relations of sets. Unlimited by relationships to other sets only the total set is, since it itself is only a subset of itself and all the other sets are its subsets. For this unlimitedness all other subsets are partially divided, such a subset of the whole is the man and his or her mind.
Aesthetics represents the doctrine about sets with more or less elements, than perceived subsets of the set of the human mind are. These sets are accessible primarily to human emotion, they are accessible to artists and potentially to every living creature, also on the basis of the relationship of a logical context and analogy with reason understandable sets of elements. The same is true for the agency relations of sets, their complementary decomposition as bad contraagency and unification as a good coagency, which represent in extrasensory form the other major form of art.
2.4.1.
Definitions
(formation and performance)
Arithmetic defines axiomatically the various scopes of numbers and basic operations with them. These scopes (coagencies) of numbers are the natural numbers (N), the non-negative integers (No), integers (C), the rational numbers (Q), the real numbers (R), complex numbers (K). These coagency are different in particular in its unit agencies or units, of which each of the numbers from the relevant scope of the numbers is composed.
The most general scope of numbers as supracocontracoagency, i.e. thus the set of numbers with the smallest number of elements is the set of natural numbers, resulting from the gradual adding of a number 1 to a number 1. This set of natural numbers has from mentioned coagencies the smallest number of elements and at the same time each element is composed by numbers of other scopes of numbers.
Unit agency in the field of natural numbers is the number 1, this unit agency is included in all the elements of this scope of numbers. Supracounit agency is the number, that we will attain after all operations with all numbers in this field, it is the number 1=0, then the result of the different operations (contra-and co- agencies) with the same numbers. The total coagency of all natural numbers is then +¥.
Numerical operations can be according to, whether it is a decomposition or composition of the numbers, divided into coagencies and contraagencies. Coagencies include the addition, multiplication, exponentiation, contraagencies are subtraction, division, roots. From these operations also a relationship of equality and inequality flows, which in the area of Philosophy of Balance can be expressed using the concepts of the same, supra- and sub- agency.
In the field of natural numbers the method of mathematical induction is used, which may be in the area of Philosophy of Balance shown as unitsuprasuprasubcoagency, which means unitsuprasuprasubagency (all elements from the set of natural numbers as natural multiples of the number one) meets certain mathematical sentence Vn (coagency). If Vn meets unit agency, i.e. the number 1, and we assume, that it conforms to the natural number k and we can proof, that it complies with the number k+1, then it complies to the whole unitsuprasuprasubagencies, i.e. to each number of the set of natural numbers as natural multiples of the number 1.
Divisibility in natural numbers can be expressed by using the Philosophy of Balance as subagency (divisors) contraagency (contraagency). Prime number factor can be expressed as unitcoagency (that is a multiple of the number 1 and itself), decomposition in prime elemnts as unitcoagencies (supra) coagency (i.e. multiple), the greatest common divisor as unitcoagencies supraagency (the largest of divisors), and the smallest common multiple as unitcoagencies subsupracoagency (the smallest of the multiples, thus supraagencies).
The real numbers are a more detailed case to natural numbers, resulting from their decomposition. Unit agency in the field of real numbers can be expressed as a number 1/+-¥=0, this unit agency is also a component element of the numbers 0, because 1/+-¥ + 1/+-¥= 0 and at the same time it is a component element of all the other numbers as (1/+-¥)*¥= +-1. This unit agency is also coagency as 1/¥+1/¥=2/¥=0 and at the same time contraagency as 1/¥-1/¥=0/¥=0.
The real numbers include rational numbers such as cocontraagency, thus dividing the numerator (coagency) by the denominator (contraagency), and the irrational numbers as the performance (with not fininshed, nonperiodical decimal development) cocontra (composition and decomposition) agency (number).
In the field of real
numbers it is also necessary to examine the composition and decomposition
operation, as a real number in itself is already a result of degradation of
the natural numbers. So the decomposition of decomposition (contracontraagency)
is actually the composition. -(-3)=+3, 1:0.1(=1:10)=1*10=10 and decomposition
of the composition (contracoagency) is actually the decomposition of 10*0.1=(10:10)=10:10=1,
-(+3)=-3.
Special scope of numbers represents complex numbers, which are more detailed case of real numbers, which combine the concept of numbers and plane projection, therefore the more complex and less numerous concept of real numbers they divide into simpler, more detailed and more numerous concept of a complex number. As the real numbers represent composition projection of 2 to +¥ dimensional space into a one-dimensional space of the line points. So the complex numbers represent the decomposition projection of 1 and fewer dimensional space and composition of 3 to +¥ dimensional space to the points of the plane. At the same time real numbers are projected in one of their possible identical projections on the points of the line. For these reasons in another explanation I refer to vector algebra and analytic geometry in the plane, which use also the detailed arithmetic and algebra of numbers in the plane. A complex unit is √-1.
2.4.2.
Arithmetic image of the world
(termination)
From the above agency analysis it is possible to derive a generalized image of the world by using the natural numbers and its basic operations.
It is possible to identify God with all Being, which symbolizes +¥ as the total coagency, total contraagency of the individual elements of the overall coagency, thus -¥ symbolizes also the God, who means thus in conformity with all the facts both the good as composition coagency and the evil as disintegrative contraagency.
Decomposition and composition as an agencies of God, with whom it falls in one and that matches also with Being, mean the good and the evil, or activity and personality of his sons (subagencies) the Angel and the Devil. Decomposition and composition, coagency and contraagency form the agency-perfectly infinite numerical operation, that is going only according to the logic of numbers to number 1=0, as a component expression of the balanced God. Therefore the sum of the total coagency +¥ and the total contraagency-¥ as their supracocontracoagency. God is therefore a balance, that is directed to continually more numerous (higher numbers) numerical operation, which are according to their nature endless.
Being can be seen as a complex numerical operation with the numbers, the unit of Being is then number 1=0, all Being is represented by the total coagency +¥ and its total contracoagency -¥. Numerical operations of Being consists of the input (formation), calculation (performance) and the outcome (termination), which is again input (formation) of other partial numerical operation (agency). Higher numbers are composition of the lower numbers, simpler agencies consist in more complex ones (supraagencies), which are divided in simpler ones (subagencies). The object and the subject as part of a Being are such a complex number operation with numbers (the agency). Operations with numbers, that make up Being, are either decomposition (contraagency) or composition (coagency).
As the complex number
operation with numbers the cocontraagency of mind can be understood too. The mind is a
numerical operation with large numbers, but at the same time it is composed of
a large number of operations with the least unit agency, i.e. number 1=0. An
example of such thinking is a binary system, on which is based the computer
work, that ultimately distinguishes only the numbers 1 and 0. Generally
speaking, that the minds of all people mean different numbers, but of
the same order. They are therefore similar. Numerical operation of
composition and decomposition (cocontraagency), which includes the number
members representing the mind of all living creatures, is able to cover
a larger part of the total of the interval (-¥, +¥). The total
mind can be identified with this interval, as it is apparent from the above
with the total of Being or God. Such a mind is controlling and it knows all
their members, the individual agencies of Being. Higher system than the mind, a
numerical operation with higher numbers, it is the emotion, by which we penetrate closer to the whole. The mind is
coagency or cocontraagency, thus it is represented by positive and negative
numbers on the large frequency. Ideas are once again the numbers from a certain
interval of absolute values of the numbers, smaller and larger numbers outside
this interval represent simpler agencies and more complicated ones than
our minds is well able to capture.
The question of how to live (ethics) is possible to answer using the number 1=0, which represents both the end of an infinite number of operations of composition and decomposition, in the simplest form of addition and subtraction of natural numbers, and secondly a balanced agency, of which composition and decomposition we come to it alone, thus the agency featuring within the infinite numerical operations the relative stability. Balanced act balances the numerical operations of composition and decomposition, so that the result was a balanced number 1=0. Given the complexity of numerical operations representing Being, the question of its balance is above all a matter of emotion. If I try not to balance the composition and decomposition in the context of numerical operations, I do not disturb the overall balance, which would be constituted in more complex numerical operation, however I cause unnecessary suffering of extreme composition or decomposition. Each of the complex agencies-high numbers can be seen as the result of previous numerical operation with other numbers, at the same time however they are also the result of chance due to the fact, that the highest number of perfect ¥, the overall agency is not in their numeric operations dependent on the outcome of the operations with a higher or the same number. I devote closer to this subject of free will and chance in algebra and combinatory image of the world. In conclusion to this issue I want to note, that this is a generalized image of ethics. In the detailed ethical image based on more special scientific disciplines the balanced behavior is essentially a moderate composition or creative agency.
What concerns the aesthetics or the teachings of beauty, we can say, that it applies in particular to the emotional perception of the total agency, therefore the entire interval (-¥, +¥). This subject of emotion goes beyond the subject of the human mind, which is only a subset of this interval. By art we penetrate to a balanced whole, to suprareasonable degradation or composition or balanced sensory Being, which is a subset of the interval (-¥, +¥).
What was said above about the natural numbers, it applies not only to natural numbers but also on other scopes of the numbers with the fact, that unit agencies and subagencies of these numeric scopes are defined differently and they are the result of numerical operation of decomposition and composition (contraagency and coagency) of the more general concepts of natural numbers.
2.5.1. Definitions
(formation
and performance)
Algebra is a mathematical science about solving equations containing one or more unknowns, or where appropriate their expressions. The concept of the unknown, and its expression is a generalization of specific concept of number (supracoagency). From the equations the inequations can be derived. As well as numbers, that represent algebraic expressions, we can even add, multiply, power (coagency), or subtract, divide, root (contraagency) them. Each unknown we can mark as suprasubagency, because it indicates a variable element (subagency) from a set of elements (supraagency).
Algebraic expressions with the unknown can be decomposed into simpler expressions subagencies and to determine a common multiple of expressions subsupracoagency or common divisor suprasubcoagency.
A special case of the equation is a function. This is a formation termination coagency. When definition scope (formation coagency) a functional regulation (performance coagency) assigns the functional values (termination coagency). Subagency of a function is its graphical representation. It can be distinguished e.g. bounded function (termination subagency), i.e.. f (x)£C in the interval xÎMx, increasing and decreasing function-formation termination supracoagency (subcoagency), i.e. the xj, xi,ÎMx, xj>xi and at the same time f(xj)>f (xi), or f(xj)<f(xi), termination formation, formation termination coagency represents the inverse function.
Logarithms (y = logax) can be expressed as the same coagency (x =ay) subagency (y). It is also possible for logarithms, or exponents as the results of the logarithms to define composition coagency and decomposition contraagency.
If we consider a right triangle as the coagency, we get the trigonometric functions for its angles as subagencies (the size of the given side) unitsubagencies (the given side about the size of 1) contraagency (their share).
As well as the trigonometric functions it occurs even in the case of vector algebra the connection of more general arithmetic with more detailed geometry. Composition coagencies and decomposition contraagencies, which are the same as their definition in arithmetic, can be performed by generalized means using the ruler, pair of compasses and protractor (synthetically), or by decomposition of these synthetic steps analytically with the number axis and the calculation of the corresponding coordinates. These coordinate calculations are basically a detailed subagency in relation to the field of arithmetic and in relation to synthetic geometry.
The geometric vector we can mark as formation (the starting point) termination (endpoint) subcoagency (part of the plane). The size of the vector is the frequency of coagency. A unit vector is unit agency.
Analytical
expression of a vector as a sum of multiples of two unit vectors a=a1i+a2j.
Even in this case as in arithmetic it is possible to define the composition coagencies
and decomposition contraagencies.
Another important concept of vector algebra is the scalar product of two vectors a and b, which can be described as subcoagencies (vector b and the projection of the vector a into the vector b) supracoagency (product), i.e. a.b= abcosj. Even in this case decomposition contraagencies and composition coagencies can be defined similarly as in arithmetic, then to carry out the analytical calculations of coordinates (the detailed arithmetic subagency).
The most typical expression of the algebra are equations and inequations containing unknowns and their expressions. In the Philosophy of Balance they can be expressed as of suprasubagencies (unknowns) cocontrasubagencies (numerical operations on one and the other side) same-, supra-, sub- agency (equations and inequations). For the above mentioned cocontrasubagencies the decomposition contraagencies and the composition coagencies can be described similarly as in aritmethic.
Quadratic equations and inequations contain co2suprasubagency, algebraic equations and inequations of higher degree are characterized by higher coagency (coefficient) of unknown. Trigonometric equation are seeking for contraagency appropriate to the angle expressing the unknown according to various formulas, that define the co- and contra- agencies of these contraagencies.
The geometric projection as well as substituting of certain number into inequations or into equation are specification of the general concept of unknown, which represents in regard to its subagencies more general and simpler supracoagency. Using these specifications is possible to find solutions to generic variables.
Equations and inequations can contain multiple suprasubagencies, thus unknowns and they may be also in the form of their supra-, sub-, same- agencies (equations and inequations).
Function or formation termination coagency are also sequences.
Members of these sequences are coagencies of numbers a1 and d, virtually q. N-th
member of sequence, an=a1+ (n-1).d, virtually, an=a1.
qn-1. Coagency has in the first case the form of the sum and in the
second case of a product, the frequency
of coagency is in both cases n. We can express the sum of all the members of
the sequence, which is again coagency.
A perfect 0 (zero) can be no longer further
decreased, an imperfect 0 (zero) can be
further decreased, an imperfect 1 (unit) can further grow, the perfect
∞ (infinity) can be no longer increased.
2.5.2.
Algebraic image of the world
(termination)
As regards God as a numerical operation with the unknowns it can be said, that God as the overall agency of Being defines and therefore he knows each unknown. But not the Good as the total coagency, which does not define and does not know the contraagency unknowns and vice versa total contraagency does not know coagency values, that in numerical operation, which are involved, are unknowns.
What concerns Being, so the context of agency implies, that in the numerical operation of future Being many unknowns occur, which in the numerical operation of equations and inequalities the numerical operations of past and present just specify. As well as partial numerical operations of simpler agencies just enter in the context of their agency termination (of the result) as a known quantities the formation of more complex agencies. Supracoagency, i.e. the general agency, which perfectly includes each equation, virtually inequation, which arise from the concept of equation, is the equation 1=0, which can be further divided into more complex equations, inequations and systems of equations. Unit agency represents an equation perfect 0=perfect 0, by which perfectly infinite multiplication as the total coagency in the form of perfect ¥=perfect ¥ we get any equation 1=0.
The same is true for the created mind, for which the future but also the present represent the equation, virtually inequation with many unknowns. The same nature have also complex agencies, that exceeds by their frequency the frequency of agencies accessible to the created mind. To the overall agency, therefore to all unknowns values every living creature passes potentially partly by its reason and to the greater part by his or her imperfect emotion.
Regarding ethics an overall agency, unit agency and the balanced supracoagency represent unknown, to which the man penetrates in particular by emotion. Emotion is a solution of the total equation, or inequation extra (i.e. beyond) reasonably and it is with the help of perception, to which non-rational facts are accessible, basically we can talk about the participation on the overall supracoagency, i.e., the interval (perfect 0, perfect ∞).
Aesthetics represents especially a particular view of the agencies of suprareasonable frequency through resources of agencies of sensory frequency. This view presupposes the resolution of complex numerical operations with many unknowns, which represent the numbers outside the interval of numbers available to the created mind. To address this complex equation, virtually systems of equations we need a created emotion.
2.6.1.
Definitions
(formation and performance)
The basic concept of combinatorics is a group, which as coagency is similar to the concept of set, elements can repeat in it however (the same subagenciescoagency) or be arranged (subagenciessubsupracoagency).
We define a
permutation, i.e. all possible ordered n-tuples of n elements, possibly with
repeating, therefore arranged k-tuples of elements (k>n), where certain elements are repeated, variation,
therefore arranged k-tuples with n elements, where n³k, with repeating they are all possible arranged k-tuples from n various elements,
where some of the elements may be repeated, and the combination, which
are groups of k elements of n elements
differing on elements, while it is not taken into account their arrangement, with repeating, where any
element can be freely repeated. In the field of Philosophy of Balance these
phenomena can be defined as contrasubagencies (different elements) subcoagency (groups)
(same-) contrasubagencies (of different elements without repetition) sub-, same-,
supra- (sub) coagency (n>, =, <k for the created groups) (supra) coagency (their set).
The classical definition of probability we can then define in terms of Philosophy of Balance as of unitcosubcoagency of unitcosupracoagency contraagency, i.e. the number of elementary results favorable to a particular phenomenon, which is a subset of the set of all elementary results of an experiment, divided by the number of all these elementary results of the experiment. As well as in the field of sets we can recognize the unification of the sets, i.e. cocontrasubagencies supracoagency, disjoint sets as contraagency and the intersection of the sets as subcoagency. The total cocontraagency of probability has a value of 1. In the case of the unequally probable phenomena the concepts of formula of probability do not represent according to the Philosophy of Balance the number of elementary experiments, but their probability.
2.6.2. Combinatorics image of the world
(termination)
God as the overall agency of the Being, the interval (perfect 0, perfect ∞) is independent of the other agency, there is not bigger or the same big number, which would restrict it, that could have contained this interval in the range of its value. For this reason God is fully independent, he has a completely free will. In contrast he specifies the formation and performance of all other component agencies.
In the field of Being as an agency the individual partial agencies are partly predetermined by performance and the formation and the termination of the other agencies, however they are partly involved in the unlimited freedom of total agency. This freedom is manifested in the level of the more numerous, more complex coagencies as free will, in the level of the less numerous, simpler coagencies as a chance.
So behavior of a man controlled by formation agency of the brain activity is partly in causal relationship predestined by relationship with other simpler and more complex agencies, partly free as a share of the unlimited freedom of total agency, partly random as the result of "free will" of the simpler, non-thinking, non-living contracoagencies, which are involved also in the limitless freedom of the total agency as its components.
In the area of ethics a chance and a free will allow a man to change his or her fate, so that a man partially destined to the evil contraagency imbalance has changed in coagency for the better and vice versa the good man has changed in contraagency for the worse. Only the way to balance is right however, as exorbitant evil the subsequent good punishes, and vice versa, just balance begets peace in human life.
Also in the art a chance plays its big part, because the emotion is not always causing a perfect view of the extra (i.e. beyond) reasonable world by sensory resources due to its imperfection in the case of many people, and so the hand of the artist is often guided by the way of chance, appropriate in particular to simpler forms of Being. A chance as well as involuntary and extrareasonable manifestation of human being (as compound supraagency) show back to its simpler and partial subagency roots.
2.7.1.
Definitions
(formation and performance)
This branch of mathematics deals at first with the definition scope of function, in the field of Philosophy of Balance this is a formation subagency of formation termination coagency. It is about increasing by the derivation or reducing by the integration of density of infinities, calculations with infinities are concerned.
In addition this branch of mathematics deals with the connection of function, which can be expressed in the field of Philosophy of Balance as of unitco- formation termination subagencies coagency. Which means, that as the defining scope of the function and so the scope of its functional values rise or decrease gradually about unit agency. This unit agency is however infinitely small, which means, that the function is increasing or decreasing steadily and continuously as the cocoagency.
In addition to the function connection the mathematical analysis deals with the limit point of function, which can be expressed in the area of Philosophy of Balance as unitco- formation termination subsuprasubagency, which means that the function approaches in the unit agencies from the top and from the bottom in its definition scope and in the field of functional values the number a, virtually f(a). The limit of the function in the point at infinity +-¥ in the field of Philosophy of Balance we can mark as unitco- formation termination supra- or sub-subagency.
The derivation in the area of Philosophy of Balance can be described as termination unitsupraagency formation unitsupraagency contraagency, i.e. the function of infinitely small increment of functional value divided by the infinitely small increment of the variable x of the given function. As it is infinitely small increment limDx®0Df (x)/Dx=y-q/x=k of tangent for q=0, the functional value of the derivation at a given point is equal to the directive of the tangent at that point.
Integral can be defined in the area of Philosophy of Balance as formation termination supracoagency (the original function) formation termination subcoagency (of tangents) subsubagency (directive) formation termination subcoagency (function of the directives of the tangents-derivation of the original function) formation termination supracoagency (of the original function). In the case of definite integral then we can approximately imagine for q1, q2=0 the equation of the tangent of the original function in the point a y1=f(a)=f`(a).a in point b y2=f(b)= f `(b).b jako f(b)-f(a)= f `(b).b-f `(a).a, where f ' is the derivation of a function, the "." is the multiplication.
2.7.2. Mathemtical-analytical picture of the world
(termination)
Mathematical analysis carries out numerous operations with the infinitely small and the infinitely large agency, limx® 0 and limx®¥ f (x). Infinitely large contraagency-¥ and coagency +¥ we can identify with God as the overall agency. By calculations integrating the total agency we understand the whole of Being, and we are getting closer to God. By the carlculations integrating infinitely small agency we also understand the extra (i.e. beyond) sensory essence of our existence in a sort of ursubstance, in fact in the nothingness, from which is composed all the Being, whether as the total coagency +¥ or total contraagency -¥.
Due to the infinity and continuity of all the Being as agency we can approach closer to its essence just in the context of infinite coagency (sum, product, exponentiation) or the endless contraagency (difference, quotient, root) or calculating integrating the value +-¥ or 1/+-¥, thus infinitely large or small agency, that this infinite numerical operation represents. In this way we can understand limx®0 and limx®¥ of function, limits limn®¥ of sequence of partial sums of infinite series, thus the sum of the infinite series.
The human mind is from the positive perspective limited only to physical (i.e. material) phenomena, which it gets through sensory perception. The context and the continuity of Being as an overall agency imply however the possibility to inspect the extrasensory agencies using the logical context and analogy or similarity. In this way we can show total and infinite or infinitely small unit agency through the material thinking and penetrate so beyond tangible (i.e. material) objects and phenomena the total and unit agency, therefore God and the ursubstance, which is nothingness.
From the standpoint of ethics we must see the balanced behavior not only from the perspective of immediate final situation, but search for acceptable compromise in terms of the total agency. Such a compromise is unshakable, since it means the balance not only from the perspective of each unit agency, more complex agency, but also of the overall agency. In practice a man finds with the help of reason and emotion immediate balance, that he or she arranges with regard to the newly arising agencies.
Aesthetics works also with an extrasensory overall, or simpler agency, which it shows through sensory means. Also here the reason is applied next to the emotion, the reason uses a logical connection and similarities of our world with the total of Being.
2.8.1. Introduction
(formation)
Mathematics can be
divided according to the total ageny and unit agency into counting with the
numbers, where unit agency is in the case of the natural numbers the number 1
and the overall agency +¥ and the geometry
in the 0 up 3 dimension, where unit agency is the point and the
overall agency is a three-dimensional space.The concept of number is
more complex concept than the concept of x- dimensional space, which means,
that numerical operations with numbers can be projected in 1 dimension of
geometric space, but the concept of number projected as a point of the line can
be decomposed in an infinite number of spaces of the lower dimension. The concept
of number is therefore more complex concept, which produces due to smaller
number of elements (virtually the bigger density of elements of given infinity)
a simpler system than the system of geometry. The above phenomenon is a result
of degrees of the total agency. At the same time from the context of the total
agency it flows, that by using numeric coordinates the geometric relationships can
be expressed in a generalized form, which the analytic geometry proves.
(subagencies)
2.8.2.1.
Introduction
(formation)
Planimetry is geometry in the plane, the overall agency represents the plane, the unit agency is the point of the plane, the cosubagencies are planar figures composed of points as a subsets of the plane or half-plane.
2.8.2.2. Definitions
(performance)
In this scope of geometry the subagency can be distinguished, namely the belonging to the figure, contrasubagency, so the non belonging to the figure, the same subagency, so the identity and diversity, or contrasame subagency and with greater frequency as supraagency and with less frequency as subagency. The size of the figure means in the area of Philosophy of Balance the frequency of agency. For planar figures of the same kind the geometric sum (coagency) and the geometric difference (contraagency) can be distinguished similarly as in mathematical arithmetic. Two planar figures may have common points- intersection or cosubagency or have zero intersection as contracosubagency.
Triangle, circle, polygon as the geometric figures are cocosubagencies, i.e. sets of points, subsets of the plane, which create own systems. Subagencies, so planar figures, which are subsets of these systems, are due to the nature of the systems again in geometric or in numeric relationships.
Geometric places of points can be described in the area of Philosophy of Balance as formation subagencies coagencies. Therefore as a set of points, that have the specified characteristics, at the same time each point, which has a prescribed characteristics, is the point of the figure.
Equivalent to functions in the math algebra represents the geometric projection in the plane as a formation termination coagency. Direct identity can be described as co- termination subcoagency and indirect identity as contra termination subcoagency. Similarly as in the case of planar figures it is true, that the projection in the plane represents cocoagency, i.e. systems, of which elements are in numerical and geometric relationships.
Similarly such as analytic geometry some geometric relations can be expressed in algebraic and arithmetic form. This is especially true for the above cocoagencies, i.e. the subsets of the plane in the form of systems, of which elements are in geometric and numerical relationships. This means, that the subagencies of these cosupracoagencies (systems) are again in coagency relations as subsystems (cosubcoagencies). The result of these relationships is the algebraic method of the solution of structural exercises, the content of the geometric figures and trigonometry in the solution of the planimetry exercises.
2.8.3.1.
Introduction
(formation)
Stereometry is more complex agency in relation to planimetry or geometry in the plane. It is geometry in the space, which is a set of infinite quantity of the planes, so it is the supracoagency of subcoagencies. Unit agency is here again the point in space, the overall agency is 3-dimensional space, the cosubagency is spatial figures composed of points as a subsets of the space, or half-spaces.
2.8.3.2.
Definitions
(performance)
To relations of subagencies, spatial figures, geometrical places of points, the geometric projection in space, volumes and surfaces of bodies and trigonometry it applies in a logical context and analogically that, what has been said about the relevant agencies in the plane.
2.8.4.1.
Introduction
(formation)
Arithmetic and algebraic mathematics relations represent in contrast to the mathematical geometric relations the more general supracoagency or system with more complex concepts, of which a smaller number is compared to the geometry, in relation to which algebra and arithmetic is simpler scientific scope as opposed to geometry. However supracoagency characteristics, i.e. of more complex higher system is, that it is already embryonically contained in each of its components, and as such we can use it to inspect and to analyze those of its components. This means, that the mathematical numerical more general properties can be searched also in the scope of their subcoagency-geometry, which is a kind of specific specification of generic numeric and algebraic relationships. The means of this specification is a coordinate system as the formation termination coagency, that assigns to each element of formation cosubagency (the x axis) infinite number of elements of termination cosubagency (the y axis), if it is about geometry in the plane, similarly it is in the space of another dimension.
(subagency)
2.8.4.2 ANALYTICAL GEOMETRY IN THE PLANE
2.8.4.2.1.
Definitions
(formation and performance)
Coordinate expressing of the total agency is the sum of all the various ordered pairs (subcoagencies) of numbers x, y, xÎ(-¥+¥), yÎ(-¥, +¥), unit agency is then subcoagency [0,0] or otherwise expressed [1/¥,1/¥], by which addition by coagency or subtraction by contraagency the each and every point of the plane can be expressed in my opinion. Planar figures as subsets of all points in the plane or subagencies coagency subagency can be expressed as a function of the unknowns x and y, in the area of Philosophy of Balance as the formation supraagency (unkown x) termination supraagency (unknown y) coagency (function), where x and y represent within the scope of the definition field of an unknown x the coordinates x, y of all points of the planar figure. Subcoagency of contracoagencies, i.e., the intersection of sveral planar figures represents formation termination subcoagencies, so subagencies of certain organized pair of unknown x and y, which correspond to the supraagencies of the unknown x and y of functions of all considered planar figures. It is about solving of systems of equations or inequations.
2.8. Geometric image of the world
(termination)
If we consider a three-dimensional space, and then the space of infinite dimensions, which is a consequence of the Being as a stepped and coherent, continuous and endless agency, then the total agency represents in the first case the three-dimensional space and more generally the perfectly infinitely dimensional space, which is from the perspective of Philosophy of Balance also the God. In the framework of this perfect infinity we can distinguish in the geometric form the sums, differences of spaces and derived operations, which represent as well as in mathematics of numbers the co- and contra- agencies. These operations are in an uncompounded form the agency of the good and the evil, to which is superior the fact of the all-embracing space, thus supracoagency representing all the Being or God.
From the point of view of a three-dimensional ontology the unit agency of Being is, from which everything is made up, the point in space, but even this point consists of spaces at the smaller size in terms of infinity and degrees of agency. This unit agency or ursubstance is a mere fiction, or infinitely low dimensional space or nothing. Each particular subspace can be broken down into subspaces of this space. From this infinitely little dimensional space is then composed everything, whether matter or spirit.
The human mind from the perspective of the geometry is a complex geometric figure filled with different points of space as four-dimensional spatial unit agencies, which are however from the perspective of an infinitely dimensional space the differently composited spatial systems or coagencies. The space of smaller than zero dimension is by the human mind hardly catchable, as well as the space of higher than the fourth dimension. From the connection and the continuity of Being as agency we can suggest on the basis of similarity and logical connection with a three-dimensional space their existence. The similarly spatial figures as the human mind can be understood even more the facts of our being.
From the perspective
of Philosophy of Balance we can accept the theory of gradual formation of a subspace
and supraspace within the creative coagency and decomposition contraagency, thus
within the infinite process of agency. From the standpoint of mere geometry the
balance can be seen in the stability of the space represented by the same
creation of new spaces by merging of spaces and decomposing of spaces. From the
perspective of Philosophy of Balance the balanced behavior can be characterized
as the balanced formation agency. The balance in the human agency is in limited
formation of four dimensional spatial figures, which
is in line with the overall balanced formation agency. In the context of
subspaces it is represented by limited decomposition of spaces, in the
framework of superspaces by limited merging of spaces, with the predominant
nature of limited merge of the superspaces. The balance of spaces is the only given,
that determines ultimately the result of all of partial, even
three-dimensional agency. Predestination of human actions by spatial
relations is only partial due to the unlimitedness of total, perfectly infinitely dimensional space
by a superior or by same dimensional space. For this unlimitedness every subspace is
partially divided.
Aesthetics represents the penetration
of the higher and lower than the four-dimensional space, accessible only by reason
in the form of context and analogy with four-dimensional space and by emotion. So
by this means of four-dimensional space accessible to human senses we get
closer to God and the essence of our existence. As the spatial Being is a
constant agency, the disintegration of the space as contraagency can be
captured as well as their merging or coagency.
2.9 ARITHMETIC AND GEOMETRY OF
INFINITY
Introduction
(formation)
In the case of non-negative number ∞ in terms
of the Philosophy of Balance of it is the overall agency, which includes simpler agencies from the arithmetic of nonnegative
numbers. Laws applied for numerical operations of ∞ are also applied in
the partial form even for numerical
operations with lower numbers, which follows from the connection and the
continuity of all agency from the perspective of Philosophy of Balance.
The calculations
in the field of arithmetic can be geometrically projected by the objects of the
same size, of points in geometry of zero dimension, of unit line segments in the geometry of the
straight line or the first dimension, of the unit areas in the geometry of the
plane or the second dimension and of unit
spaces in the geometry of three-dimensional space. The number of these objects equal
to ∞ represents then the overall agency, or subagency, which is again
continuous and continuously happening.
Arithmetic of a number ∞ we can project once
again geometrically, which stems from the nature of the geometry as a
subagency, therefore the special scope in relation to mathematics. Geometry
shows the general term of number in geometric objects and their relationships
in geometric relationships. General laws of arithmetic are applied once again
in geometry and the laws of geometry are applied in general form in arithmetic,
which follows from the continuity and connection of all agency from the
perspective of Philosophy of Balance.
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
The number ∞ represents a complex coagency,
then the result in the case of divergent
sequences of the endless number of mainly coagency mathematical operations.
Among coagency mathematical operations of arithmetic, as I have already said in
the Philosophy of Balance of mathematics, there are addition, multiplication
and exponentiation, where the unit agency of these three operations, from which
are composed the both of the others, is the addition. On this basis we can
define the unit agency of number ∞, which is the sum of
an infinite number of numbers 1, i.e. ∞j=l+l+l+… . From this unit agency all the
other numbers of value ∞ are composed. The number of these unit agencies in
a specific number ∞ we find out ∞/∞j and the number
of a particular ∞ we once again obtain by multiplying of this number of
unit agencies by the number ∞j.
Arithmetic of the number ∞ projected in the geometry we are crossing the only one dimension and it brings us
into a higher dimension of mathematical coagencies, virtually to the lower
dimension for mathematical contraagencies, which are the mathematical inverse
operations of the above mathematical coagencies. The geometric projection in
the first dimension of the countless ∞ number of mathematical coagency operations of non-zero
final number, which can be projected as line segement, is a straight line,
regardless of the number of ∞j in a particular number ∞,
by that we multiple, and regardless of the length of the line. In this sense,
you can talk about the same value and
different density of all the numbers ∞, regardless of how many of ∞
j they include in themselves.
However the line is already the object of a 2-dimensional space with zero-width.
A non-zero width we get by multiplying of the line again by incountable number
∞ , thus 1*∞2.
By the last consideration above we got to a special
issue of the arithmetic of infinity, thus counting
operations of the number ∞ and 0.
The number zero represents the actual unit agency in the field of arithmetic of
numbers. In the framework of the geometric projection in the second dimension
it can be thought as a straight line, thus a plane of zero-width and area. From
the last consideration in the previousl paragraph it stems, that a plane strip
of width 1/∞j is equal to 0, or a straight line with a width
of 0. In other words 1/∞j is equal to 0, where the number 1
represents a line of length 1 and the number 0 the point of this line or number
1 a plane strip with a width of 1 and the number 0 a straight line or number 1
three-dimensional space of dimensions a=1, b=1 and c =∞ and the number 0 a
plane strip with a width of 1, etc. If there is a particular infinity
∞=2*∞j, or ∞=(1/2)*∞j, then the
dimension of a line will have double or half size.
From the above it follows, that the value of the number 0 and ∞ in terms of more dimensional
space and its arithmetic can be different depending on the number of unit
agenciesof the number 0, which is
l/∞j, and the number ∞, which is the number of ∞j
contained in them. Different values gain then also their mathematical coagencies
and contraagencies. In addition in the case, that the number of unit agencies
in number ∞ is equal to incountable ∞ again, or 1/∞ in the
case of the number 0, these are the geometric objects in the area of higher or
lower dimension again.
Calculations with a perfect infinite
and perfect zero:
=x
Or:
==
Author:
Dalibor Grůza
Time:
09/04/2012 06:53:12
Post:
quoted:
Post of Bolshevik
Doctor, I wonder, what would you say to your client,
if he issued you a bill for legal services, let us say, 10000, - CZK and he or
she would not pay you anything on the ground, that under the Philosophy of
Balance 1 = 0 and thus 10000 x 1 = 10000 = 10000 x 0 (substitution according to
the Philosophy of Balance) = 0?
Bolshevik,
according to the above implication
10000=1=0=∞, as it consists of
∞ zero-units parts.
Therefore 10000=10000x1=10000x0=0=1=∞ applies, because
∞=∞x1=∞ . The above-mentioned implication can be expressed
geometrically, so that, if we consider it as a unit the length of a geometric
point of 0 meters, the line of a length 1meter has ∞ of these zero units,
it is the obvious mathematical fact. Or
in other words a geometric point as the space of zero-dimension is infinity for
the point of the space of the minus first dimension etc., to perfect zero,
which one can no longer divide, or perfect infinity, which one can no longer increase. For perfect zero it is not zero meters but
zero of all units, i.e. things because zero meters mean the absence only of
metric units and it admits the presence of other units, i.e. things such as
geometric points of above zero-dimension space, zero meters or unit zero is not
perfect nothing, i.e. perfect infinity is then according to me equal
to zero of all units, i.e. things from zero meters, eg 0 meters divided
by the perfect zero, because in my opinion, everything is perfectly infinitely
divisible, and never in my opinion the end of the division, even if we will be
more and more perfect, in other words in my opinion, we will be increasingly
similar to God, however we can never cope Him, that is, as to me no creature
will ever be able to precisely calculate perfect infinities and perfect zeros,
as to me our calculation will be more and more precise, but in my opinion
always only approximate, so in my opinion all creatures are waiting perfect
endless journey to cope perfect infinite
uncreated God. In other words, in my
opinion perfect zero times perfect infinity can be certainly equal to anything,
any unit-zero, because the unit zero divided by perfect zero equals to perfect
infinity, and in my opinion, thus unit-zero times perfect infinity may also be
equal to perfect infinity, because in my opinion unit-zero divided by perfect
zero is equal to perfect infinity, see viz http://forum.filosofie.cz/forum/topic.asp?TOPIC_ID=1375 : Ráj začíná vědeckým pokusem na mé zahradě, http://forum.filosofie.cz/forum/topic.asp?TOPIC_ID=1250 : Shrnutí filosofie rovnováhy v binárním kódu 1a 0.
3.1.1
INTRODUCTION
3.1.2
DEFINITIONS
3.2.1.
INTRODUCTION
3.2.2 KINEMATICS
3.2.3 DYNAMICS
3.3 THERMAL AND
MOLECULAR PHYSICS
3.4 MECHANICAL
VIBRATIONS AND WAVES
3.5.1
INTRODUCTION
3.5.2 ELECTRICAL
FIELD
3.5.3 ELECTRIC
CURRENT IN METALS
3.5.4 ELECTRICAL
CURRENT IN LIQUIDS
3.5.5 ELECTRIC
CURRENT IN GASES
3.5.6 MAGNETIC
FIELD
3.5.7
ALTERNATING CURRENT (AC)
3.5.8 PHYSICAL
CHARACTERISTICS OF ELECTRONICS
3.5.9
ELECTROMAGNETIC VIBRATIONS AND WAVES.
3.6.1
INTRODUCTION
3.6.2 LIGHT AS
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
3.6.3 OPTICAL
DISPLAY AND OPTICAL SYSTEM
3.6.4
ELECTROMAGNETIC RAYS
3.7 SPECIAL THEORY OF
RELATIVITY
3.7.1 SPECIAL
THEORY OF RELATIVITY
3.7.2 NEXT
DIMENSION
3.8.1.
INTRODUCTION
3.8.2 QUANTUM
PHYSICS
3.8.3 PHYSICS OF
ELECTRON PACKAGING
3.8.4 PHYSICS OF
ATOMIC NUCLEUS
3.8.5 BINDING
ENERGY OF NUCLEI AND NUCLEAR REACTIONS
3.9.1
INTRODUCTION
3.9.2 SOLAR
SYSTEM
3.9.3 BASIC
INFORMATION ABOUT STARS
3.9.4 STRUCTURE
AND EVOLUTION OF THE UNIVERSE
3.9.5
ASTROPHYSICAL PICTURE OF THE WORLD
(formation)
3.1.1 INTRODUCTION
(formation)
The object of
physics as a whole (formation subagency of
formation agency) is a movement. This movement according to its frequency is examined as by
fields of physics dealing with the macroworld (supraagencies) as mechanics,
optics, or astrophysics, so by the fields of physics dealing with the
microworld (subagencies) as a molecular physics, thermal physics, acoustics,
thermodynamics, electricity and magnetism, atomic, nuclear and particle
physics, and wave optics, possibly astrophysics. The movement as a phenomenon
(the agency) in the world of phenomena (the overall agency) can be
characterized as a performance agency and especially as a cocontraagency.
Contraagency is movement, because opposed to coagency it is characteristic
for creating a distance from the whole, by contrast in the coagency movement there occurs approaching
towards the whole. At perfect motion (termination agency) in the case of
coagency only the whole moves in relation to other wholes, all its parts are in
a zero-distance and against each other without any collisions, at contraagency they
are in an infinite distance or with collisions.
By its object physics differs from mathematics, of
which object is a number as coagency or unit agency in the case of the number zero,
either as cocoagency for positive numbers or cocontraagency for negative
numbers. From this perspective, also the frequency of the movement gains the numeric
values as coagency. Due to the nature of the movement as vector or formation
termination cocoagency as a movement in a certain direction or termination
formation cocontraagency as a movement in the opposite direction the concept of
movement is more special concept than more general concept of number.
Mathematics with the basic concept of a number (supraagency) is so more general
scientific discipline than physics with the
basic concept of movement (subagency). In other words the concept of a number
is more numerous total composed of unit agencies than the
concept of movement as the less numerous total composed of the same unit
agencies. As a result mathematics is more general science seemingly more simple
due to the less number of more general concepts than the physics.
Physics as more specialised science in relation to the more general
mathematics and even more general Philosophy
of Balance is possible to see in
terms of the concepts of these more general scientific disciplines. This
option follows from the nature of the world as an agency, a coherent and
continuous whole. This means that complex concepts of mathematics and
Philosophy of Balance (supraagency) include in itself simpler concepts of physics
(subagencies),
from
which they
are
composed. Using of these set concepts arising from unification of elements with
identical properties in the conceptual (agency) analysis of sentences of physical
sciences allow us to explore these concepts of physics (the elements of the set
concepts of mathematics and then of Philosophy of Balance) in the new vertical
(in the context of physics) and horizontal (in the context of mathematics and
Philosophy of Balance) contexts.
3.1.2 DEFINITIONS
(formation of performance)
In the introduction we divided the physics
disciplines according to their subject into the physics of macroworld (subject
is supraagencies) and physics of microworld (subject is sub-and unit agencies).
In conformity with the foreword and its interpretation of the issue of an
object and a subject in science the physics explores the physical properties (subagencies of movement) and their mutual
interaction (their cocontraagency). The laws, principles and theories of
physics can be described as the performance (according to the effect) formation
(ideas) subsupraagencies (i.e. more or less effective ideas). The basic units
of physical quantities are unit agencies of subagencies of motion. Derived
units are then their mathematical cocontraagencies, or physical cocontracounit
agencies. Measurement can be marked as unit contracosubagency contracoagency,
i.e. the interaction between measuring equipment, that determines on the basis
of certain property the number of units of quantity of a particular agency. At
the measuring device it can be unit-, co-, the same subagency, i.e. indicating
directly the units of given quantity or unit- contra- the same subagency, i.e.
specifying units of other quantity and
calculation of the quantity on the basis
of their known relationship (mathematical cocontraagency). Measurement errors
can be marked as contraagencies and elimination of these errors on the basis of
the mathematical remeasuring as contracontraagency.
Subagencies
(performance)
3.2.1. INTRODUCTION
(formation)
Mechanics is the branch of physics, that explores the movement of tangible (i.e. material)
objects in the macroworld, i.e. the performance of supracontracoagency.
Mechanical movement is the sum of an infinite number of unit agency movements
in our microcosm. However the connection and fluency of the world as an overall
agency imply, that laws of motion valid
in the macroworld are valid in partial
form also for motion in microcosm (subcoagency). In other words by
sentences of mechanics as complex subcoagencies also the sentences and the
phenomena of microphysics fields can be expressed, as I defined it below. These
sentences of mechanics are however valid in amended or restricted form due to
the synthetic nature of the sentences of mechanics compared to analytical
nature of sentences of physics describing the phenomena of the microworld. This
continuous and fluency (indivisible) view on physics through the scope of the
physical mechanics as the most general science of physics enables us to see physics
as a single whole built on the foundations of the sensory phenomena, which are
the subject of mechanics. If we then perceive mechanics as a general supraagency of physics, then the
rest of its scopes is its special subagencies, from which this supraagency is
composed.
From fluency (indivisibility) and connection of all the
agencies in the world as the overall agency the nature of the total and its
partial movements as a single agency follows that only our mind and senses divide
by perception of the individual
properties (subagencies) such as weight, size, time, temperature, etc. These
subagencies are at the same time subcoagencies, as a part of a single movement,
so they are mathematically and physically connected and they fluently go from
one into the second according to the laws of their connection, while
maintaining the quantity (frequency) of the variable characterizing the
movement as a whole composed of the above subagencies.
The mechanics consists of kinematics and dynamics.
Subagencies (performance)
3.2.2 KINEMATICS
Introduction
(formation)
Kinematics deals with movement in macroworld in terms of the
most common sensory quantities, i.e. the dimension
and time, which in the context of their mathematical subcontracoagency mean
the speed and acceleration. What has
been said about the relationship of mechanics and other disciplines of physics,
it applies mutatis mutandis about the relationship between the kinematics and
dynamics. Kinematics is the general science and it explores the general
phenomena of motion, which are further decomposed into simpler due to the
universality of kinematic phenomena but more complex due to the number of
variables of investigated phenomena and sentence of dynamics. Here the laws about the relationship of more general
to the specific in the opposite sense apply, as they are commonly perceived,
with the above consequences.
Kinematics is however only simple generalization of
motion in macroworld and it is not its compact image (formation subagency), to the overall view of the movement in
macroworld it is needed to use analysis from the field of mechanical dynamics and
to apply the speed to the next most important sensory quantity, which is the
weight. Thus we obtain the relationship, that is a complete description of
motion in macroworld, namely the analysis of the speed, virtually dimensional
and time relationship of sub2contracoagency on the speed and weight sub3contracoagency
(i.e. a relationship consisting of three subagencies).
Definitions and relationships
(performance).
Unit agency of movement from the viewpoint of kinematics is
immobility or movement characterized by variable of speed m/s divided into infinitely partial
movements characterized by this quantity m/∞, divided by s/∞, where
m is the meter and s is the second. A specific speed as a contraagency of
quantity of time and dimension is then
the sum of an infinite number of agencies, where the formation and termination
fall in one. Therefore in terms of the dimension of endless number of motionless
positions of tangible (material) body, or a point in the kinematics of a tangible
(material) point, which are in terms of time lasting an infinitely short
moment. The resulting speed is then the
composition of the endless number of material bodies existing at the infinite
places for infinitely short moment. Thus the unit agency of movement
(m/∞)/(s/∞)×(∞/∞). From this unit agency it is then
composed as an overall agency meaning the total physical movement. Considering
connection and fluency (continuity and infinity) of an agency this overall movement characterized by
variable speed is equal to [(m/∞)/(s/∞)]×(∞x/∞x),
x=∞. By contraagency I understand the movement of two and more tangible
(material) bodies or points in the direction from themselves or their
collisions, by coagency it is towards each other and without collisions. Furthermore
it is possible to distinguish between coco (cocontra) agency such as accelerating movement and
contraco (cocontra) agency as slowing movement. This contra, virtually coagency
subagency (or time) shows the deceleration, virtually the acceleration of
movement. The overall movement means the vector sum of total contraagency and
coagency, therefore [(m/∞)/(s/∞)]*(∞x /∞x
)+[(-m/∞)/(s/∞)]*(∞x /∞ x), x=∞.
The acceleration or deceleration is
subcontracoagency of speed and weight, which include them in itself in the form of subagencies. At the
same time it is a termination formation agency like the force, because its size
is determined by the size of the speed in the past, thus by the previous agencies.
At the same time it is cosubagency, because it is the result of contracoagency
of sensory perception of speed, thus the idea,
which is not already perceived directly by senses. For acceleration the
relationship of the general and the special applies mutatis mutandis, as it was
defined for the relationship of mechanics and other branches of microphysics.
In the case of a choice of axis of three-dimensional
coordinates identical to the rectilinear motion, meaning constant value of two
same subagencies of quantity of dimension it is rectilinear motion of a tangible (material) particle. In the case
of coagency relationship of two of these coordinates with the beginning of the
coordinates in the center of the circle and the plane specified by two
coordinates identical with the plane, in which a circle lies, this circuit movement can be expressed x2+
y2= r2 of these two dimensions. According to the same
agency of the speed it is a steady movement, according to coagency of acceleration
and deceleration it is a movement evenly accelerated and decelerated.
From the connection and the fluency of movement as
agency then flow out the relations of thought subagencies, i.e. of the
dimension, of time and of the velocity and acceleration as the
subcontracoagency relation of partial quantities of motion of contracoagency as
a part of an overall relationship characterizing the whole movement.
The trajectory and speed as properties of the
kinematic motion are however relative to the system you choose. The reference
system can be understood as subsubcoagency of the overall agency or as a movement system,
which is a subset of the system as the sum of total kinematic motion. If we expressed
the total agency as the sum of all movement as a vector sum [(m/∞)/(s/∞)]*(∞x
/∞x )+[(-m/∞)/(s/∞)]*(∞x /∞
x), x=∞, then the frame of reference is the same sum for x ≤
∞, where for x = ∞ it is the overall movement, therefore the world
from the viewpoint of kinematics. If we then consider the movement in the first frame of reference as starting
(formation agency), then variables (unitcoagencies) characterizing this
movement need to be adjusted by the number of unit agencies of movement
attributing to the unit quantity of
movement of the first frame of reference
in the second frame of reference. Due to the speed so it can be coagency
for faster systems or contraagency for slower systems. Contraagency therefore the
slowing movement in one frame of reference may appear as coagency, i.e. the
accelerated motion in the second frame of reference. So the movement seems relative in terms of reference systems.
However this does not apply, if we choose as first reference system the overall kinematic motion, as it has been
described by a mathematical relation above. This total kinematic movement
already contains in itself the other reference systems and their relationships.
So we get the absolute quantity of kinematic motion.
In the case, that unit agency will be only trajectory
s divided by t/∞, then we can calculate the instantaneous speed or speed v divided by t/∞ of immediate acceleration of a tangible
(material) particle or the body.
Kinematic picture of the world
(termination)
The total
kinematic movement represents in Philosophy of Balance the total coagency, or God. From the
perspective of Philosophy of Balance of agency it is due to the infinity and
continuity of this motion as the number of elements, of which this movement is
composed, equal to infinity. The overall movement as an overall agency has on
the other hand a constant frequency, which is also fixed in isolated systems,
which is in fact only the overall agency. Other isolated systems as a partial
movement of the total movement are just a fiction of our mind, since the
movement as the agency is in fact indivisible. The movement is directed either
to the integration, i.e. the movement of the bodies to each other without any
collisions such as coagency, or disintegration as the mutual movement of the bodies away from each other or
collisions, i.e. contraagency. Both of these basic types of movement compose a
whole movement as a God in the form of an Angel and a Devil and they create so
the infinite whole of Being.
In fact each
composed movement and also the total kinematic movement is contracoagency,
i.e. integration in relation to some movements and disintegration in relation
to other movements, i.e. contracoagency. The total coagency of these relative
movements is then supracontracoagency, which is neither contra- nor co- agency
and it contains also both kinds of agencies such as higher coagency. Unit
agency of kinematic movements is motionless body in zero time interval. The
sum of these unit agencies, characterized by the speed of both types of
movements, i.e. integration and disintegration, gives the overall movement as a
whole Being. From this unit agency are also from the standpoint of the
kinematic motion composed all objects as complex unitcoagency of total
cococontraagency, both spiritual and material. The frequency of these unit
agencies in total but also in sub- agency is equal to ∞.
As the complex
kinematic movement can be understood also the cocontraagency of mind. The
mind is a complex movement made up however in the final result of the
movement unit agencies. However we can generally say, that the frequency of
motion as the mind of the individual people is different from the aspect of
unit agencies but of the same range. They are therefore similar. The overall
movement involving the mind of all people is able to cover a larger part
of the movement of the whole Being than the mind of the individual human Being
or a subset group of people. Total mind can be identified with the total
kinematic motion, which includes all of the unit agencies of movement and their
component parts. It is the whole Being or God. The process of thinking or
the formation of agency and the performance and termination of the agency is
not separated here, which is in fact indivisible and only our mind it divides artificially.
Even more complex movement than the mind is a human emotion. The mind is
composed integration and disintegration movement. Mind, emotion and ideas are
the movement of the great frequency of unit agencies of movement and they cannot
well cover the kinematic movement, which has the same or greater frequency of
unit agencies, and the movements, which have a lower frequency of the unit
agencies of movement, than is the interval of frequency of kinematic movement
catchable by human mind. These extra
(i.e. beyond) thought and extrasensory agencies can be imagined only by
using a logical connection and similarity of everything agency.
The question of
how to live (ethics) is possible to answer by the notion of
supracocontraagency, which represents the motion without the collisions within
the movement of integration and
disintegration, which is however relative, and that to the maximum extent. It
is the average movement corresponding to the total movement, of which
integration and disintegration in the framework of the Being we get it alone,
therefore the movement characterizing itself on context of infinite kinematic
movement by relative stability. If we do not try for average movement in relation to my
personality as a component of motion of the overall movement, I will not
disturb overall balanced movement, only there will be the multiple integration
or disintegration counter-movement according to the law of action and
reaction and I cause myself a pain. Complex movement can be seen as the result
of the interaction of the individual movements (their math cocontraagency), but
they are also the result of chance such as the independence of the perfectly
infinitely partial unit agency of kinematic motion, or of its whole.
What concerns
the aesthetics or beauty, so we can say, that it applies in particular
to emotionally perceived overall kinematic motion. This object of emotion goes
beyond the object of the human reason as a simpler motion. Through art we
penetrate a balanced whole as balanced kinematic integration and
disintegration, whether in the interval of unit agency frequency of our mind,
or simpler or more complex movement outside of this interval, and that is in
this case also in the form of an imbalanced integration or disintegrative
kinematic motion.
3.2.3 DYNAMICS
Introduction
(formation)
In terms of the
dynamics the kinetic movement as a
subagency is divided also into the interaction of speed and weight. Speed and
acceleration as the result of a complex agency is so related and it includes in
itself already the effect of weight.
Dynamic physical movement represents in relation to the physical movement of particles
in our microcosm a summary of these movements, and their generalization,
where the laws of this dynamic physical movement apply in the partial form also
for the physical movement of particles in our microcosm.
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
To assess the relationship of an individual movement
towards the total movement the dynamics uses the fiction of the partial
movement system that is isolated and therefore it represents the overall
movement, that is in fact from the standpoint of the Philosophy of Balance infinite, and therefore indivisible. The
overall infinite, continuous and indivisible movement only our mind divides artificially to
illustrate the fact of the overall movement. This partial isolated total movement
system is in terms of the theory of physics the isolated material point and isolated system.
Frame of reference, in which the body is at rest or
in the linear movement, is steady inertial
frame of reference and reference system, in which the body is moving with
acceleration, is non-inertial reference
frame. Which system is at rest,
and which speeds up or slows down is not relative in respect of these two
systems, however in relation to the overall movement, i.e. in relation to the whole of reference systems we arrive
to the absolute relations. These relations are calm or have rectilinear motion
of unit agency of inertial system, i.e.
isolated tangible (i.e. material) particle, which is alone the smallest
inertial frame. Relationship to the overall movement, i.e. to the biggest
inertial system is mediated by time and distance, i.e. ∞*s/(∞*t), s/t
represents the average Universe velocity when negligible weight, where s is the
trajectory and t is the time. Movement in all inertial motion systems is of the
same type and apply the same equations for speed and weight or only for speed
when negligible weight.
As I have already stated, physical phenomena can be generally described
as the movement consisting of the
movement of unit agency, which is the steady state in infinitely short
time. At the same time the movement is the agency, which is indivisible and
coherent, and only our mind separates it on the various components of the movement
perceived by our senses. These ingredients, such as weight, trajectory and time, are also a complex movement. These
components are together indivisibly linked again, this is therefore a kind of
reality, from their relationships whether mathematical contra-, co- agencies we
gain once again partial movements, which are a component of the overall
movement.
For a description of the movement we need to select the
relationship, that puts into the simplest connection all basic quantities
perceived by our senses, i.e. the weight, the trajectory and the time or speed.
This simplest relationship describing indivisible movement will be so unit
agency, the essential expression of the whole and the parts of the movement,
therefore the physical reality. All other relationships describing the movement
will be the extension, then contracoagencies of this basic relationship. This basic relationship of movement represents
the relationship for momentum p=m*v=m*s/t, where m is the mass and v the speed,
s the trajectory and t the time. All other relationships describing the
different kinds of physical movement are then derived from this basic
relationship. Here I mean first the relations of mechanical energy, but also of
the total energy in relativistic physics, but also the relations of
thermodynamics, optics and microphysics, where there are the appropriate kinds
of physical movement.
From this connection of physical movements for
example flows the link of the law of conservation of momentum with the law of
conservation of energy, hence the law of conservation
of mechanical energy and the conservation of electric charge. Link to the law of
conservation of momentum and of energy is possible to prove from the
relationships derived in relativistic physics, specifically in the Special
theory of relativity. We are considering the zero-mass particles, then its all
energy is mechanical energy. Mechanical energy consists of kinetic energy and
potential kinetic energy. Potential kinetic energy represents other kinds of
energy, whether mechanical or others, for example the heat, which can be
converted to kinetic energy. It follows from this, that, if we convert the
total energy of the body into the kinetic energy, and we calculate it, we
obtain the total energy of the body. In practice this means, that the body we
convert into a one-way stream of photons-electromagnetic radiation of the speed
of light of the same relativistic mass and energy as this material body. The
total resting energy of the photon of this body will be E=m0c2,
m0=0, m0 represents a zero relativistic mass of photon
moving at the speed of light c. The total kinetic energy of the photon of body
would be E=mc2-m0c2= mc2-0=mc2,
i.e., equal to the total energy of the photon, where m is the relativistic
weight. Potential kinetic energy is equal to 0, and the photon energy is
represented only by its kinetic energy. However the same is true for the body
as a whole, as due to the non-zero total energy of the photon and the final total
energy of body expressed in the form of electromagnetic radiation its total
energy is equal to the kinetic energy Ef*x = Et , where Ef
is the kinetic energy of the photon of the body, x number of photons moving at
the speed of light in so expressed body and Et the total energy of
the body.
The law of conservation of momentum applies to
isolated material body as an isolated inertial system p=mfc (=po)*x,
where mf is the relativistic mass of the photon moving at the speed
of light c, po the momentum of the photon and x number of photon forming in summary energy of the body, p I will refer to further by the
concept of relativistic momentum, po is the relativistic momentum of
a single photon. Due to the fact, that c is a constant and p is a constant, it
is also for the relation Et= E*x= mfc2*x, and
therefore the law of conservation of energy applies, which we have inferred
from the law of conservation of momentum. There, where I am talking about the body,
we can also talk about isolated motion system, expressed also by relation p=m*v,
where the law of conservation of momentum and energy is applied too.
Now to the unit agency of movement expressed by the
general formula m*v, from which all the physical movement is composed. Already
in the field of kinematics we have expressed this unit by the relationship (s/∞)/(t/∞).This unit agency is still position of
the body in an infinitely short time, when its weight is neglected. If to this relation for the speed the variable
weight m comes also, then this motion can be expressed by unit agency (m/∞)*(s/∞)/(t/∞) and it is still the position of the infinitely light particles for the infinitely
short moment, which means that this particle exists for infinitely short period
of time, its origin, performance and termination fall so from view of agency Being
of Philosophy of Balance in a single, they merge. Definition of the unit agency
of movement implies roughly, that each body is composed of photons at a
standstill, which are however also composed of the above individual movements.
The whole of Being as an infinite physical movement can then be expressed as a product of
this unit agency, which generally has the nature of the same agency (it is
identical for all the physical bodies) and ∞ in
the relationship [(m/∞)*∞x]*[(s/∞)*∞x]/[(t/∞)*∞x],
where
x is the number of the dimension of the space of movement and it is from the
perspective of Philosophy of Balance of agency also equal to ∞. However
at the same time there is limitation for [(s/∞)/(t/∞)]*∞2/∞2≤c,
which is the speed of light.
From the law of the conservation of movement,
virtually momentum and energy it flows that the overall movement is fixed and it
is the sum of the unit agencies of movement as defined above. Unit agency
movement represents one point in the space-time continuum, i.e. the sum of the
movements in the infinite sum of the points, i.e. the sum of the movements in
the infinite points in the second dimension of space-time, consisting of
infinite points in the first dimension of the space-time, etc. It is about an
infinite sum of unit agencies.
In the field of physics of macroworld, which
represents the mechanics, we see a so-called mechanical energy, which is represented by the kinetic energy and
potential kinetic gravitational energy. If ignoring the kinetic energy of
the field of particles physics and other potential energy than gravitational, the
law of conservation of energy applies.
Energy is defined as the basic relation W=F*s, it is equal to the work as the result of
a mathematical coagency of the trajectory s and the force F. From the
definition of motion as p=m*v=F*t, where t is the time, it suggests, that
derived relation for the movement is W=F*s=p*v, where p is the momentum and v
is the speed. Law of conservation of mechanical energy flows then from the
above relationship for relativistic momentum and energy.
Here it should be noted, that the equation for kinetic energy E=(1/2)mv2= (1/2)ma*at2=
F *s, where a is the acceleration of the unit meter divided by the second to
the second exponent, and s is the trajectory of the unit meter, unit of force
F=ma is the Newton of the unit kg *m*s-2,
it
is also valid for potential (gravitational
kinetic) energy E=mgh=mg*(1/2)gt2=(1/2)mvd2,
where vd is the speed of the body at an impact in the
free fall on the surface of the Earth, and g the acceleration of the Earth.
Quantities of power Pp=W/t, where W is
work and t the time, and of efficiency ή=P/P0 , where P is
power, then, represent partial motions of the total movement or mathematical
contracoagency of the above unit agency of the physical motion.
If we take the Universe as a whole, then according
to the knowledge of physics it can be considered in the whole as a homogeneous
and isotropic, i.e. we can contemplate its uninterrupted and continuous nature,
as it postulates the Philosophy of Balance of all agency. Therefore we can
think about the average value of the
momentum and energy per unit of space or volume, which promotes in all physical movement gradually thanks to
the continuous nature of the physical movement of particles and bodies of the
world in the ultimate consequence of above defined unit agencies of this
movement. To the connection of the momentum and the energy I wrote above.
Mathematically can be this phenomenon expressed by
relation for the balance force F1=∆E/s=[(E1-E2)V1/(V1+V2)]/s
for two adjacent momentum fields, virtually tangible (material) bodies, or
particles (hereinafter referred to also as momentum fields) of macroworld,
where F1 is repulsive force of the first momentum field in the case
of positive value and the attractive force of the momentum field in the case of
negative value, ∆E the change of the total relativistic energy of the
momentum of the observed field, E1, 2 is the total
relativistic energy of the elected momentum fields, V1, 2
is the volume of the momentum fields, s the distance between the centers of
adjacent particles, or material bodies, or the neighbouring momentum fields,
∆t time of interaction of momentumch fields and t total time of
straightening the momentum of particles
as a result of acollisions. I proceed from the fact, that
∆E=∆W=F*s, where ∆W is work, or energy, that needs to be done
to restore the balance, and that is by a force F (hereinafter referred to only as
balance force) acting on the trajectory s required for restoration of the
balance through colliding particles after time t. I suppose, that an
equalization of E1 and E2 will occur in time t, otherwise the
second part of the above formula for the balance force is not valid and only
the first part of this formula will apply, which is given by the overpressure,
virtually underpressure due to the nearby momentum field. The forces caused by overpressure or underpressure (vacuum) of the neighboring
momentum fields are according to the Philosophy of Balance of physics the reason
of all the motion in the Universe.
The average momentum, or energy per unit of volume
is due to the collision of particles,
excluding perfectly zero-mass particles, i.e. photons not at the speed of light,
but in the endless number. The momentum fields arise, where the average density of the local mobility
pushes through, which affect again each other by collisions of particles.
The result of these collisions of particles is, that the momentum field and
particles with supra-average momentum reduce its momentum density and particles
and momentum field with sub-average local mobility increase the density over the
time. In other words collisions of particles cause this repulsive forces
between momentum fields, virtually particles with a sub-average local mobility
density or between two momentum fields, virtually particles with a
supra-average local mobility density and attractive
forces between the momentum fields, virtually particles with sub-average
and supra-average mobility density.
The action of such local balance forces is limited
by the period before balancing of energic, or momentum densities in the superior
systems, or the Universe in infinite time. Universe
balance force acts between motion systems with great momentum given by the
total weight and speed with values approaching ∞, local balance force
between systems with low mobility. Universe balance force represents the sum
(coagency) of local balance forces. The effect of these balance forces is due
to the collision of particles and bodies according to the law of conservation of
momentum m1v1+m2v2=m3v3+m4v4,
where mxvx are the variables weight and speed, even in a
vacuum as I mention below.
Gravitational
field represents the sum of the movement
unit agencies in the form of the action field of these forces, this partial
movement, as I stated above, represents a portion of the total movement of unit
agencies meaning the change of the speed of movement of particles at zero
weight at zero time multiplied by the number of unit agencies in the given mass.
In my opinion gravitational field represents the momentum field and this is consistent
with the action of the balance force between the two momentum fields due to
the attractive, in particular gravitational force caused by underpressure seemingly
a more perfect vacuum forming interspaces of more massive bodies due to its
very low absolute momentum.
If we consider above mentioned link between energy and momentum of a body,
then we can say that the gravitational field is acting on a particle with
non-zero total energy or with zero energy (i.e. the absolute vacuum) in zero
distance, which stems from the relationship Fg=χm1m2/r2
for m1= 0, where χ is a gravitational constant with a value of
approximately 6.67*10-11 N*m2kg-2, m1,
m2 are weights of both bodies and r the radius of the distance of
the two bodies.
To calculate the
attractive gravitational force we
can use the relationship for potential gravitational energy E=mgh, where h is
the height of the level, in relation to which we determine the potential (kinetic)
energy, the relationship for the gravitational force Fg=mg and the
relationship for the total relativistic energy E=mc2. If we consider
a photon at a distance r from the center of the gravitational field, that grants
potentially it the speed of light, when
it impacts in the center of gravity, then its potential kinetic energy is equal
to the difference of the total immediate energy before impact, which is equal
to 0, and a non-zero total energy, when it impacts at the speed of light in a
zero-height, which is equal to the kinetic energy of the particle upon impact,
or Ep= mdc2-m(=0)c2=∆mc2=mdc2,
where md is the relativistic mass at impact. For potential kinetic
energy of this particle then also the
relationship Ep=mgh, h=r applies. Relationship ∆mc2/h=Fg
is then equal to the force, by which is particle of zero-mass and energy, virtually
relativistic momentum, if it does not move at the speed of light c, attracted
to the center of gravity. If we divide so obtained gravitational force by the
weight of a body in a gravitational field, so we get the gravity acceleration of
this gravitational field.
The above mathematical definition of the gravitational forces implies, that it
is also the specific case of local balance
force, when there is however no spreading of the movement, but its slowing down. In other words the body
with the force of gravity is an area with a lower density of the particle
mobility than mobilitydensity of this
particle outside the momentum field, that reduces by balancing momentum by collisions of particles also the momentum of these
particles with much greater momentum in its surroundings, including the vacuum.
Before the reduction of momentum its increase can often occur, when the body
with lower mobility density attracts by above mentioned balance force the area
with the aforementioned excess of mobility density. After the collision of
these two bodies not visible increase of the momentum of the heavier less mobility body and a noticeable reduction in the momentum of less
massive body happen. The total momentum is maintained.
A circular, elliptical or parabolic movement around
the gravitational field in the case of tangible (material) objects is the
result of composing forces, gravitational force Fg and the
centrifugal force Fo, which means the movement or relativistic
momentum, virtually their folder perpendicular to the direction of centripetal
force. In my opinion in the case of the rotation of the space bodies this is a
remnant of the motion of particles and effect of stellar dust before the
formation of larger bodies and thus the formation of larger gravitational
forces, or momentum fields. It may be also the result or the proof of the
existence of momentum fields, where the substance of a larger density
concentrates in the center of the rotating momentum field with a lower speed
and substance of low density on the border of this momentum field. -
In the case of cosmos speeds necessary for
separation from the gravitational field there must be greater force acting on
particles than the force of gravity, or its kinetic energy must be greater than
its potential kinetic energy due to gravity, represented by the product of the
gravitational force and the distanece from the center of gravity according to
the relation W=F*s and Fg=mg. Such value of kinetic energy we reach
with the particles of microworld by the release from supra-average energetical,
virtually relatively momentum dense body due to the natural balance forces or
artificially granted speed as the work of man.
If we consider the
body as a material point or the movement p=m*v, then the overall movement
we approach by the relationship p=m*v*∞3, whereas a
three-dimensional body is composed of infinitely many points in three
dimensions. The relationship of p*v then represents the average momentum of one
point of four-dimensional body. Thus again spatial unit agency of movement
system forming the body. From the kinetic unit agency of this point
(m/∞)(s/∞)/(t/∞) then is composed each relationship
expressing a partial mechanical movement but also the total physical movement,
such as in mechanics the moment of force M=Fd, where d is called the arm of force,
shear force of shear friction Ft= fFN, where FN
is a compressive force and f is shear friction factor, that is different for different qualities of connected
surfaces and different materials of bodies, the resistive force Fv=ξ*FN/R,
where ξ is the arm of rolling resistance (its unit is the metre), R is the
radius of the body, the pressure in the liquid and gases p=F/S, where F is the
compressive force, which acts perpendicular to the surface of the liquid of content
S, a unit of pressure is the pascal (Pa), volumetric flow rate Qv=S*v,
when the fluid with speed v is flowing through the cross-section of the content
S, the law of conservation of mechanical energy in liquids and gases (1/2)ςVv2+pV=constant,
where the first member represents the kinetic energy of the liquid on the unit of
volume and the second member represents the pressure potential energy at unit
volume, which at the same time is equal
to the pressure of the flowing fluid, the density of a liquid is ς, V is
the volume of the liquid, or the relationship of the aerodynamic resistance
force F=(1/2)CςSv2, where C is the coefficient of resistance,
ς air density, S is the contents of the cross-section of the body
perpendicular to the direction of movement and v the size of the relative
speed. They are mathematical contracosubagencies of the total movement
expressed by the general relationship m*v.
Similarly one can imagine the whole Universe, virtually Being as physical
movement centered in a single point in space, then the speed of movement of
this body was equal to 0. The kinetic energy would also be equal to 0, and from
the law of the conservation of momentum would pass, that m=∞, due to anticipated expansion of the
Universe and the consequent non-zero vector of the overall speed of the movement of the
Universe. In any case then there would be a quantity of an average energy for
the unit of space of four-dimensional space as the proportion E/V, virtually
average relativistic momentum p/V, where E, p and V apply to the Universe as a
whole, V is the volume of the Universe.
Dynamic picture of the world
(termination)
Number of unit
agencies of the total energy, i.e. p=m*v in relation to the E=mc2
of Universe is according to the law of conservation of energy or momentum
fixed, but due to value of quantity E of the system of the Being the number of
such unit agencies is equal to ∞. This corresponds to the assumptions of
eternity and infinity of God as all Being from the perspective of pantheism of Philosophy
of Balance of agency.
If the movement represents the physical
relationship m*v, then because of continuity and connection of all agency from
the perspective of Philosophy of Balance, the overall agency is equal to
∞m*∞s/∞t, where the proportion of ∞s/∞t is equal
to the maximum of c, thus the speed of light. It is the total physical movement
in four dimensions.
3.3 THERMAL AND MOLECULAR PHYSICS
Introduction
(formation)
From the mechanical motion of material objects in
the macroworld we go to the reality of physical movement of the much smaller particles in our microcosm. This
movement is agency in terms of the description of the mechanical movement of
the relation p= m*v both in space and time and it includes also continuous and
uninterrupted permanent positions of the particles in zero time interval with
zero weight in an infinite number. This fact of unit agencies we are approaching
with shrinking mass and the dimensions of the particles, i.e. in physics of
microworld.
The physics of microworld explores so the physical
movement in the above sense again, but in the microworld. A knowledge of continuity
and connection of all agency established within the Philosophy of Balance suggests,
that the laws of physical movement in
the area of macroworld are applied also in partial form in the physical
movement within the microworld, physical movement in the area of macroworld
is the sum of the physical movement of the particles within the reference
system. For the relationship of physics of the macroworld and the microworld the
relationship of general and special applies, as I indicated it in the
introduction to the Philosophy of Balance of physics.
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
The molecule as a particle has a very low weight
approaching 0from the viewpoint of macroworld of physics. Here we can apply the
model of the physical movement of unit
agency described by a relationship in the field of physics of macroworld in
the form p=(m/∞)*v.
Brown's continuous and chaotic movement of molecules is in my opinion the result of the interplay
between the attractive and the repulsive
balance forces. A small distance at the action of these forces can be
explained by the low absolute momentum of particles, in the larger absolute
momentums either the bodies of greater weight acts, which are close to the
average momentum and the repulsive
balance forces can be neglected, or at larger number and at acting of
microparticles the average momentum of system comes close to the average local
momentum density and imbalance arises only in a small area. By a small distance
and highly supra-average mobility density the
large size of attractive forces of the particles of an atom can be
explained, and thus a large potential kinetic energy of these systems.
To describe the physical motion of the particles in
our microcosm in addition to weight and speed another basic sensory quantity accesses and that
is the thermodynamic, virtually Celsius
temperature. From the postulate of connection and the continuity of
everything agency, hence the physical movement of macro- and micro- world, formulated
in the Philosophy of Balance, it follows, that in the case of temperature this
is the character of the movement, which the human senses perceive. Physical
movement is in fact indivisible whole, from the perspective of Philosophy of
Balance the agency characterized in the macroworld by the relationship p=m*v or
by the relationship E=mc2=Ek+Ep=W=F*s=(1/2)*mv2+mgh,
where Ek is kinetic and Ep potential (kinetic) energy,
these relations shall also apply for the temperature. The temperature
represents thus the character of the movement.
The above can be documented in the case of an ideal
gas, when the temperature difference of bodies is to be understood as a
function of the difference of their kinetic energy per unit of volume. Due to
the fact that all the energy of an ideal gas is kinetic energy, it is true,
that the temperature difference of bodies is caused and the function of difference
of their total energy per unit of volume. In other words the basic unit of
temperature is the derived unit of weight, speed and time.
The above statement follows from the relation for
the heat, which receives (releases) the body of given substance, if it has mass
m and its temperature changes by ∆T, Q=m∆Tc=(1/2)mv2, c
is the specific heat capacity of the unit kJ(kilo Joule, i.e. a unit of
energy)*K-1 (Kelvin, unit of temperature T, in addition to the
convertible Celsius temperature °C, known also with the letter t), implying
∆T= v2/(2c) in the case
of heat received by an ideal gas turned into the energy of this ideal gas. In
the case of a zero-energy of ideal gas before the thermal exchange the Q is
equal to the total energy of ideal gas. From the relationship of central
quadratic speed of gas molecules, which took all the energy in the thermal exchange
vk=(3kT/m0)1/2, it flows after putting in,
that vk=vk [3kN/(2cm0)]1/2
, where k is the Boltzmann constant k = 1.38 1023JK-1,
rn0 is weight of molecules and N number of molecules of the
substance, and it follows, that m0=3k/(2c). From the relationship
for energy received by this ideal gas Q=(1/2)Nm0vk2=
(1/2)*[3kN/(2c)]*T*2c=T(3/2)kN it flows, that the temperature is a function of
the energy of ideal gas divided by the number of molecules, that have the same
volume, and therefore the function of the energy per unit of volume.
Generally it applies from the first law of
thermodynamics, that Q =∆U+W or the heat supplied to the system Q is
equal to the sum of the changes in the internal energy of the system ∆U
and work W carried out by the system. If the system does not perform any work,
then the heat supplied to the system is equal to the increment of internal
energy or growth of potential and kinetic energy of the particles. If there is no mechanics energy during these
planned processes, this increase of potential and kinetic energy is equal to
the increase of total energy. Due to the nature of the heat increment equal in
the above cases to the increase in the total movement expressed as increment of
the total energy E=∆mc2 where ∆m is relativistic mass
change, and given to the relation Q=cm∆T, where c is the specific heat
capacity, it can be concluded, that in general a thermodynamic temperature is a
part of the movement and function of the total energy of the body. Variables of
speed and weight in terms of momentum relation as the general equation of the
physical movement p=mv as a general supraagency already include then quantity
of thermodynamic temperature. The total energy is then made up of potential
kinetic and kinetic mechanical energy of the body and the particles.
For solids
unlike gases attractive forces are dominat, apparently due to the large
relative weight (in relation to the volume), or mobility density of molecules
and the small distance between them. On the contrary for gases there are
repulsive balance forces due to the relative small weight, or the mobility
density of the molecules and the great distance between them. For liquids, these forces are approximately
of the same size. In the case of polycrystals
and single crystals local or universal (all) balance forces will apply to a
greater extent during their creation. In the case of amorphous (i.e. shapeless)
solids were applied rather attractive forces. When changing the state from
solid to liquid and gaseous, the potential kinetic energy of particles represented mostly by attractive
forces is converted to kinetic energy and the repulsive balance forces and vice
versa while reversing change of state.
At the surface
tension of the liquid attractive forces of liquid are applied in the case
of prevailing attractive force in molecules on the surface of the liquid inside
of the liquid. These surface molecules have
the potential kinetic energy. Due to the attractive surface forces the minimum
surface of the fluid in its steady state is, since the molecules on the surface
of the liquid tend to move inside and surface shrinks. However this applies
only in the case of less attractive forces above the surface of the liquid than
in the liquid for the environment as the interface of gas and liquids.
Attractive forces within the liquid cancel each other. Thermal volume expansion
both of liquids and gases is caused by the growth of the kinetic energy of the
particles, and therefore the repulsive balance forces. In the case of saturated steam, i.e. of the same
number of molecules, which are leaving the surface of the liquid and which are
from steam returning to the liquid, attractive and repulsive balance forces of
gas and liquid are in balance.
In practice the conversion of attractive in a
repulsive balance force or potential kinetic in kinetic energy applies in the
case of breaking up the structure of the substance, and changing of the
attractive force of relatively heavy particles (due to their distance) on the
repulsive balance forces of relatively light particles (due to their distance),
which offset the momentum with the surroundings of a smaller momentum. These
cases occur in particular in the burning
of working substance in the combustion heat engines and cooling machines.
Here kinetic energy represented by the thermal motion changes in mechanical
kinetic energy of heat engine.
Respectively in the case of cooling machines the kinetic energy of the particles increases,
and the repulsive balance forces and substance are performing the work and
consuming energy, which it receives in the thermal exchange, by which it cools
the environment, where the energy density or temperature is dropping, and the
kinetic energy of the particles is decreasing and the repulsive balance forces are
reduced and the substance emits energy, thereby warming the other environment.
3.4 MECHANICAL VIBRATIONS AND WAVES
Introduction
(formation)
Mechanical vibrations and waves are a physical
discipline, that is a special case (subagency) of the general discipline of
mechanics (supraagency), of its
kinematics so of its dynamics. Physical movement described in the mechanics and
its laws are so valid in the partial form also in the mechanics of vibrations
and waves. Mathematical expression of this special physical movement is more
complex and it deals with less general, more numerous and simpler agencies than
the mechanics. The dependence and continuity of everything agency postulated in
Philosophy of Balance imply applicability of above mechanical mathematical
relations also in this field of physics.
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
Oscillating
movement can be understood as subagency-partial
movement of the circle motion, such as its projection to the y axis. The harmonious oscillating movement is
partial physical movement of uniform movement on the circle, therefore its
projection to the y axis.
From the viewpoint of kinematics the unit
agency of the oscillating movement is the
movement, of which speed is equal to 0, while variable ω, which has at the
uniform circular motion the importance of angular speed, and which we call for
oscillating processes an angular frequency, it is equal to 0, and the amplitude
of ym=r=0, which corresponds to the relationship v0=rω,
where v0 is the speed of the movement on the circle, and r the
radius of the circle and to the relationship v= v0 cosωt, where
v is the speed of the oscillating motion. From this relationship, where 0=(1/∞j)*x,
where x≠∞ and ∞j represents unit agency, is then composed each
harmonic oscillating movement described by the variable v, which includes ∞ of the above unit
agencies of oscillating movement.
Coagency of above unit agencies of the oscillating
movement is the compound vibration consisting of an infinite number of unit
agencies components, that have the same frequency. The period of oscillation
T=∞, the frequency of oscillation is f=1/T=1/∞=0, which stems from
the relation for angular speed of unit agency ω=2π/T=2πf=0 as
above mentioned for the unit agency of
the harmonic oscillating motion. For the resulting vibration of these two unit
agencies are valid intial coordinates x,
y of the position vector r,
x=2*0*cos0=2ymcosφ= ymcosφ+ ymcosφ,
y=2ymsinφ=2*0*sin0, where ym are identical amplitudes
and φ the initial phase of both unit agencies and the initial stages of
both unit agencies of the harmonious oscillating movement.
At a dynamic
description of the harmonic oscillating motion there are several kinds of
balance forces. A necessary condition is also a displacement from balance by
some third force. This third force delivers energy to a balanced system of the pendulum, or momentum necessary to
overcome gravitational forces, or momentum field of the Earth, and this energy
is initially of the kinetic nature, under which influence the pendulum deflects
as a result of local balance force, or momentum field of pendulum leaves the Earth
momentum field, the momentum of pendulum is dissipating however by the increase of the local momentum of the Earth
and kinetic energy is converted to potential kinetic energy of the Earth, and
the pendulum deflects once again by the action of gravitational forces or by raising
of the local momentum of Earth in the opposite direction and the momentum of
the Earth reduces up to the point, when it comes to the maximum dissipation of
momentum and gravity force prevails again. In fact however the momentum of pendulum
does not dissipate only by increasing of the momentum of the Earth, but also by
friction.
At the initial developed force and kinetic energy,
when the frequency of the oscillation is greater than the frequency of the customs oscillation or momentum of oscillator,
the attractive force of the oscillator (damping) increases, this force reduces
the effect of the initial kinetic energy and the amplitude of the displacement reduces
too. Customs frequency of oscillator performs a customs value of the energy or
mobility density, at which the gravitational forces act at minimum, at the larger displacement of mobilitydensity
the attractive slowing balance forces of oscillator are acting increasingly.
By mechanical
waves is spreading the
physical movement. Whereas in the view of the Philosophy of Balance also a
matter represents the physical movement of particles of zero weight in the
infinite sum of these movements, possibly in the final number, if these
particles move at the speed of light,
from this perspective also the matter can be transferred by waving.
Unit agency of
mechanical waves is the wave of
the v=0, T=∞, x=vτ, where τ is the time by which the vibration
is delayed compared to the beginning, y=ymsin2π(t/T-x/λ),
where λ is the wave length, and T the period of oscillation and where ym=0
and y=0. From this unit agency all the oscillating movement is created by their
interference, where the number of interfering unit agencies is equal to
∞. The equation of this interferential waving for two unit agencies is y=(2ymcosπd/λ)*sin2π[(t/T)-(1/2)(x1+x2)/λ],
where d is the distance from sources of waves, λ is the same wave length
of both unit agencies and ym the same amplitude of both unit
agencies. Given the value of ym=0, and also y=0.
In terms of the dynamics of mechanical vibrations its
cause is an attractive and repulsive
local balance force of particles
as defined in the previous chapters, the attractive balance force works between
particles attractively, repulsive balance force works repulsively at dissipation
of energy or mobility density.
Radiation of vibrations is caused by kinetic
deflection of the of particles from the balance position and by the action of
attractive and repulsive balance forces between the particles, which renew the
balance status of these forces. Impacts of adjacent particles cause spread of
the movement induced by the above mentioned forces in all directions, where
there are particles. As a result of the dissipation of movement, virtually
energy due to the influence of local balance forces in relation to the surroundings
so there is a gradual decline in vibrations. As a result of the large
difference between the momentum and energy of neighboring particles the reflection of waves occurs , and as a
result of its spread in all directions and interference its bend. At the standing vibration the energy, or its momentum transmits on a
limited section in both directions back and forth, the total energy of the
system is not changing, only the kinetic energy, which triggered the waves,
changes to a potential kinetic energy.
At the movement
of the source of the waves against an observer or conversely their relative
speed is changing and so either by the sum or by the difference of their speed,
thereby also subcoagencies are changing or derived quantities such as wave length
and frequency, which means less, virtually larger number of unit agencies in
the description of mechanical waves, so as I defined above. It is so called Doppler effect.
3.5.1. INTRODUCTION
(formation)
From the perspective of Philosophy of Balance all
the agencies in physics can be marked as physical movement, for which due to
the connection and the continuity of all agency, as it follows from the nature
of the agency as a continuum, justified in the context of Philosophy of
Balance, the relationship of the physical mechanics of p=m*v applies, where p
is the momentum, expressed as the product of mass and velocity. From this
perspective, both the electric and the
magnetic agencies are two different physical movements, for which p1=
m1v1, p2=m2v2 is differing
only in the weight of the smallest particles, which are the carriers of
electric charge, or carriers of the magnetic field, and of their speed. Between
these particles are then again attractive and repulsive forces in accordance
with the physical mechanics and they have mechanical potential kinetic and
kinetic energy.
Subagencies
(performance)
3.5.2 ELECTRICAL FIELD
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
Electric charge as the basic unit is the kind of physical movement as a whole expressed by the general
relationship p=m*v, unit coulomb (C),
in
the case of zero charge it is the
local balance momentum between the electron and the proton, in the case of the unit negative charge it is the
momentum of one electron, in the case of
the unit positive charge it is the momentum of one proton. It suggests also
a different weight of the carriers of this charge of electrons and protons, where
me (the mass of the electron)<mp (the mass of the proton).
The result of this divergence of momentum against the local average mobility,
virtually energy density, which is a neutral charge, is the effect of local balance forces, where
consistently charged particles are repelled due to repulsive balance forces and
disapprovingly charged particles are attracted due to attractive balance
forces, while renewing the local average momentum.
From the definition of the charge as a physical
movement defined by Q=p=m*v, where m and v move within a certain interval and smallest
limit values of m*v represent further in the context of electric motion the indivisible electric charge e. When
exceeding the limit values of electrical charge as the physical movement we get
to the physical movement of a different kind, such as magnetic field or thermal
movement. The intervals of the other kinds of physical movement overlap however,
i.e. at the common values of m*v the heat movement and magnetic field may indicate electric charge.
Electric charge as a kind of physical movement is portable in the interval of values of m*v
for this particle and by it represented physical movement.
Mediation of the electrical current by only so called free electrons farthest from the nucleus
of an atom is due to the relatively small distance, which reduces the effect of
local balance (attractive and accelerating) forces, which tie the electrons to
the nucleus. The local balance forces as a result of the positive charge as
source of electric current so they are able to overcome these weak attractive
forces of electrons to the nucleus of an atom.
The characteristics of a particle with an electric
charge as a kind of physical movement represented by the formula p=m*v implies the law of conservation of
charge, as well as a partial law of conservation of momentum, virtually
total energy for particles with a certain value of m and v.
The equation for the electric force Fe=k*|Q1*Q2|/r2
, where k is a proportionality constant depending on the characteristics of the
environment, in which the charge Q1, Q2 distant r metres
act at each other by its mutual forces Fe and -Fe, is
similar to the relation for the gravitational force due to its derivation and
relation with the relationship for the total energy of the system of two
bodies. The equation for the electric field intensity E= Fe/Q, the
unit is so (kg*m/s2)/(kg*m/s) =1/s, and it shows the ratio of
momentums per second. The equation for the electric potential at a point A of electric
field in the vicinity of charge Q is φA=W/Q0, where
W is the work performed by forces of the electric field when moving a positive
point charge Q0 from point A to the point of zero intensity, its
unit is volte (V), i.e. (kgm2/s2)/(kgm/s)=m/s
the same as the equation for the speed. The same unit has voltage U=φ1-φ2. The equation for
the capacity C=Q/φ, the unit is
(kgm/s)/(m/s)=kg and it represents so the weight of the particles, which the
wire carries.
Distribution of
electric charge only on the surface arises from the
interaction of balance forces, when those forces are trying to restore the
balance state of the momentum or energy by emitting of these particles outside of these electrically
charged wire.
3.5.3 ELECTRIC CURRENT IN METALS
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
The equation for the current I=∆Q/∆t, where ∆Q is the total charge of
particles, that pass through the chosen transversal cut of wires for time
∆t, current has unit ampere (A),
i.e. kgm/s2 and it represents the amount of physical movement per
unit of time, and at the same time the result of repulsive and attractive balance
forces I=(Fgt1+Fot2)/t.
Connection of electric energy as mechanical motion
of particles is arising from the conversion of this energy in the appliances to
light, heat or mechanical energy, when by composing or by decomposing the movement
of electrons me*ve
is created the movement of a different kind m*v, e.g. thermal, luminous
or mechanical in intervals of values m and v own to this kind of movement. This
change stems from the transmission of energy particles of different m and v in
the interval of their common values. In contrast a different kind of motion is
converted to an electrical charge at work of so called enprinted forces of the voltage source, which transmit the charged
particles from the places with lower potencional to a location with a higher
potencional and they ensure so the terminal voltage of the electrical circuit.
The equation for the electric resistance is R=U/I, resistance has unit ohm (Ω), i.e. (m/s)/(kgm/s)=s/kg and it represents the time, in
which the particles at unit weight pass through a conductor. In contrast the conductivity (conductance)
represents the weight of particles, which pass through a conductor per unit of
time, the relationship is C=I/R and the unit is farad (F), i.e. kg/s.
The origin of the resistance according to the theory
of electron conductivity are the collisions of conductivity electrons with ions
of the grid, that are acting by their attractive forces against the movement of
the electrons in the direction of positive electric charge. With increasing temperature
the kinetic energy and momentum of ions increase also and collisions are more
frequent. A special phenomenon is superconductivity
consisting in a sudden decrease in resistance of materials to virtually zero at
a certain temperature.
Kirhof laws for
the current in node, ∑k=1hIk=0 mean,
that the quantity of incoming motion, virtually momentum and outgoing motion
from a node is the same and for voltage on the resistors and electromotive voltage
of resources in the loop ∑k=1nRkIk=∑j=1mUej,
it means that the sum of the differences in the speed of particles before and
after resistor is equal to the speed of the particles in the source voltage.
For the serial connection the sum of the differences
in the speed of particles at each of the resistors is equal to the difference
of speed of particles on all resistors, thus R=∑k=1nRk
from relation IR=∑k=1nRkIk
=U=∑k=1nUk. Furthermore in the case of
series connection from equality of amount of movement in time through the whole
circuit: U:U1. .... Un =R:R1: .... Rn,
which stems from the relation U/R=U1/R1= .... =Un/Rn
(":" and "/" is divided or by other words over) or I=I1=
... =In ("=", is equal to). In parallel connection the same
speed of the particles is involved in all branches of the U, and the sum of the
amount of movement (momentum) of particles in the time of individual branches I1+I2+
.... +In=I, where I is the amount of movement of particles in time entering,
virtually leaving a common node. Consequently I=∑k=1nUkRk,
and also U=U1= ....... =Un, and thus Rl=R1I1=
...... = Rn1n, thus I:I1 ..........In=1/R:1/R1.......l/Rn.
Performance of
electric current represents the
movement, virtually energy performed by particles with an electric charge, this
movement is transformed by gradation and degradation into a different kind of
movement, a different interval of values of m and v in the relationship of the
physical movement of p=m*v. On principle when this conversion of the motion
there is the loss, for example release of thermal energy in the conversion to
mechanical movement, this means, that pe=me*ve
motion of the electrons is equal to p=pt(=mtvt)+pm(=mmvm),
where pt is the thermal movement of particles in the interval mtvt
of heat movement and pm mechanical movement of the particles in the
interval mmvm of mechanical movement. The proportion of pe/pm
is then the efficiency of the appliance providing mechanical work.
Another example of gradation and degradation of the
heat motion is thermoelectric effect,
when thermal motion, virtually radiation in the limits of the common values m
and v induces the electric movement.
3.5.4 ELECTRICAL CURRENT IN LIQUIDS
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
Carriers of electrical
current in the electrolytes are positive and negative ions with higher than
average local mobility density in the case of positive ions and with a lower
than average local mobility density in the case of negative ions. As a result
of local balance forces are positive ions attracted to the negative electrode,
and vice versa, and by taking over, or by giving out electrons, virtually positive
and negative ions the neutral atoms of the average local momentum and energy
are formed.
The total weight
of excluded substance of neutral atoms in
the case of taking of positive ions by negative ions of the electrolyte can be
expressed by relation m=m0Q/(ez)=m0Vvmv/(mevez),
where m0 is the mass of the molecule, e the elementary charge, z is the
number of elementary charges needed for exclusion of the one molecule, mvVv
overall charge penetrating through the electrode surface, meve the
elementary charge, and that in both cases expressed by the quantities for the
weight and speed as physical movement.
Breakdown
voltage Ur represents the
minimum voltage, which is needed to accelerate, virtually slowing down the
particles in electric duple layer with
the average momentum and speed of particles, i.e. the voltage that is created
on the interface of metal and electrolyte by neutralization of ions. After,
that the acceleration by the speed of the particles of external voltage source happens
in the case of the anode or slowing down in the case of cathode of particles of
neutral double layer, the electric current is steadily going through the
circuit from the source.
Chemical voltage sources in the case of galvanic cells are resulting in the
reaction of the neutral metal of a positive electrode with negative ions while
creating neutral atoms, free electrons are drawn off to the negative electrode,
where positive ions react with the negative electrode, from which they take electrons,
which are replenished by electrons coming from the outer circuit from the
negative electrode. The cause of this phenomenon is the effect of balance forces,
which must be greater than the attractive forces within neutral substances of both
electrodes and of the electrolyte, which react mutually.
3.5.5 ELECTRIC CURRENT IN GASES
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
Carriers of electric
charge in the gases are positive and negative ions and electrons. To
overcome the attractive forces own to neutral atoms of gas is used ionization, it is the energy or
momentum supplied to the electrons in the atoms necessary for their release.
Due to the charakteristics of electrical charge as a physical motion p*v it is a different kind of movement, for
example of the heat, of ultraviolet radioactive or x-ray radiation, which
deflects an electron from its orbit and the electron is moving outside the
field of attractive forces of the nucleus of the atom (similarly to cosmic
speeds and gravitational field of the Earth). As a result of the balance forces
of the outer source of charge, virtually of the electric field so the gas
becomes a conductor of electric current. Due to the attractive forces of the
gas atom it leads to recombination of
the ions, when the opposite charged particles join in a neutral molecules.
Generally Ohm's
law applies, that at increasing the difference of the speed of the
particles, thus the voltage between the poles of an electric field, the current
or physical momentum (motion) is also increasing at a time. At a certain limit
of the difference of the speed of the particles, the voltage U, as a result of
increasing attractive local balance forces the motion, virtually momentum in
time is not increasing, thus electric
current I, because all of the accelerated particles by ionizing, i.e. the
unbalanced physical movement was slowed by recombination. If we proceed with
increasing the voltage, then the ionization by radiation is connected to the
ionization by the physical movement of ions and thus the next attractive
balance forces are overcome, that access to the attractive forces of the atoms.
The movement of ions, virtually of electrons of gas
in the electric field at high voltage will probably turn into other kinds of
physical movement of the particles, whether it is the thermal movement or the
movement of the x-ray or the light radiation described again by relation p=m*v
with a different interval of values of the mass m and speed v.
3.5.6 MAGNETIC FIELD
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
The magnetic
field as well as the electric field is
in terms of the Philosophy of Balance complex unit agency, which is the
physical movement as described by relation p=m*v. Both physical movements are
partially independent and partly common, or the values of m,v belongs to the
two intervals, of which intersection is non-empty set, or a magnetic field induces an electric field and vice versa. The independence
of these fields means in turn the law of conservation of charge, i.e. a kind of
physical movement derived from the law of conservation of momentum and energy.
The same is true about the law of conservation of mechanical energy in the case
of mechanical movement, but if we do not
include its induction of different kind of movement, e.g. the heat. So it is the law of conservation of energy as the
total movement of total p=m*v and the law of conservation of charge p=m1v1 .
In relation to the unit agency as moving particle of zero
weight then the space represents the sum of such movements and electric or magnetic
field the organized movement generated by repulsive and attractive balance forces,
as I defined them in mechanics. I'm going back to the ancient concept of ether, that explains upon the
principles of mechanics the physical field. These zero-mass particles I
described also in the section of mechanics.
Unlike the electric field and charge induced by differences
in energy and momentum density and by forces balancing these differences and
renewing the average local energy per unit of space volume a magnetic field is probably differences in
momentum, not quantitative as for electric charges but qualitative, in the direction of the vector v in relation of the momentum as the
description of magnetic movement in the form p=m*v. It suggests the same mass and the opposite direction of the
carriers of magnetic field in atoms, thus the electrons.
From the direction of the magnetic induction lines
changing according to the direction of the current one can conclude, that the
movement of electrons in a conductor is not straightforward, but it has also the
shape of a spiral, so it is circular in the planes perpendicular to the wire. This
spiral movement of the electrons in the wire induces then by collisions with
zero-mass particles their circular motion and circular magnetic lines around
the wire.
Balance forces balancing the direction of movement
or speed v in the movement of the
magnetic field mv to the average local
balance momentum mean then, that the opposite magnetic poles of a magnet and of
the conductors with the same direction of current, which attract by the magnetic force, cause the magnetic field with the
opposite direction of motion of the particles of zero weight.
Magnetic induction is defined by the relation B=Fm/(Ilsinα)
for direct wire with current I, with the active length of the conductor in a
magnetic field of 1, the angle α, which grips the wire with magnetic
induction lines and force Fm, by which the magnetic field acts on
this wire. The unit of magnetic induction is N/(A*m)= kgm/s2/[(kgm/s2)m]=1/m and it
means the ratio of acceleration of the magnetic movement to the quantity of
electric movement per second to meter of the active conductor.
Magnetic induction flow (scalar
quantity) in a homogenous magnetic field Φ=B*S=m2*
l/m=m, where B is the magnetic induction, S is the content of planar area, e.g.
the surface of plane thread perpendicular to the magnetic induction lines, and it
means the ratio of the acceleration of magnetic movement to the quantity of
electricity per second multiplied by the meter of area.
Magnetic induction of a thin wire with a current
B=μI/(sk), where I is the current, s is a distance different for direct
wire, thread and coil and k is a constant. μ=(sB/I)*k with unit s2/kgm
is a constant called permeability
characterizing magnetic properties of environment of magnetic field and it means
the quantity of electricity of momentum per second in reversed value for a
specific environment.
Magnetic characteristics of the substances are
caused by the reversed direction of motion of electrons with the same energy in
the atom. By attractive forces of magnetic or electric field the elementary
magnetic fields are oriented for ferromagnetic substances with an effect of so
called exchange forces between neighboring atoms in accordance with the ambient
magnetic field and they intensify the
effect of the magnetic field.
The change of the electric movement, thus the movement of electrons in a magnetic field of
wire, translates as well as a change of induced electric current or movement in time
induced by magnetic movement. The equation for the induced electromotive voltage
Ui=-∆Φ/∆t means so a middle value of Ui induced
electromotoric voltage in time ∆t, i.e., the speed of the particles,
which they move along the trajectory ∆s, that the wire moves in a
magnetic field, which stems from a relationship Ui=B∆sl/∆t=(l/m)∆sm/∆t=∆s/∆t,
where 1 is the active length of the wire, ∆s is distance, that wire makes
in time ∆t and ∆sl is a change in the content of area traced by
wire during this time, product B∆sl is a change of magnetic inductive
flow ∆Φ and Ui induced electromotive voltsge. The unit is m/s or speed.
When changing the current in the coil, the induced
magnetic field changes also and thus it induces
the electromotive force in a wire of the coil Ui=-∆Φ/∆t
and Φ=L*I, where the inductance of the coil is L=Φ/I and the unit is
s2/kg, which represents the reversed value of the electric movement
per second per meter of width.
Magnetic field and electric field as a kind of
physical movement of the particles at zero weight have also their energy, which
stems from its mathematical definition of its momentum p=m*v. Energy of magnetic field of coil (i.e.
inductor) is described by the relationship with the unit Em=(1/2)LI2
=(s2/kg)*kg2m2/s4=kgm2/s2=J.
Electromagnetic field stems from the above-described
properties of the transformation of one kind of physical movement in a
different kind of physical movement within the range of the common values of m
and v, where these fields represented by the movement in this interval can move
one in the another.
3.5.7 ALTERNATING CURRENT (AC)
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
The nature of the electric current as a movement
described by the mechanical momentum equation p=m*v stems also from principles of
alternating current, for which the relations derived for the harmonious
vibration mechanical movement are
applied. It follows from the relation for the immediate value of the AC voltage
u=Umsinωt and v=vmsinωt=vmcos(ωt+π/2),
where Um is the amplitude and ω is angular frequency, v is the speed of
the particle and vm, its maximum speed. The equation for the
instantaneous value of the alternating current is i=(Um/R)sirnωt,
where R is the resistance of the resistor, with a unit I=(m/s)*(s/kg)k=mkg/s2,
where k is a constant.
For circuits
with the resistor, the capacitor and the coil are valid the relationships
for the resistance of the resistor
R=Um/lm with the unit s/kg, for inductance XL=Um,/Im,=ωLs,
where L is the inductance of the coil, with the unit (k/s)*(s2/kg)=s/kg,
which is, again Ohm, and for capacitance
Xc=Um/Im=1/(ωC)=1/[(k/s)kg]=s/kg with the
unit, that is the Ohm again. The opposite speed of particles in relation to the
inducted electrical motion for coil causes the displacement of a curve of the current in relation to the voltage curve by
φ=π/2 radians. Further the momentum of the particles per second, or
the current is the highest at the time, when the voltage on the uncharged capacitor
is zero, which causes, that the current goes ahead of the voltage or the speed
of the particles by φ=π/2.
From the nature of the magnetic and the electric field
as physical movement of p=m*v with partly shared and partly different interval
of values m and v follows the possibility of transformation of the electric
field or current in a magnetic field, or the flow and therefore the existence
of electric motors and transformers.
3.5.8 PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF
ELECTRONICS
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
An example of the functioning of the balanced
electrical attractive and repulsive forces are semiconductors, where free
electrons, e.g. the electrons remoted enough from other particles, i.e.. with a
minimum of attractive forces,are moving
from place to place from place with more
to place with less electron density, virtually with a smaller to a larger
density of momentum of the physical movement given averagely by the relation for momentum
p/V=m*v/V, where V is the volume of the system. It follows from this, that in
the same composition of semiconductors at higher temperatures the amount of
physical momentum per unit of volume of collisions of particles increases,
virtually by the transformation of the different species of this movement, i.e.
the recombination of holes and free electrons,
i.e. to restore the local mobility balance. At the semiconductor with the non-same composition, given by other
substances occurs this restoration of balance between the holes and
electrons as the majority carriers of charge of different semiconductors. At
the same time however these attractive forces and the partial restoration of
local mobility of balance causes nonzero, or locally inbalanced charge of additives.
Semiconductors are used to produce two basic kinds
of semiconductor devices, the diode
rectifiers and transistor amplifiers. Rectifier uses the fact, that the
current passes through a variety of semiconductors (see above) in the direction
of restoring of local balance between electrons and holes in semiconductor but
not vice versa except in the case of destruction of diode-rectifier, when
electrons gain such momentum, that outweighs the attractive forces within the
atom. And in the case of transistor amplifier there is used the steady movement
of semiconductor electrons and holes, which intensify together with permanently
charged particles moving in the direction of input voltage the same with balanced
movement of a variety of semiconductors the
input voltage.
3.5.9 ELECTROMAGNETIC VIBRATIONS AND
WAVES
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
Electromagnetic
vibration mediated by the electrons as
carriers of electrical and magnetic field represents a common electromagnetic
physical movement caused by balance forces as a result of the average local
mobility density, in the final result of the average Universe momentum density
as the sum of local densities of all physical motion, mediated by collisions of
particles and bodies. It is so the
transformation of the energy momentum difference in the difference of direction
of speed, i.e. of a pure mobility.
In the oscillating
circuit so the amplitude of the voltage of the electric movement of
electrons induced by a maximum difference of energy of electric poles of condenser
is converted into the amplitude of the magnetic induction of the magnetic
movement of electrons induced by the difference of directions of the speeds of
electrons in the coil winding, which acts on electrons in the opposite
direction as the direction of the electric current by collisions with these
electrons, and it causes the charge of the capacitor (i.e. condenser) again
with opposite polarization.
Electromagnetic waves represents the kind of
physical movement expressed by relation p=m*v, and a composite of the two
movements resulting from the action of two local balance forces balancing the
average energy momentum of electrons moving in the same direction and direction
at the speed of electrons of the same energy. Electromagnetic waves can be propagated through space by collisions with other particles or by
conversion into a different kind of physical movement in the framework of the
common values of the interval with these kinds of physical movement. During
dissemination in space it can be also collisions with particles of zero mass
and speed in a vacuum, from which is composed all the Being, as I have already
stated above.
To the resonance
of the electric oscillating circuit it can be noted, that, if we consider all
Being for the physical movement of the different values of weight and speed in
relation p=m*v, then at a certain electromagnetic movement it is the maximum
local displacements of balance of momentum occurs, for a higher value of
momentum the increasing local balance forces resulting from local balanced
momentum mediated by collisions of particles limit the oscillation, or the
momentum. The maximum displacement of the momentum represents the own vibration
of the electromagnetic oscillator.
3.6
OPTICS
3.6.1 INTRODUCTION
(formation)
Light as a physical fact is once again the kind of physical movement expressed by the
relationship for momentum p=m*v.Like any other movement described by this
relationship of mechanics it is composed of unit agencies of physical movement
as described by 0kg*0 m/0s, which creates in an endless number the light
movement. The arithmetic infinity implies that zero can once again have a
different value depending on, whether a final number is divided by ∞ or
∞x, where x>1. According to the knowledge of theory of
physics the light is the movement of
particles photons of zero rest mass at the speed of light. The speed of
light is then the maximum speed, i.e. speed is equal to the speed
∞m/(x*s), where x<∞ and
composited thus from infinity unit agencies
0kg*∞m/(xs)=ykg*zm/(xs)=∞(0kg*0m/0s), where
0<x,y,z≥∞, where m is the meter, s is the second and kg is kilogram.
When describing the motion of the light I go back to
the ancient concept of the ether. As a vacuum is also composed of unit agencies
of physical movement in m*v=[(x/∞)kg (y/∞)m]/(z/∞)s, so ps=∞*pv,
where ps is the momentum of
light and p v is the momentum of vacuum. By the movement
of light occurs the transmiting of the
kinetic energy of the photon to neighbouring photons, i.e. to particles of
zero mass ps/4=∞pv/4=∞pv, without
changing the momentum of the light and the light is spread in all directions.
In the case of an infinite density of
photons equal to infinite or a nonzero mass of the colliding particles,
then occurs the change of the momentum of a photon of light ps/∞=∞pv/∞=xpv,
where x<∞ and the absorption of light.
Subagencies (performance)
3.6.2 LIGHT AS ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
Light is made up of a stream of photons, which are transverse waves. At the same time the
photon as particle of zero rest mass and zero dimensions is
based on the observation, that the rays, that intersect each other, they do not
affect and they are running through the space independently one
on another. This finding is confirmed by experience in physics called the
principle of independence of light rays operation.. By the grouping of photons and their diffusion the
creation of places with substantially higher mobility, or energy density occurs,
which attract under the influence of an electric field other photons. Electric
field we characterized as an attractive force between grouped particles with higher and lower
momentum (or mobility density), and by acting the local balance forces mediated
by collisions of particles with higher momentum with particles of substantially
lower momentum. After the grouping of photons local balance repulsive forces comes
to work, as higher mobility density at a given point is slowed down by the
surrounding environment of the lower mobility density while reducing attractive
local balance force by releasing the needed quantity of energy to the
surroundings. Repulsive local balance force is mediated by the collisions of
particles of the higher momentum with particles of lower momentum.
As the waves are the transverse waves, magnetic fielde works, mediated by
particles of the same energy but different direction of momentum, and therefore
different momentum, perpendicular to
direction of movement of the light intermediated by electric field, as I
described it above.
Light speed is
the maximum speed, i.e. the maximum deviation of the
average Universe speed allowed by universal (all) balance forces. At the same
time the arithmetic of infinity implies, that even in zero rest mass of photon
the momentum may be different, depending on the value of x in relation x/∞=0,
where x < ∞.
Different weight
in the relativistic relation p=m*c for the momentum of the photon causes
different
frequency and the wavelength in relations for the speed of light
c=λ*f=p/m=p*l/m,, where λ is the wavelength, and f the frequency, i.e.
at he greater the weight the momentum increases also and at greater weight the wavelength
may be reduced and the frequency may increase.
Spread the light
Spread of the light I described at the beginning of
this chapter. Spreading of light in
wavefronts results from the mechanical-physical characteristics of light,
where by the collision of photons, that are spread in all directions, the neutralizing
of the momentum occurs except in the direction of the wavefront of light spreading.
Reflection and
refraction of light
For the refraction
of light the relationship sinα/sinβ=v1/v2 applies,
where sinα/sinβ is sinus functions of the angles α and β,
which a refracted beam includes with a perpendicular of impact of the light beam on the border of both environments, α in
front of the slot and β behind the slot, v1/v2 is
the proportion of the speed of light in two different environments, v1 in front of a slot, v2 behind
the slot. If we ignor the photon's momentum, passed to the surrounding
environment, then psv=ps2, where psv., is the
momentum of light in a vacuum, and ps2 the momentum of light in
another environment. When the light passes from another environment into the
vacuum m v*vv=m2*v2 applies, from it vv/v2=m2/mv=
sinα/sinβ follows, therefore the greater is the speed of light in the
second environment v2, the smaller is mass of particles in the
second environment m2 and the smaller is the angle αv of
the refraction in vacuum, where vv is the speed of light in a vacuum
and mv the mass of vacuum particles.
Similarly this applies, when the refraction of light
from vacuum into another environment, while ignoring the momentum of the
particles, that become bearers of light, compared to the momentum of the photon
of light in a vacuum. Similarly we can extend these relations on the transition
between the momentum denser to the
momentum less dense environment and vice versa, if we ignore the momentum of
the photon passed to the outside environment.
Dispersion of
light
Dispersion of
light
is related to the different mass of the photon at a standstill, the x/∞kg
for light, as it follows from the arithmetic of infinity. This means that light
is composed of photons of different frequency and momentum, which in a vacuum
has a constant speed of c of the photon, but in a different environment, where
is the variable relativistic weight of the light carriers m>0, these
components of light refract at different angles. When the light components with
higher frequency, thus lower mass of the particles refract under the bigger angle
of refraction.
Interference of
light
Interference of
light can be observed only at coherent
light waves, the waves of the same frequency. By an interpretation of balance
forces I pointed out, that the same frequency is related with the same value of
the balance forces and that is dependent on momentum. It follows that f1=
f2, and hence v1/v2=λ1/λ2=m2/m1=1.
In other words at the same momentum of light waves
by collisions of particles it does not occur to increase the momentum of the
waves, and therefore its frequency, but rather it intensifies the light on the
same frequency.
Bending of light
Bending or
diffraction of light is related in my opinion with the
refraction of light and that as a result of changes of the average momentum
density of the environment. Both is then the result of spread of light, as
described above.
The relationship asinα=kλ for position of
interferential minimums of lit slot, where a is the slot width, λ is the
wave length of light, and k = 1, 2, 3 an order of interference minimum, can be
converted to the equation for refraction of light (kλ/a1)/(kλ/a2)=a2/a1=(sinβ/sinα1)/(sinβ/sinα2)=sinα1/sinα2=(m1/m)/(m2/m)=m1/m2=(v2/v)/(v1/v)
=v2/v1, where m and v are the
speed of light in vacuum and m1 and v1 the mass and speed
of the particles of light in front of the slot and m2 and v2 the weight and speed of the particles
of light behind the slot and therefore the wider is the slot a2, the
smaller is a change of an angle of light, or angle α2 included
by the light with a perpendicular of beam of light behind the slot, the smaller
is a proportion of the average weights of the particles before and behind the
slot and the smaller is proportion of the average speeds of the particles
behind and in front of the slot, i.e. the ratio of the speed and mass of the
photons.
Polarization of
light
During light vibrations based on momentum the electric polarization occurs by the balance
forces, which is however completely chance. In the event, that the moving
photons collide with particles of greater momentum, which allow movement in one
direction only, in the other directions the deceleration motion of photons occurs
by passing their momentum, virtually absorbing the light, then there is the
polarization of light in only one direction of motion.
3.6.3 OPTICAL DISPLAY AND OPTICAL SYSTEM
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
The light represents the physical movement expressed
byrelation m1*v1, the contact optical environment by relationship
m2*v2. After the passage of light through this optical environment
the light represents the physical movement
mv= m1*v1+
m2*v2. The
curvature of the surface of the lenses is causing continuous refraction in converging lens or dispersed refraction
of light in concave lens.. Mirrors are comprised of substances,
that represent the physical movement of relatively great mobility density,
where the direction of the speed of their particles is directed outside of
their substance. An example is water or mercury, and this movement describes
the mechanics of liquids.
From the equation for the focal length of the lens
1/f=[n2/n1(=v1/v2=m2/m1=sinα1/sinα2)-1](1/r1+
l/r2), where f is the focal length of the lens and r1, r2,
the radius of curvature of optical surfaces and n2 the
refractive index of the substance, from which the lens is made, and n1 the refractive index of the
environment, it follows that the wider
the lens is and the larger the mass of particles of the lens is, the greater is
the slowing of light and the greater is the angle of refraction behind the lens
to the difference in the speed of light in the lens and behind the lens.
3.6.4 ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
The description of the light implies, that the light of a higher frequency and shorter
wavelength is represented by a motion of the particles of greater weight, as relativistic
so the rest, and vice versa, from this perspective the waves of the
heaviest particles represent radiation γ (gamma), for which γ
(wavelength)/m (meters)=10-12 to 10-14, and the lightest radio
radiation, for which γ (wavelength)/m (meters)=102 to 100,
among them are television and radio waves. VHF (very short waves), for which
γ (wavelength)/m (meters)=100(=1) to 10-2,
microwaves, for which γ (wavelength)/m (meters)=10-2 to 10-4,
infra-red radiation, for which γ (wavelength)/m (meters)=10-4
to 10-6, ultraviolet radiation, for which γ (wavelength)/m (meters)=10-8
to 10-10, between the infrared and ultraviolet radiation occurs the
light. In addition there is the x-ray radiation for which γ (wavelength)/m
(meters)=10-10 to 10-12. With frequency is also related
energy and momentum of radiation, where the light with the heaviest particles
has the biggest momentum and energy and vice versa.
The energy radiated by a black body at a rising temperature with the largest share at a
wavelength of γ max represents in my opinion the equivalent of the
resonance of oscillator, in other words at the greater frequency the reduction occurs
due to the balance forces, which allow the maximum value of fluctuation of
momentum or energy for a given frequency of a body.
The quantum nature
of light E=h*f, where E are quanta, i.e.
the amount of energy emitted gradually by the light, the variable h is the
Planck constant h = 6,626*10-34 (Joule times second), f is the
frequency of light, it flows from the duality of the physical movement, because
the movement expressed by p=m*v always has the particle nature of the weight rn,
while the unit agency of zero weight created by the infinite division of particles
is fiction.
The relationship
E=h*f stems from the fact, that each
photon, or particle means an increasement of momentum, or weight and thus
increasing the frequency due to the influence of balance forces. At the same
time the increase in the momentum means at the same time the increase of
energy, which stems from the context of momentum and energy shown in the
mechanics. The relationship E=h*f can be overwritten as E=h[=mv (photon)/(mv)
(light)]/s(per second).
Luminescence means, that the radiation of shorter wavelength (and
greater frequency) and therefore greater momentum causes in the substance of
the lower momentum of photons by the collision of particles the radiation at longer wavelength (and lower
frequency), thus of lower momentum, than the above radiation has, which is the
originator of this luminescence, the total momentum is maintained however therefore.
With the momentum of particles of substances is related
the formation of the spectrum of substances in the collision of particles of
radiation with particles of substances.
X-ray braking
radiation as a result of slowing down the
movement of electrons comes probably from the increase of momentum of particles
in the surrounding environment, that takes in a collision a part of the
momentum of electrons. Characteristic
x-ray radiation flows from collisions of particles of metals, or from their
release from metals due to their increased momentum resulting from collisions
with electrons, and this action of balance forces.
3.7 SPECIAL THEORY OF RELATIVITY
3.7.1 SPECIAL THEORY OF RELATIVITY
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
The maximum speed is according to this theory the speed of light c. This speed is the maximum speed permissible and
limited by work of the universal (all)
balance forces, the greater speed we
would probably only be able to achieve through the destruction of the Universe.
In other words through collisions of particles the
limit of maximum speed occurs, when the higher speed than the speed of light
produces such accumulation of particles due to supra-average mobility density, that
increasing momentum is constantly reduced by collisions with attracted
particles of lower momentum.
The speed of
light corresponds so to the endless time, to the zero-length and endless weight. It
is a concentration of mass of the Universe into a single, endless standing
point and in the case, if the Universe would
move at this speed.
At the same time the Einstein formulas for time are the
proof, that time, length and weight are
convertible to speed. In other words zero time in the system moving at the speed of light means a non-zero
time in the rest system, infinite length in system with the speed of light
gains finite value and zero weight in the system with the speed of light is
non-zero. In other words all the agencies in the macroworld are represented by
a motion of the photons in the microcosm, that currently has zero rest mass,
time and macroworld has infinite dimension to it.
The result of these considerations is the
confirmation of the photon as a building
element of macroworld, in my concept called unit agency, which moves at the
speed of light and at the same time it confirms, that by the speed as physical
motion all the other basic quantities of macroworld, i.e. the weight, time and
length can be expressed. Further, all objects of macroworld can be converted into
a stream of photons, which mediate inter alia the movement of light.
3.7.2 NEXT DIMENSION
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
How can I define
the basic variables of our dimension, we use for this a special theory of
relativity by Albert Einstein. The basic premise of this theory is, that the
maximum possible speed of our dimension is the speed of light.
In my opinion
the speed of light is the intersection between our and the next dimension, i.e.
the maximum speed achievable in our dimension and minimum speed achievable in
the next dimension, in the case of the speed of light it is the Divine dimension.
We come to the following relativist relations in our and next dimension.
√(l-c2/c2)=0, which is the denominator of the
relativistic relations for time, length, and weight. Assuming, that in the
numerators of these relations is ∆t=l=m0=0, then the result of
this share is -∞≤m, ∆t0,10=+∞, as
this proportion can be rewritten as (1/+∞=0)/(1/+-∞=0)=x, -∞≤x≤+∞.
Due to the fact,
that all of the time, weight and length according to the Philosophy of Balance
of physics is also convertible into speed and they can be converted into a
stream of photons at light-speed of zero rest mass, in zero time, zero-length
and thus express any object in our world, we get to complex values of the rest time
and length, weight in the moving system. This is a different mass, which stands
in contrast to the vast form of mass in our dimension. Even more the nature and
the existence of other mass manifest in the next dimension.
From this it follows,
that we use for Einstein's relationships
of the special theory of relativity the basic
assumption, that the speed of movement in the next dimension exceeds the
speed of light. We come to the following relativist relations in the next dimension.
√[1-(c2+x)/c2)]=√(-x/c2)=i√(x/c2),
for x>0, where i is a complex unit, which forms the denominator of the
relativistic relations for time, length, and weight. Under that assumption then
the result of the proportion for the our length and time ∆t, ∆l=∆t0,
∆10*i√(x/c2), where ∆t0,
∆10 is the difference of resting time and length, and
∆t, ∆l is the difference of moving time and length at the greater speed
than the speed of light (c) by the x-variable, for next dimensional mass m=m0/i√(x/c2),
where m0 is rest mass and m is moving weight at speed of light greater
than the speed of light c by the x-variable, and i is a comlex unit. Therefore
the increase in length and time in our dimension is reflected as a decrease in other
length, and other time in the next dimension and the increase in weight in our
dimension as the increase in the other weight in the next dimension as a result
of the reduction of the above number x representing speed (i.e. one of the
forms of energy, or relativistic mass, or the movement consisted of time and
length, except mass) as a result of the law of conservation of energy. We get
to a concept of other time, other lenght and other mass representing the
different mass of the next and our dimension. The line between the next and our
dimension, between mass and other mass of both dimensions is light, i.e..
particles, perhaps even at a non-zero rest mass moving at the speed of light, it
is the Divine dimension, perhaps at an infinite energy, and absolute vacuum.
The light source
is the Sun and the stars, which arise and cease to exist. There arises the
balance between mass and other mass, the length and the other length, time and
the other time, to put it simply, between energy and other energy, which due to
the non-complex and complex variable of
relativistic mass in our and next dimension and relations of Einstein's
special theory of relativity for a relativistic energy E=mc2, and
for vector of relativistic momentum p=mv, where E is the total relativistic
energy, m is the relativistic mass, v is of speed of system and c the speed of
light, E obtains also non-complex and complex value and finite or infinite
value, in our Universe it seems to be only a final and non-complex value,
further the relationship for expansion (i.e. expanding) of time
∆t=∆t0√[1-(v2)/c2)], where
∆t0 is the difference of the time in the resting system or in
the system of the lower speed than in a system of higher speed v (v is a scalar
of the speed), where variable relativistic time at the difference of time
∆t applies. Furthermore the equation for the contraction (i.e.,
shortening) of lengths l=l0√[1-(v2)/c2)],
where l0 is the length in the rest system or in the system of the
lower speed than in a system of higher speed v (v is a scalar of the speed),
where variable relativistic length l applies, and also the relationship of m=m0/√[1-(v2)/c2)],
where m is the relativistic mass and v speed in the system of higher speed (v
is a scalar of the speed) and m0 rest weight in the stationary
system.
Therefore we can
say, that there are two conflicting forces of mass and other mass, where the
balance is caused by constant creation and destruction of the stars or the
penetration of light between the dimensions. While it can be assumed, that the
energy released by the destruction of stars is equal to the energy consumed for
their creation and the law of conservation of energy is valid in the next and
our dimension.
Relativistic image of the world
(termination)
Due to the content interconnection of
our dimension, which is the basis for the next dimension, and the next
dimension, which is its superstructure, we can explain the mutual penetration
and interdependence of these dimensions manifested in contradiction of all not-Being
in these dimensions. Common dimension of our dimension and next
dimension are dimensions of the speed of light, virtually electromagnetic waves and
of absolute vacuum, so they act in our dimension through the constant speeding
up its particles in the form of conversion of light into matter, if the speed
of light photons are absorbed by the mass, and vice versa, converting mass into
light-emitting photons
From the
standpoint of mathematics of our dimension this corresponds to the operations
with positive and negative numbers except 0, inequalities with the exception of
equations, subtraction, division and roots, virtually addition, multiplication,
exponentiation, thus ideas, that are contradictory as well as light and vacuum.
In biology this contradiction
seems to be manifested in the form of autotrophic and heterotrophic organisms,
that feed on inorganic substances, or in the second case on organic substances,
in particular on other organisms. Again here there is a contradiction between
the destruction and creation, vacuum and light.
Just as the
thoughts of a human are destructive and creative much like the nature, that
creates and destroys organisms at the same time.
The reason of these
contradictions between destruction and creation is in my opinion the
penetration of the Being and of not-Being in our and the next dimension. In the
words of Philosophy of Balance this is the contracoagency, thus destruction of
formation and cocontraagency or formation in destruction, and so in the form of
complex destruction such as cocontraagency or other matss or any other energy
in terms of our dimension, or a complex formation as energy or mass from the
standpoint of our dimension, which are in my opinion in both dimensions
connected by light and vacuum.
How is it possible
to influence our dimension by the next dimension in all areas of life as are
philosophy, religion, history, political philosophy and law, mathematics,
physics, biology, chemistry, and last but not least the chess, the basics of
psychology, sociology and economics. In my opinion it is, because the Philosophy
of Balance understands the Being as the agency, which is united, continuous,
contiguous and similar.
Therefore in
philosophy there are directions, that prefer good over evil vice versa evil
over good. At religion it is talking about good and evil impersonation. In
political philosophy there is a single government of the dictator and of a
broader group or democracy. The law can be a dictation of the individual, it can
also be a social contract among all members of society, it can or cannot accept
the death penalty there, where it would be on the spot the life sentence. In
psychology a person may be accepted same as any other person or he or she can
be accepted differently one from another, for example the rich from the poor,
already since his or her childhood, therefore from the beginning with
consequences for the whole life, the social behavior may have the nature of the
violence or of the contract with the minimum required, virtually educational
element of forcement. Just as chess or any other games can be played
aggressively or defensively with mirror repeated non-defensive moves.
What is a path from
the eternal dispute between our and the next dimension, i.e. between mass and
other mass or energy and a different energy. In my opinion it's about reducing
error, that is unrecoverable due to the ambivalent agency nature of Being. In
other words, if all creatures of our dimension start to act in accordance with
the agreement with the creatures of the next dimension, then after the finite
long time due to a finite total Being, thus the energy about the size of W=x
allocated on our and the next dimension due to the the limitedness of the
highest achievable speed in these dimensions the size of the error will be
equal to (x/2+x/4+x/8+x/16+…=x, x≠1, thus negligible from the perspective
of both dimensions.
In other words
over the time the errors of mankind will
be deleted from generation to generation or within one generation, if it wishes
and thus also the punishment, that causes the fact of the next dimension in the
form of the penetration of other energy, as I have already said above, the
largest possible reduction of the flow of energy between the two dimensions
will occur.
Ultimately it will
be not a penalty and mistake but the game for an error, which will be purely
formal, it will be a conmpetition between our and the next dimension and it will
be awarded only symbolically. One will be the winner one time, the other will
be the winner second time and it will rotate, in other words it will be a
merciful victory and defeat.
What way leads
to a final settlement of so limited good of mass and evil of other mass in our
dimension, it is to cause the least possible death and pain. We are all an
essential part of reality, whether bad or good, that is counted on, it is not
possible to accept dimension and to refuse
next dimension, because it is a unity and a part of ourselves.
Otherwise in an
attempt to destroy the other mass we only increase the flow of energy between
the two dimensions (space-times).
Literature: http://www.novinky.cz/veda-skoly/279473-nasa-chce-dohnat-star-trek-a-cestovat-vesmirem-nadsvetelnou-rychlosti.html : pst, Novinky, 2012
3.8.1. INTRODUCTION
(formation)
Microcosm, represented by microparticles and their
interactions is once again composed of unit agencies, that make up the smallest
physical movement described in the mechanics and that is the kind of a complex
physical motion. In physics of microworld
the the transferability of speed on the mass, length and time is clearly
manifested, thus their uniform nature
as of physical movement described in the special theory of relativity. In
addition here particle quantum nature of all agency is manifested,
when only unit agency as infinitely divided movement represents the net
movement of a particle of zero rest mass, other movement is a complex unit
agency, thus the motion of the particles.
Subagencies
(performance)
3.8.2 QUANTUM PHYSICS
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
The photoelectric effect, when photons transmit by collision
with the electrons of the substance them momentum or energy and they increase
their momentum, where hf=Wv+(l/2)mev2, where Wv
represents the output work, which is needed to overcome the attractive force of
the substance, or of the force, that accelerates the movement of the electrons
in the direction of substance movement and (1/2) mev2 represents
the kinetic energy or the momentum of the photoelectron after overcoming the
attractive force of the substance.
The nature of light as a stream of photons and
electromagnetic radiation, that is described in the text about the light, thus electromagnetic
waves are a consequence of differing mobility, virtually energy density of
grouped and diffused photons and they imply also from the relationship
E=hf=hc/λ and p=mc=h/λ from which flows λ= h/(mc) and f=c/λ
=mc2/h . From these two relations it is obvious, that with the higher weight of the photon the wavelength
decreases and the frequency of the electromagnetic waves increases. And it
also implies, that the light as the movement of p=m*c has at low frequencies rather
the nature of the waves, the speed prevails and at the higher frequency is more
pronounced particle nature of radiation,
the weight prevails.
The position of the micro particles and the momentum cannot be
determined by microscopic physics with absolute precision using de Broglie
waves and Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle it can only
be determined by the probability, with which the micro particles will be located
at a certain location area. This was verified by experiment, when photons were
launched under the same conditions of input versus slot, when photons fell
in different places, but the most probable place of their recurrence was most
common.
The movement of
the microparticles (composed apparently of photons at the speed lesser or equal
to the speed of light) as a measure of the probability stems
from their nature as an infinitely partial physical movement, where its
movement is partly determined by the movement of other photons and collisions
with them and partly independent, because
in terms of human recognition, there are no smaller partial particles, from
which a photon would be composed, or its momentum.
Author:
Dalibor Grůza
Time: 14/04/2012
07:27:16
Post:
Wave characteristics of particles according to the
relation λ=h/p=h/(mv), de Broglie waves arise directly from
the special theory of relativity, or of the transferability of the weight,
length, and time on the speed, i.e., that all mass is composed of photons
moving at the speed of light of non-zero relativistic mass, or in the endless
quantity apparently of point particles of zero relativistic mass and moving at the
lower speed. Then at the same time similarly as light the other substances are also of wave and
particle nature. These waving of photons of substances has zero momentum, if it
is formed by the moving photons shot from solid substances of lower speed, than
the speed of light is, otherwise it is the transformation of the substance on a
stream of photons, or light.
To bound
particles corresponds working of the attractive balance force, that
predetermines due to the high local momentum of a body the momentum i.e., the
size and direction of movement of particle, on which it acts. The result of the
attractive balance force is a reduction of the total momentum of the free
particles by limiting their movement by the forces binding them to a specific
space. The impacts of particles shot by the body cause a local increase in the
momentum of the particulate photon with the highest momentum, which overcome so
the bond forces and they leave the body in the form of light or of shot particles
with higher weight, than has the photon. This reduces the momentum of the body
and the weight deficit of bound particle
occurs. As a result of restrictions of the waving movement of the photon
particle occurs also the quantization of
their wavelength and consequentlyof their other quantities, such as energy and
momentum, etc.
3.8.3 PHYSICS OF ELECTRON PACKAGING
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
Electrons as
particle with smaller absolute mobility are attracted due to the action of the
nuclei of atoms, which have a bigger absolute momentum through collisions with
the photons, or a density of their momentum is balanced with the momentum
of the nuclei of atoms and a balance state is instaled. The effect of this
attractive force weakens with a distance from the nucleus of an atom, with this
distance decrease also energy, or momentum of the electrons sufficient to
overcome the binding force, or the momentum of nucleus of an atom. The electrons farthest from the nucleus of
an atom cause so the most the change of the momentum by the collision of
particles and they determine the chemical properties of the substances If
the atom has less than 4 electrons in the outermost subskins s and p from the
nucleus of an atom, these electrons have a low momentum corresponding to the
momentum of the atom, which increases with
collisions with electrons of an atom, which has more than 4 in a chemical reaction.
Electrons with increased momentum overcome then the binding forces of the atom
nucleus and they bind to the nucleus of an atom with the greater momentum of
electrons in the outermost subskin. Atoms with large momentum of electrons in
the outermost subskin are then stable.
Stimulated forced
emission of light is caused by the
excited state of the atom, thus at atoms with electrons with great energy or
momentum distant from the nucleus, by increasing of this momentum by collision
with photons of radiation, there is a large overcoming of the binding (attractive)
nuclear forces at photons in the electrons with great momentum, which will be emited
in light by stimulated emission of the laser.
3.8.4 PHYSICS OF ATOMIC NUCLEUS
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
The nucleus of
an atom consists of protons and neutrons, the positively charged proton has a
considerably larger mobility density but less total momentum than the neutron. In
my opinion however both particles represent the kind of physical movement composed
of the moving photons.
The above findings arise from the equations of the fission
of the protons and neutrons 11p→10n
+01e +00v with the energy
consumption and with the release of energy, where 00v is
the antineutrino, 11p
proton, 10n neutron and 01e electron. If we can
deliver enough energy, then we obtain the fission reaction 11p→10n
+1e +00v (=10p)+01e+0,0v,
from which it follows, that energy in
the form of momentum is transformed into positively and negatively charged
particle of nonzero weight, when the input and output of this compound reaction is a proton. This composite reaction
demonstrates so the link between the energy, virtually momentum represented by
the moving particle (i.e., the physical movement of p= m*v) and mass and charge.
3.8.5 BINDING ENERGY OF NUCLEUS AND
NUCLEAR REACTIONS
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
The effect of
balance attractive force accompanies bound particles, that predetermines due to
the high momentum of the nucleus the momentum, i.e. the size and direction of
movement of particles, on which it acts, in the given
case of the bound nucleon (i.e. any particle of the nucleus). The result of the attractive force is reduction
of momentum, virtually mobility density compared to the free nucleons by
limiting their movement by the forces binding them to a specific space. By
the impact of a shot (particle) in the
nucleus a local increase in the momentum of nucleon constituted by the
photons with the highest momentum may occurs, which will thus surpass the
binding forces of the atom in the form of by it created particle (i.e. nucleus,
electron) and it leaves the nucleus as radiated particle. As a result of
increasing the momentum of photons, or particles radiated by them in a short
time there will not be a dispersion of momentum by collision with other
particles of an atom due to fewer number of collisions in so short time. In
other words the output work W will reduce. It releases the energy, or momentum corresponding
to the momentum of the shot particle, and thus the energy drops, virtually the
momentum of an atom, not just for the
momentum of the projectile but for momentum of radiated particle. By this
decline in overall momentum, virtually energy the relativistic mass deficit of the nucleus can also be explained, which is the difference between the
total mass of free nucleons and the real (experimentally observed) mass of the nucleus,
which is made up of them. Photons with a higher mobility are apparently quarks and their momentum is increased by
the collision with gluons created again by photons. To release gluons,
or atom of helium nuclei, electrons and positron it do not have only to occur by
artificial increase of momentum of quarks
with collision of outside gluons, but also with collision of gluons inside an
atom, or molecule with higher than the
local balance momentum , so particles are
gradually released and the process is called radioactivity.
3.9.1 INTRODUCTION
(formation)
Astrophysics examines the physical and chemical properties of the
space bodies and the interstellar environment, in other words it deals with the
Universe as a whole or its essential parts. In both cases from the perspective
of Philosophy of Balance it is a complex agency, which seems to be due to the
continuity and the connection logically connected with all the other events in
physics. This is so in both cases similarly to other subjects of Physics the
complex physical unit agency or complex
movement expressed by the relationship for momentum p=m*v. From the
standpoint of physics also space-time as a four-dimensional
space represents a complex movement expressed by this relationship. The connection
and the continuity of all motion as the unit agency of physics imply then the
ability to derive characteristics of the Universe from the observed
electromagnetic radiation as part of the overall motion of the Universe
movement.
In relation to other branches of physics it is the applied subagency of general
disciplines of physics of macroworld and microworld. As well it would be
possible to define biophysics, physics of chemistry, etc. This is a special
subagency, which is more complex due to the greater quantity of simpler
concepts of astrophysics in context to the simpler or more general fields of
physics of macroworld and microworld, which explore the general regularities
and concepts. It's a similar
relationship as between the physics of macroworld and microworld in physics.
Subagencies
(performance)
3.9.2 SOLAR SYSTEM
Definitions and relations
(performance)
It is assumed, that the solar system was formed more
than 4.6 billion years ago from cloud of interstellar matter. The individual
particles moved with different vector of momentum p, it can be assumed, that the particles with a higher value of momentum
began to predestine particles with smaller value of the momentum, due to both
reciprocal collisions and shooting particles with lower momentum, thus it led
to the work of forces at a greater distance. This force then we call gravitational force. It led to the
creation of momentum fields of particles
at the same momentum that grew gradually and by its concentration it formed
from gases the solids. In other words a cloud of interstellar matter of the
field with uniform density and speed transformed into the mobility concentrated field, or within the relation p=mv
was reduced speed and increased the weight, but not
universally but locally, thus creating the planets and the Sun.
Compared to the concentration of the substance the repulsive balance forces started to act
transmitted by the collisions between the concentrated areas and areas with a
low concentration of a substance, what initiated compared to the concentration
the increase of the share of shot, virtually of emitted particles, in other
words at a large enough density the Sun began to shine. Within the relation p=m*v the transformation of the m to v occurred in the form of radiation, and the
v to m in the form of creation of heavier elements in the context of nuclear
reactions.
The movement of
bodies in the solar system is governed by
universal gravitation law, virtually gravitational forces, further it is caused
by the force of solar radiation, of the magnetic field and the solar wind, in
all cases in my opinion it is the result of a collision of particles in
ultimate consequence up to zero weight. These particles form bodies and their mobility fields have a
certain momentum corresponding to the movement
of these bodies and their momentum fields, as a result of their high
absolute momentum then by collisions of particles
they determine and affect the momentum of the other bodies and gravitational forces come to action.
Similarly, it is in the other cases of force action, when the collision with
the momentum field affects the momentum of particles and bodies.
The foregoing implies, that the highest absolute
momentum has the surroundings of the Sun, here the planets with the highest mass density are also formed, which
decreases with distance from the Sun. Low
density of far surroundings of the Sun is related to the decrease of its
momentum field with increasing distance, which is related to lower size of the
gravitational forces. The lower mobility density is also related with a lower
concentration of particles and a larger radius of more distant planets. Then in
my opinion similar patterns are in the vicinity of large planets with a large
absolute mass, which create their own mobility field.
The exception to this schema are comets, that have great speed, or speed
momentum to escape the reach of the
gravitational momentum fields of planets. This is, because thanks to the high
speed the time of effect of momentum field of the planet is limited and it does
not occur a sudden but a slow adaptation of momentum of comet and momentum of the Sun, through collisions of particles of these
momentum fields.
3.9.3 BASIC DATA ABOUT THE STARS
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
The stars were apparently created as in the case of the Sun by concentration of momentum fields, in other
words by the transformation of the speed of the movement of cloud of
interstellar substance into the weight of this motion in relation p=m*v
describing the founded mobility field arisen from this cloud and this cloud
itself. When a large enough local concentration of momentum of particles at one
point it occurs by the balance forces by collisions of particles between space
of low and high momentum the shooting of
particles in the form of radiation
on the one hand, and the continuing concentration of particles in the form of creation of heavier chemical elements
on the other hand. The places with great local mobility density are created representing
the ongoing conversion of speed momentum field into the mass mobility field and
parallel conversion of mass momentum field (with a higher absolute weight) into the speed
momentum field in the form of stellar radiation.
The center of
the stars is of absolute vacuum and by it attracted substance of great density
and weight. This is again
made up of particles of ultimately zero weight, i.e., the photons, which in
case, that they do not move at the speed of light, represent a pure movement
expressed by the speed v and they embody
wave motion. This waving has a minimum wavelength and high frequency
approaching to 0 in the case of the wave
length and ∞ in the case of frequency.
The above written degree of development of the stars
is the main sequence. Followed by the stadium of the red giant, when the conversion of speed momentum field of a star
into the mass mobility field, i.e. the formation of heavier chemical elements
applies to the other layers of the star, at the same time the conversion of
mass momentum field into speed one increases by the influence of balance forces,
which is not only for microparticles but also the entire upper layers of the star,
which increases its volume.
By effect of balance forces, when the collisions of particles
of a star with high momentum with particles with low momentum of the surface of
the star are causing the sharp increase in the momentum of these particles with
lower momentum manifested as an
explosion of a supernova. The conversion of speed momentum field into the weight
mobility field may stop by the restoration of balance between conversion of
weight into the speed of radiation and speed into the weight of the heavier
particles by the influence of lighter particles by the pressure of the degenerated
electron gas at white dwarfs, by the
influence of neutrons at neutron stars
, or the concentration of momentum field may continue by formation of heavier
particles at black holes, when the mobility
density of this field determines the momentum of the photons by collisions of particles,
the gravity does not allow to escape to electromagnetic radiation from the star.
Physical description of conversion of speed momentum field into the weight mobility field
while radiating particles, i.e. the conversion of mass momentum field into
speed mobility field, represents a reduction
in the absolute values of momentum, temperature, force, mass, and pressure and
increase of the local values of these variables. The temperature represents
then the sensory representation of motion, or momentum and energy per unit of volume, when the bodies with the same
temperature can vary in weight and the speed of movement of particles and
mutatis mutandis the heat exchange occurs by the collision of particles as in
the case of momentum.
3.9.4 THE STRUCTURE AND EVOLUTION OF THE
UNIVERSE
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
The Universe, similarly as the stars and the solar system, probably
formed from the cloud of the substance, the density and the temperature was
huge. In other words it was a predominantly mass mobility field characterized
by the relationship of physical momentum p=
m*v. Effect of balance forces
between particles of mass momentum field of very high value of the momentum and
the surrounding momentum fields with lower momentum may be represented by,
where appropriate, areas of upper and lower dimension than our space-time cause
an abrupt change in the momentum by the
collision between particles of these other-dimensional momentum fields and
the Big Bang. So the weight mobility field
changed to the speed mobility field represented by spreading Universe with
a homogeneous substance of lower density and temperature. At the same time
there was an apparent emitting of received energy, or the pass of momentum to
next-dimensional space. Thus a huge cloud of interstellar substance was formed,
which corresponds to the speed momentum field, that began to concentrate again by the transformation into mass mobility field. A relic of this
speed momentum field is homogeneous (uniform) and isotropic (i.e. having their physical values the same in all
directions) composition of the Universe from the perspective of spatial cubes
with a length of side 100 M(ega pc.
Note: For the expression of the distance of the
stars in the astrophysics as a side unit the parsec (pc) is used, which is
associated with the trigonometric measurement of distances. The basis is the
specification of the annual parallax of π, i.e. of a star, or the angle
under which we would have seen from the star the great half-axle of elliptical
trajectory of circulation of the Earth around the Sun, i.e. angle involved by its
arms built partly from this star, perpendicular to this half-axle into the
middle of this half-axle, represented by the Sun (i.e. the arm about the size
of r) and then by the second arm going from this star to the top of this
half-axle on the perimeter of that elliptical trajectory of the circulation of
the Earth around the Sun. Unit parsec is defined as the distance, from which we
would have seen the great half-axle of trajectory of the Earth (i.e. a line with a
length of 1AU-astronmical unit roughly defined as average Earth-Sun distance, 1
AU = 149 597 870 700 m, A light-year, unit symbol ly is a unit of distance,
which light travels in a vacuum in one Julian year, 1 ly is roughly 9,46*1015m.)
at an angle of 1"(i.e. one second of angle). The angle, of which size we
chose as equal to one, we call unit angle. The unit angle in arc measure is the
radian (rad), which means an angle that on a circle of unit radius cuts off the
arc of circuit of a circle part of unit length. In the so-called degree measure there is used the unit angle of angular
degree, which is defined as 1/90 of right, i.e. perpendicular angle of π/2
(i.e. approximately 1,57, i.e. approximately Ludolph number π=3,14159) radians, except this it is used 1/6 of angular
degree=1angular minute (´), and 1/60 of angular minute=1 angular second
("). Between the distance of the size r expressed in parsecs and the
annual parallax of π expressed in angular seconds the relationship r=1/π
applies. The annual parallaxes of all stars are smaller than 1. The nearest
star Proxima Centauri has an annual parallax 0,763 ", its distance is
approx. 1.3 pc. For converting of a unit of parsec to meters applies the
relation, 1pc is approximately equal to 3,086 1016m. Sinus, i.e.
sin0=0, sinπ/2=1, sinπ=0, cosinus, i.e. cos0=1, cosπ/2=0,
cosπ=1, in the case of sin and cos it's about the same wave displaced on
the x-axis by π/2. (see http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sv%C4%9Bteln%C3%BD_rok
, http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Astronomick%C3%A1_jednotka
)
By the gradual transformation of equally dispersed
stellar substance at the Big Bang, hence the speed momentum field into the
weight mobility field shaped gradually the concentrations of particles by the action
of gravitational forces by collisions of particles with different vector of momentum
of mass mobility field in the form of superclusters
of galaxies, clusters of galaxies, the local group of galaxies, galaxies and
globular star clusters. The position of stars corresponds to the average
momentum, which corresponds to the sum of the momentum of each of the particles,
that make up the mobility field of interstellar matter created by Big Bang at
the formation of the Universe, a supernova in the formation of our solar
system, etc.
3.9.5 ASTROPHYSICAL PICTURE OF THE WORLD
(termination)
Astrophysics
accepts in general the theory of expansion of the Universe because of the relict radiation of the observed
Doppler effect at red displacement in
the spectra of the galaxies, and further by solving the equations of general
relativity of Albert Einstein, these equations imply, that the Universe is
either shrinking or expanding, so that there cannot be a balance state, when
the Universe is at rest.
From the characteristics
of the Universe as the physical movement p=m*v, where in terms of all
dimensions it leads to conservation of momentum, virtually energy, follows the
movement of conversion of speed into the weight and vice versa, or radiation into
substance and vice versa. This conversion of speed momentum field into the
mass and vice versa is not continuous, but it occurs when a certain critical
value by the formation of nuclear reactions, explosion, or bang.
Currently we are
in the stage of conversion of mass into the speed, or the gradual dispersion of
particles by radiation of the stars. It can be assumed, that in achieving
the critical value of currently ongoing expansion of the Universe the re-explosion occurs.
The history of
the Universe of all spaces can be seen as constant transmition of movement from the
superiority of the mass quantity into speed one and vice versa, which
corresponds to the above mentioned by astrophysics supposed instability of shrinking
and expanding Universe. At this physical motion in my opinion the absolute deviation
between the mass and the speed increases constantly and so the heavier bodies
still arise and faster movement (i.e. radiation). When it reaches the extreme deviation,
the concentration of the substance in
a single point occurs, which is still at the infinite weight moving at the
infinite speed, which stems from the law of preserved total momentum, and
energy.
In other words increasingly complex or simpler organisms
will form, than it is today, at the creation of infinitely fast and mass
perfect organisms in an endless time to merge with God or with all Being.
Scientists
estimate the age of the Universe at 13.7 billion years old. (see http://www.novinky.cz/veda-skoly/279982-hubbleuv-teleskop-odhalil-tisice-galaxii-vzdalenych-miliardy-svetelnych-let.html : 2012, Mys Canaveral-mif, Novinky, ČTK
)
4.2.1
INTRODUCTORY DEFINITIONS
4.2.2 STRUCTURE
OF ATOM
4.2.3 MENDELEJEV
PERIODIC LAW
4.2.4 MOLECULES
4.2.5 CHEMICAL
REACTIONS
4.3.1 INTRODUCTORY
DEFINITIONS
4.3.2 CHEMICAL
ELEMENTS
4.3.3 INORGANIC
COMPOUNDS
4.3.4 PHYSICAL
CHARACTERISTICS OF SUBSTANCES
4.4.1
INTRODUCTORY DEFINITIONS
4.4.2 OVERVIEW
OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
4.4.3 REACTION
MECHANISMS
4.4.4 ORGANIC
CHEMISTRY IN THE MODERN SOCIETY
4.4.5 NATURAL
SUBSTANCES
4.5.1
INTRODUCTORY DEFINITIONS
4.5.2 ENZYMES
4.5.3 ENERGETICS
OF BIOCHEMICAL PROCESSES
4.5.4 METABOLISM
OF CARBOHYDRATES
4.5.5 METABOLISM
OF LIPIDS
4.5.6 SYNTHESIS
OF FATTY ACIDS
4.5.7 METABOLISM
OF LIPIDS AND CARBOHYDRATES
4.5.8 NUCLEIC
ACID AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
4.5.9 PROTEINS
AND THEIR METABOLISM
4.5.10 IMMUNE
SYSTEM
(formation)
The object of
chemistry as a whole (formation subagency
of formation agency) is mostly the movement
of electrons, or chemical reaction. This movement depending on the type of
chemical elemenr disciplines of general, inorganic, and organic (the subject is
more complex carbon compounds) chemistry explore.
By its object the chemistry is different from physics, of which object is a general movement in
the world of phenomena. The movement of electrons mediating the chemical
reactions is so more special term than the movement in the context of physics.
The subject of chemistry is not the movement of particles in the nucleus, which
the nuclear physics examines, but the structure of the nucleus is the subject
of chemistry to the extent, to which it determines the kind of chemical element
on the basis of its proton number. Chemistry is a more special discipline than
physics, which is more special than the mathematics, that is more special than
the Philosophy of Balance.
Chemistry as more special science in relation to the more general physics and even
more general mathematics and Philosophy
of Balance can be seen in terms of
the concepts of these more general scientific disciplines. This follows
from the nature of the world as a coherent and continuous agency. This means,
that complex concepts of physics, mathematics, and Philosophy of Balance
(supraagency) already include in itself the simpler concepts of chemistry
(subagency), from which they are composed. The use of these set concepts
resulting from the unification of the elements of the identical properties in
the conceptual (agency) analysis of sentences of chemical sciences allows us to
inspect these concepts of chemistry (elements of set concepts of physics and
then of Philosophy of Balance) in the new horizontal (in chemistry) and
vertical (in the context of physics and then of Philosophy of Balance)
relations.
Subagencies
(performance)
4.2.1 INTRODUCTORY DEFINITIONS
(formation of performance)
Chemistry can be distinguished between general chemistry as a science about
general principles common to all chemical disciplines, inorganic chemistry as a science about the chemical elements,
reactions and compounds with the exception of the vast majority of compounds of
carbon and organic chemistry as the
science of carbon compounds and their chemical reactions with the exception of
simple carbon compounds, which are the subject of inorganic chemistry.
The subject of
chemistry is primarily a movement of electrons within the package of an atom of
the chemical element, at which by the influence of changes in bond between the
electrons and protons the different chemical compounds are formed. It
is the physical movement of the particles in the framework, of which by the working
of repulsive and attractiove forces the balance is installed when changing a
chemical compound. The protons, electrons and neutrons of an atom do not change
as in nuclear physics. To describe the type of the element the fact of the
number of protons in the nucleus, which bind electrons, is used then.
The weight of mass
corresponds
to the quantity of the momentum of a substance, or of the momentum of particles
and their weight, that make up the substance. According to the special theory
of relativity of Albert Einstein is the mass transferable to the movement of
photons with a zero rest mass, virtually energy.
Energy can be expressed as the momentum of the substance
and of its particles and the momentum,
which can be obtained by converting the particles to the movement of photons
multiplied by their speed. Link of momentum and energy has been demonstrated in
the Philosophy of Balance of physics.
Substance
quantity is
the number of particles in the substance, the mol was elected per unit, how
many atoms of carbon is contained in the nuclide of carbon 12C weighing 12 g. The number of these particles
is according to Avogadro constant NA=6,022*1023 mol-1..
Molar mass in
the mols is the number of particles in the mols on 1 kg of the substance.
An interesting unit is the average mass of an atom, the so-called atomic mass unit
1u=1,66050*10-27 kg. It is one twelfth of the mass of the nuclide of
carbon.
Relative atomic mass is the number of ideal atoms,
which a particular substance receives, which we gain by dividing of its mass by
atomic mass constant.
Chemical substances can be divided into chemically pure substances, which are
the elements, that represent in the final
result the physical movement of approximately the same properties of the
variables of this movement m*v in each of its parts, i.e. the same number of
atoms, molecules, groups of ions, corresponding to the formula unit, thus
ultimately they seem to have the same number of protons and electrons for each
atom, it has constant properties, similarly for compounds for each molecule. It
is different in the case of mixtures, where are the greater differences ,
whether it is a homogeneous (uniform), colloidal (dispersed) or heterogeneous
(diverse) solution.
Formulas of
substances are the stoichiometric for one molecule, molecular, which indicates the same for
all compounds, in addition there is a
constitutional formula in developed or rational (simplified) form, which
expresses the constitution of the molecule, i.e. the way in which the atoms in
the molecule are bound. Further the
geometric formula showing the spatial arrangement of molecules with the
same configuration (grouping). Conformational formula expresses the
spatial arrangement of molecules of the same compound generated by rotation
around single bond. Electron structural
formula for an atom depicts the valence electrons of an atom by the point,
electron pair by two points or line and bond electron couple by a line between
two atoms.
A chemical
reaction is in terms of the physics an
electron movement within the electron-proton bond from the inbalanced state, in
which the chemical forces renew the balance condition. There are reaction starting
substances, reaction products, they are collectively called the reaction components.
Furthermore we divide the reactants into substrates (base material), that are
concerned, and reagents.
The law of
conservation of mass at a chemical
reaction stems from the unchanged size of momentum in reaction, or from the law
of conservation of momentum.
The law of
conservation of energy stems also at
the isolated system from unchanged momentum (m*v), virtually momentum of
particles and particle mass moving in
this way. Link to momentum and energy has been demonstrated in the Philosophy
of Balance of physics.
The law of
constant merging proportions stems from the balance characteristic of
the substance, when the balance of elements is constituted in the only way.
The law of
multiple merging proportions is
related to the fact, that the balance at similar substances is constituted
in a similar manner, in other words the movement of electrons in valence layer
for the same elements is the same for the purpose of achieving a balance,
irrespective of the amount of merged elements.
The law of
constant volume proportions while merging the gases. The volume of
gases represents the space of nothing, i.e. of shown vacuum, with a small
proportion of elements, that is preserved when merging.
Dalton's atomic
theory can be explained, so that atoms
of the same element are the same, or the balance of the movement of repulsive
and attractive protons and electrons, virtually neutrons is a constant for the
same elements. At chemical reactions does not change the atoms to other atoms
for the reason, that there is not given sufficient movement, or momentum to
release protons from the nucleus, as it is in the case of the field of nuclear
physics.
What concerns the chemical equation, so occurs the maintaince of the amount of movement m*v and a weight of particles, in the final
consequence of movement m*v, if we transform
the substance into a stream of photons. For the above reason there must be
maintained the number of electrons, protons and chemical elements, that do not
change in chemical reactions.
In other words, if the charge or a local imbalance
of starting substances exceeding of the balance value (the predominance of
protons) or the lower balance value (the predominance of electrons), so the
same local imbalance is kept for the product of the reaction. The same is true,
if there is on both sides of the equation the local chemical balance.
Subagencies
(performance)
4.2.2 STRUCTURE OF ATOM
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
Atom generally consists of protons, electrons and
neutrons. In my opinion a neutron represents the stable form of mass, the
local, but also in four-dimensional space-time the universally balanced
particle. By its disintegration it forms a proton and an electron and
antineutrino 10n →11p +0-1e
+00v. Therefore at the nature of the atoms its character does not depend on the number of
neutrons, which essentially mean the same balance state, but on the number of
protons as part of neutron with the maximum mobility density. Elements with the
same number of protons and neutrons are called isotopes of different nuclides.
4.2.2.1 QUANTUM MECHANICAL MODEL OF THE
ATOM
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
It is in relation with the fact, that by the endless
division of substance we get infinitely light particle virtually of zero
weight, it is waving (similar to the previously introduced concept of ether). Yet even this particle will
have the material nature, quantum
mechanics talks about wave–particle duality. At the same time this
primordial particle do not have the formation predestined by other smaller particles,
it is only affected by the mutual interactions with other particles, we can
talk about the principle of uncertainty.
Therefore the wave
function determines the probability of the occurrence of the particle, of the
electron at a particular point, we can talk about the density of probability.
On this basis we create orbitals, while it is true,
that the electrons more distant from the
nucleus have more different momentum.
Order of orbital determines the main quantum number n and hence the amount of energy, by the delivery
of energy we can get the electron into excited state of higher orbital.
The secondary
quantum number 1
indicates the angular momentum, thus the local mobility balance or imbalance in
the orbital, which is further balanced by other orbitals.
The magnetic
quantum number m
specifies the component of the angular momentum regarding the magnetic forces,
if the atom falls into the magnetic or electric field, in other words the
direction of the vector v, which specifies also the local mobility balance, or
imbalance.
Electron density shows according to the uncertainty principle a space
of probability. Electrons with the same n form the skin, with the same n and 1 form the subskin.
The state of a atom with the lowest energy level is
called the basic status, it is so,
because this is the most stable locally and universally (all) balance state.
The opposite situation would cause a chain chemical and physical reaction,
where the local overweight would attract more lighter and repulse the harder
substances or particles.
With the vector of speed v is related according to
my opinion the fourth quantum spin
magnetic number, in short spin, when it is a movement, that is opposite to
the movement of the first electron. This number may be only 1/2 and -1/2 and it
is related to the magnetic pole of the atom.
With a minimum of energy is related also the electron configuration of the atom,
where electrons are added, so that the resulting atom had the lowest energy
density.
4.2.3. MENDELEJEV PERIODIC LAW
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
Elements are sorted and determined by proton number (i.e. the number of protons
in the nucleus of an atom), which causes a major local mobility overweight of
atom nucleus. The higher is the atomic number, the more inbalanced nucleus of
the atom is in a table of elements.
The elements in one line-period are
similar in the imbalance of the nucleus. The elements are placed into 16
columns, groups and they are characterized
by the same number of valence (powerful, active) electrons, thus by similar
bonding characteristics. Because the valence
electrons have the most different momentum,
they have the largest share on the properties of the compounds.
By delivery of considerable energy the electron can
be separated from the element, it is
the ionization energy, ionization energy is equal to the negative value of the
orbital energy, at the same time is released the electron with the most
momentum, i.e. with the smallest negative relevant orbital energy.
Ionization energy increases with growing proton
number, when the density of the mobility of electrons decreases, but also of protons,
but at atoms, where in the valence layer there is low electron momentum because
of a small number of electrons in the valence layer, it may be lower again.
Electron
affinity
is the energy released during the formation of the anion from the
electroneutral atom in a gaseous state, i.e. the increase of local mobility
density of an atom causing movement in the direction of lesser mobility density
of the atom nucleus and release of the energy.
The rest mass of the electron 9,10938291x10-31
kg, i.e. 0,511 MeV *c− 2 (see http://physics.nist.gov/cgi-bin/cuu/Value?me|search_for=abbr_in! : The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), U.S. Department of Commerce, Reference on Constants, Units, and Uncertainty, Fundamental Physical Constants, electron mass), of the proton 1,672621777x10-27 kg, i.e. 938,256 MeV*c−
2 (see http://physics.nist.gov/cgi-bin/cuu/Value?mp|search_for=abbr_in! : The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), U.S. Department of Commerce, Reference on Constants, Units, and Uncertainty, Fundamental Physical Constants, proton mass) and of the neutron 1,674927351×10-27 kg, i.e. 939,550 MeV c 2.
The speed of light in a vacuum c=299792,458 km*s-1 (see http://www.example.com/wiki/Fyzikalni_konstanty
). Rest (apparently incorrectly resting properly should be the approximate
relativistic energy E=mc2, see my calculation below) energy m0c2,
where m0 is the mass of the relevant particle, c the speed of light
in a vacuum, and it is of proton 938,272046 MeV, of electron 0,510998928 MeV
and of neutron 939,565379 MeV. The proton is a subatomic particle with a
positive elementary electric charge i.e. 1,6*10-19 C, and the mass
of 938 MeV/c2 (1,6726231×10− 27 kg, therefore
the total mass of a proton is equivalent to approximately the total weight of
the 1836 of electrons). (see http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proton
) The speed of the electron with kinetic energy of 1 eV is approximately 593
km/s. The speed of a proton in the same kinetic energy is then just 13.8 km/s.
Electronvolt can be converted into derived unit of energy of SI system, joule,
according to the relation: 1 eV = 1,602176565*10-19 J. (see http://en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/electronvolt
) I.e. with the kinetic energy of 1 eV the electron has approximately (in
particular the influence of by me omitted value of so-called standard
uncertainty, referred to in the above mentioned values of the rest mass of the
particles in the parentheses, see e.g.. http://physics.nist.gov/cgi-bin/cuu/Value?me|search_for=abbr_in! (-The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), U.S. Department of Commerce, Reference on Constants, Units, and Uncertainty, Fundamental Physical Constants, electron mass) the rest mass of the electron,
the electron mass me 9,10938291 (40) x 10-31 kg, standard
uncertainty 0.00000040×10-31 kg) relativistic energy E=mc2,
relativistic mass m=m0/√ (1-v2/c2), and
E=0,51100199, i.e. in certain units and with this kinetic energy of 1 eV a
proton has relativistic energy about E=938,256 in the same units, if the size
of the proton is 10-15, and the size of the electron 10-18
(see Literature below) then the relativistic energy density of the
electron and of the proton, both with a kinetic energy of 1 eV, is the same
order of magnitude, because 938,256 (i.e. the approximate relativistic
energy of a proton)/1000 = 0,938256, which is approximately the same order of
decimal system 10-18 with relativistic energy density of the
electron 0,51100199 in the same units, neutrons have different relativistic
energy E, e.g.. according to the different temperature, differences can be in
the order of up to 1016 of specific units. (see
ojs.ujf.cas.cz/~wagner/prednasky/spektroskopie/neutrony/interakce.ppt : Interakce neutronu s hmotou, WÁGNER, Vladimír, 2005)
Literature:
Zoe posted: Mon, 10.
April, 2006, 9: 29 am post subject:
Michal wrote:
No, that I would want to
stand for such a model of the atom. But, if we will consider the proton as an
infinitely small object, we can have in the vicinity the curvature of
space-time, which we just want (even infinite). In addition Maxwell's equations
imply the existence of "electromagnetic
mass", and that is the larger, the smaller is the dimension of the charged
particle (even infinite for a point charge).
In the vicinity of the
proton (if it actually was a point object, which it is not), certainly yes. If
the speech was about electrons and those are circulating in a distance of 10-10
m from the nucleus. And it is quite a distance on a quantum level. There is
nothing easier than to take a calculator and to calculate the gravitational's
orbital for an electron in a hydrogen atom ".
Michal wrote:
So we say, that the proton does not bend a
spacetime, we must assume its size. How?
And how kvantovka (i.e.
probably quantum theory) resolves it? Can I calculate somehow the
"size"of for example electron? Or if I say it otherwise, can I
calculate the collision of two electrons into an arbitrarily close distance?
Of course, you can. The
diameter of a proton is something around 10-15 m, the average
electron diameter is 10-18 m. The fact is, that at the electron it is given more
by our current abilities to measure. It is similar with the electron as with
Jupiter. When you're sinking into deeper and deeper dense atmosphere of
Jupiter, also it will not be at all clear where to begin to count its surface.
The gas will only continuously grow thicker and with rapidly increasing pressure
it will gradually change into the liquid, which will become more and more
compressed. Only maybe near the very center you come to the solid phase. Solid
core may be however smaller than the planet Earth. Does that mean, that Jupiter
is in fact smaller than the Earth and the rest is made up by the atmosphere?
It's certainly not . Well, and it is similar with the electron. The firm
"ball" in the middle is probably the wire at size of the Planck
length. But all around still belong to an electron, and up to a distance of 10-18
m.
Vojta Hala posted: Wed,
12. April, 2006, 9: 57 pm post subject:
1) according to the
theory, which we describe the microcosm up today and it is called the standard
model, all elementary particles (electrons, quarks, etc.) are of point structure.
However the theory does not include gravity.
2) OTR (i.e. general
theory of relativity) is on small scales failing, in particular because of the
point characteristic of particles and
divergent curvature of the spacetime in their vicinity. Experimental
confirmation of OTR (basically it is Newton's law of gravity) on small scales
is today approximately in the order of millimetres according to my knowledge.
About the behavior on smaller scales there are no confirmed reports.
3) what Zoe poses as the diameter
of the particles is in fact an effective cross-section (or its root
multiplied), which is something significantly different. It's just a value
illustrating the sort of probability of collision with another particle. But it
is just, what Zoe wanted to tell by comparing to Jupiter. I'd not rather call
it the diameter.
4) The superstring theory
solves many of the problems, so that the particles (string) has a non-zero
size, and therefore it is not possible to bring two together infinitely close,
thus subplanck distance virtually does not exist. Crude, but effective. ;-)
(see http://www.aldebaran.cz/forum/viewtopic.php?t=515&sid=d32063acd2d5c2ad7eb153bfb06e1c47 : Spolek ALDEBARAN GROUP FOR ASTROPHYSICS (zkratka AGA), Praha)
Note: Giga (symbol: G) is
a prefix in the metric system SI denoting a factor of 109, i.e. it
indicates a billion, i.e. 1000000000 of the basic units. The prefix comes from
the Greek γίγας, meaning huge. (see http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Giga
). Mega (symbol M) is an SI prefix denoting 106. indicates a
million, i.e.. 1000000 SI of basic units. The prefix comes from the Greek
μέγας, meaning great. (see http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mega
)
Planck length is a physical constant. It is simultaneously also a unit of length equal
to approximately 1,.6×10-35 m. This is the basic unit in the Planck
units frequently used system of natural units. Planck length can be defined by
three fundamental physical constants: the speed of light, Planck's constant and
the gravitational constant. Current theory considers the Planck length for the
shortest achievable distance, by which we can learn anything. (see http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Planckova_d%C3%A9lka
)
4.2.4 MOLECULES
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
Molecules are groups of atoms. Molecules can be of same atoms, of different atoms or macromolecules. Further molecular ions exist, which represent local imbalance in momentum,
in other words a positive ion has greater mobility densityand negative ion has lower
mobility density, than neutral balance mobility density is.
During chemical reactions the formation of compounds
by chemical bonds occurs. And that's
the ion bond, where the
electromagnetic binding forces (local balance forces) operates between positive
(with larger) and negatively (with lesser) charged (mobility density) ions. Or
it can be covalent bond, based on
the sharing of electrons (most commonly their pairs) between the atoms. There
is the share of two electrons and the creation of the common part of the
electron packaging on the basis of similar electrostatic forces, when variably
occurs a greater and smaller momentum density, or positive and negative charge
of one atom and the other atom.
Bond dissociation
energy represents the momentum or movement,
which disrupts this bond by the impact to the bonding electrons.
Just as we can speak about atomic orbitals, there are molecular orbitals, where are similar
principles as at atoms. Concentration of electrons in covalent bond creates a new molecular bond orbital with reduced
movement or mobility, but it also creates a second molecular antibonding
orbital with an increased movement of electrons, the occupancy of this antibonding orbital would lead to an
increase in momentum, virtually energy and the breaking of molecule. The
formation of the second orbital is conditioned by the balance status of the atom, thus of protons and electrons. The
covalent bond can be formed by one, two or three electron pairs.
The force of a covalent bond is so determined by the
difference of momentum of electrons between the bonding and the antibonding
orbitals.
At the molecules
with one central atom the local balance forces are repelling common
orbitals with lower or higher electron mobility, which arise between the nuclei
of the merged molecules. In other words the structure of the neutral molecule
corresponds to the momentum field, where the nucleus with a high momentum repel
each other, between them there are the electrons, which balance the higher
momentum, further bond electron pairs, that have lower momentum and energy, are
compensated with the antibonding orbitals, where electrons should have higher
momentum or energy.
The bonds of the atom are governed by the so-called octet rule, or valence electrons in the
number 8 create a relatively stable atoms. At the same time these octets of valence
electrons are formed as relatively stable compounds. Using the local balance
forces it can be stated, that, if at the valence layer there are at least 4 electrons,
they have quite a large momentum, otherwise they transfer the electrons and
momentum is lower in relation to the above 4 valence electrons.
Another kind of bond is called coordinating bond, when the atom has two free valence electrons.
These substandard local momentum
density of electrons and their surrounding in atom (the electron is point quickly
moving particle and electron alone has supraaverage momentum density) are
balanced by attractive momentum forces of other atoms, which depends mainly on
their positive charge, or greater mobility density, than is the balance mobility
density of the neutral atom. This attraction is called electronegativity X=I+A,
where I is the ionization energy and A electron affinity.
At two molecules with different electronegativity
there is formed a dipole, where in
an atom with the greater mobility density, which attracts electrons, there is formed
a negative charge, and with lesser mobility density, that transfers electrons, there
is formed a positive charge.
Ionic bond is an extreme case of covalent bond, but it also
assumes the existence of two ions.
Among other so-called intermolecular forces the van
der Waals forces belong. Electrons are particles in motion, this movement can
lead to temporary dipoles, i.e. the imbalance in momentum, of which consequence
is attracting of molecules, among which operate from the same reason also the
repulsive forces and the result is a medium balance distance between molecules.
The energy of these random but regular van der Waals bonds is less than the energy
of covalent or ion bonds, but e.g. the so-called hydrogen bond conditions the permanence of the arrangement of
proteins and nucleic acids. As a result of these forces some molecular crystals
can be formed too.
4.2.5 CHEMICAL REACTIONS
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
At the certain moment there is a local balance mobility, which is disrupted
however by external influences, because it is neither an isolated nor the total
reaction system. And it leads to a
chemical reaction, which lies in the regrouping of the atoms and the
establishment of a new local mobility balance.
During chemical reactions as each for example physical kinetic motion of
particles the speed kinetic and force dynamic nature of the reaction occurs.
When splitting the bonds it can be the symmetric splitting, homolysis, when each element helds an
electron, or heterolysis, when ions are created. At the same time both
reactions of splitting the bonds can occur and the creation of new bonds at the
same time.
The reactions can be reduction/oxidation, at
oxidation the positive charge increases,
it is fundamentally a destructive reaction, at reduction a positive charge decreases, vice versa at
negative charge, virtually at oxidation number, it is fundamentally the
composition reaction, synthesis. At the same time it usually occurs at once the reduction and oxidation of substances
within the reaction.
Reaction
rate can be calculated as the derivation of a substance quantity to the derivation of
time, therefore the substance quantity of the substance in the time limiting to
0 and so by multiplied reversed value of stoichiometric coefficient of a given
substance.
Reaction speed is part of the momentum of the particles in the reaction, momentum
overlaps also with the temperature, which is a measure of the momentum (as I
showed in the Philosophy of Balance of physics), thus by increasing the
temperature the speed of reaction will increase.
According to the theory of the
activated complex approximation of molecules leads to disruption of the
balance and to working of the local balance forces. As a result some of the bonds
cease to exist due the lower momentum, the other ones are formed, it leads to a
chemical reaction. During catalysis the catalyst (in English approximately: grafter) increases the momentum of the substances in reaction, but alone it does not bind
and it does not form compounds due to its stability, apparently due to its
valence electrons. If there is the bond of the catalyst, this bond is interrupted as a result of
stronger bind of reacting substances and catalyst is excluded.
We distinguish between reversible
and irreversible reactions, and the spontaneous reaction, without energy
supply they are irreversible, because they are not caused by the movement from
the outside but by the permanent renewal of the overall balance.
The internal
energy of the system U is the total energy diminished by kinetic energy and potential energy in the
system as a whole. The heat supplied to the system at a constant volume is used
to increase its internal energy, or motion.
During
isobaric processes, when the pressure is constant (p=constant), the enthalpy is introduced H=U+pV, where p is the pressure and V volume
of the system. At the isobaric process then the heat delivered to the system is
used to increase its enthalpy, one could say of potential kinetic energy of the
particles, without changing the kinetic energy of particles, which would mean
an increase in their movement and also in their pressure.
Similarly it is at a constant temperature (isotermic process, where the temperature T=constant, iso means the
same). Another is the situation when the
isochoric process, where the volume V=constant, at volume unit Qm=∆U is valid, where Qm
is the molar heat, where the motion will increase and thus also the kinetic
energy, temperature and pressure at the unchanged volume.
Reaction heat ∆H (or
∆U) is the heat (energy) accepted, if the reaction is
isobaric, non-isochoric and if the temperature is the same. At the same
temperature so inevitably there must be a change in pressure or volume, so the
temperature could be maintained.
We divide reactions to exothermic,
if the system emits heat to the surroundings, endothermic, if the system absorbs heat and endorgenic, when Gibbs
energy increases. Gibbs energy change includes both the enthalpic member
(reaction heat ∆H has on the value of ∆G usually decisive
influence, with the temperature it does not change too much) and the entropic member
(it characterizes the change in the homogeneity of the system at a given
temperature-with increasing temperature its influence on the value ∆G
grows). G=H-TS, where T is the temperature and S is entropy, i.e. the homogeneity of the
system.
According to the first
thermochemical law the reaction heat of a certain reaction and reaction heat
of the same ongoing reaction under the same conditions in the opposite direction is up to its sign the
same. According to the second law of
thermodynamics the same reaction heat is necessary to transform the same
substances, either all at once or gradually.
Merge heat is the heat, that is released in reaction. In decomposition of a supraaverage mobility energy of a complex substance
to individual atoms with lower momentum, virtually energy there is usually the
release of energy and vice versa. (1/2) N2(g) + (3/2)H2(g)→2NH3,
∆H°298 =46 kj mol-1, C6H6(l)+(15/2)O2(g)→
6CO2(g)+3H2O(l), ∆H°298 =-3300 kj mol-1, for organic compounds, as in
the case of the last chemical reaction there is established and tabled so
called calorific heat, it is the
kind of reaction heat of oxidation reactions. It can be said, that more complex
compounds arise freely from the effect of heat, mostly solar heat, at decay the heat releases.
For the calculation of the reaction heat
is true, that it is the sum of the merge heats of reaction products disminished
by the sum of the merge heats of starting substances. The merge heat of compound
is reaction heat of reaction, where from the elements in the standard state one
single mol of this compound in standard condition is formed. The merge heats
are determined and tabled primarily for inorganic compounds. Reaction heat is also the sum of the combustion heats
of starting substances reduced by the sum of combustion heats of products of the reaction. The combustion heat is the reaction heat of a reaction, in which
one mol of this compound in standard state will oxidize into the most stable
oxides (final oxidation products in the standard state). Combustion heats are
established and tabled primarily for organic compounds.
Second law
of thermodynamics introduces the entropy, which
indicates the heat exchanged with the surroundings (the heat reservoir-bath)
and it examines its transformation on the work. Mathematical expression of the enthalpy ∑i Qi/Ti, where Qi, Ti
are heat and temperature exchanged by and own to bath. For a general circular process,
for irreversible process ∑i (Qi)ir (i.e.,
irreversible, i.e., non-reversible)/Ti< 0, for the return
process ∑i (Qi)rev (i.e. reversible, i.e.
reverse)/Ti = 0.
The change
of entropy at the reversible isotermic transition of the system from the state A to
the state (B) the relationship ∆S=SB-SA= Qrev/T describes, the entropy change is important at the adiabatic process, i.e. in the thermally insulated system, if the
transition is reversible, the entropy does not change, for irreversible
processes the entropy is increasing. As all the spontaneous processes are
non-reversible, the entropy grows in isolated adiabatic system so long, as the
system is not homogeneous. At the homogeneity of the system just a reversible
agencies may happen, the entropy of the system is maximal. Spontaneous agencies can be characterized not only by increasing
the entropy but also by the increase of the probability or by increase in the inorderliness.
For a description of the chemical reactions in the isobaric and isochoric processes we use in particular Gibbs
energy G=H-TS, thus energy of the system after deduction of the influence of
the received energy, virtually surrendered by the thermal exchange. When we
change the status of the system, there ∆G=H-T∆S-S∆T applies. We use the entropy
for the description of adiabatic systems. During the exothermic analytical (decomposition) reaction (∆H<0,
∆S>0) the spontaneous reaction occurs, the reduction of product momentum,
heat exchange and hence enthalpy increase. During the exothermic synthesis (composition) reaction (∆H<0,
∆S<0) reduce of the momentum and energy of the product occurs, at the
heat exchange there is the surrender of energy, at low temperatures the
reaction takes place spontaneously, with the growth of temperature the enthalpy
decreases and a tendency to spontaneous process decreases (∆G>O). In
the endothermic analytical
(decomposition) reaction (∆H>0, ∆S>0) the momentum,
virtually energy of product and also thermal exchange increase, at low temperatures
the reaction does not occur (∆G>0), at the increase of temperature the
value of the enthalpy increases and the positive value of ∆G is shrinking
and the reaction can take place spontaneously. During endothermic synthesis, i.e. composition reaction (∆H>0,
∆S< 0) energy, virtually the momentum of the product grows and the
thermal exchange decreases, these reactions are spontaneous, because both
members contribute to increasing the ∆G.
Chemical balance is the state of the system, in which its composition does not change, although there are still chemical
processes. The effects of these processes cancel each other, the established balance is dynamic balance. The balance is characterized by zero change of the
Gibbs energy. In some open systems (in particular, the chemical, physical and
biological ones) a steady state may
be established. It is such a state of the system, in which the maintaining of
harmonious composition of system is accompanied by a constant change of energy
(the system constantly receives energy from its surroundings, the change in
Gibbs energy is not zero). About dynamic balance we can consider from the
perspective of all the dimensions of Being, from the perspective of one
space-time it can be considered only about the steady state.
The ratio of the concentrations of reactants and products gives the equilibrium constant of the reaction.
This is a constant for all the same reactions, similarly the constant for pressures
of gases can be expressed. In heterogeneous systems, where not all of the components
are in the same state, or phase, there are only the partial pressures of the
gaseous substances or concentrations of the substances present in the solution.
Equilibrium system can be affected by changing in the concentration of the substances,
by changing the pressure, by changing the temperature, by catalyst, or by
changing the momentum of the system by the impact of other particles.
As well as the neutron can be divided into a proton and an electron, we can
dissociate all the neutral molecules. Acid
is a substance capable to surrender a proton to other substance, it is a proton
donor, virtually the cation or in other words it is a substance with a free
orbital, that it can fill out by the common sharing of the electron pair of the
other substance, acids are therefore acceptors (recipients) of the electron pairs. The alkali is then a substance capable
of accepting a proton from another substance, it is the acceptance of proton.
Or in other words it is a substance with a free electron pair, which it can
share with other substance, the alkalis are therefore donors of an electron pair.
During the proteolytic reaction the acid passes
its proton and it becomes an alkali, from the alkali by accepting a proton an acid
becomes, the acid and the alkali of the substance form conjugated couple or
proteolytic system. Electrolytic dissociation leads to formations of proteolytic
(mobility) equilibrium characterized by an equilibrium constant Kc.
In the same way an alkali can be electrolytically dissociated. The water is
also dissociatable but only in minor extent Kv=1*10-14,
this constant is important for the calculation of dissociated constituents of
other substances.
At the reaction of an aqueous
solution of acid with aqueous hydroxide (aniont of salt) the water is formed (eg.
reaction: H3O+(aq)+OH-(aq)→←2H2O
(l), i.e. the chemical reaction of an aqueous solution of acid with aqueous
hydroxide or alkali starts to join the vast majority of ions H3O+
and OH- to neutral water molecules), therefore these reactions were called the neutralization, the opposite process of this reaction
is the hydrolysis of salts. A byproduct of this neutralisation is a salt
solution (see example below), some of the salt ions (e.g. Cl-(aq),
Na+(aq), see the example below) can act (regardless of whether the
solution of salt was formed by neutralization or by solving the salts) in the given
solvent (water) as acids or alkalis. In reaction of
these ions of salts with water separate ions H3O+ and OH-
are formed, which cause, that the aqueous salt solution can be neutral, acidic
or alkaline. For example. HCl(aq)+NaOH(aq)→←H2O(l)+NaCl(l)
or ionic notation of this reaction: H3O+(aq)+Cl-(aq)+Na+(aq)+OH-(aq)→←2H2O(l)+Cl-(aq)+Na+(aq),
i.e. from aqueous solutions (aq) of hydrogen chloride and sodium hydroxide substances
(l) as water or sodium chloride (i.e. common salt) are formed, or for example
in the lab, hydrogen chloride is prepared by the reaction of sulfuric acid with
sodium chloride (common salt) NaCl+H2SO4→NaHSO4+HCl
. To produce sulfuric acid, which is used as a means of neutralization and as
a product of hydrolysis virtually in all industrial sectors, is used
catalyst vanadic carbon manufactured from ammonium metavanadate, which in principle is fundamentally manufactured
from amines, therefore of the organic compounds of nitrogen (N) of animal or
nonanimal origin (see http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oxid_vanadi%C4%8Dn%C3%BD , http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chlorovod%C3%ADk
, http://projektalfa.ic.cz/v_sirova_k.htm
)
Note: ENCYCLOPAEDIA Britannica 2011 ULTIMATE EDITION nebo http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/622801/vanadium-processing
.
Vanadium is extracted from carnotite as a coproduct with uranium by
leaching the ore concentrate for 24 hours with hot sulfuric acid and an oxidant
such as sodium chlorate. After removal of solids, the leachate is fed into a
solvent extraction circuit where the uranium is extracted in an organic solvent
consisting of 2.5-percent-amine–2.5-percent-isodecanol–95-percent-kerosene.
Vanadium remains in the raffinate, which is fed into a second solvent
extraction circuit. There vanadium in turn is extracted in the organic phase,
stripped with a 10 percent soda ash solution, and precipitated with ammonium
sulfate. The ammonium metavanadate precipitate is filtered, dried, and calcined
to V2O5.
In reaction of the salt with water (this proteolytic reaction
is called hydrolysis of salts) may occur the following cases, there is a cation (in
the case of solution of salts with strong acid cation), there is an anion (in
the case of the salt solution with strongly alkaline anion), neutral reaction
(in the case of salt solution with a strong acid cation or strong alkaline anion)
or it is not subject to hydrolysis (in the case of salts solution with a cation
or an anion, that do not react with water). Due to the neutral balance nature
of the water the dissociation can occur in all ways, it may cause splitting of
the anionic and the cationic bonds.
When reaching the local
mobility density in a solution its saturation occurs and other
substances already do not solve or the momentum of the ions is not affected.
By oxidation representing fundamentally
the destructive reaction, e.g. merging with the oxygen
in the combustion or respiration of living creatures (see http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oxidace
) we call a reaction, in which a reactant passes its electron, therefore it is reducing
its overall local momentum, however it is increasing its mobility density, reduction
is representing a
fundamentally destructive reaction, the opposite of oxidation,
in which a reactant accepts an electron, thus it is increasing its overall
local momentum but it reduces its mobility density. Oxidation and reduction
occur mostly in one reaction, and the resulting charge is
then the same or zero. An example of a oxid-redox reaction is electrolysis.
At secondary batteries it is reversible process, oxidized electrons reduce and
then they oxidize again.
Reactions in chemistry either
reduce mobility density of the reactant, then it is fundamentally synthesis
(composition) reaction often caused by the adoption of the electron through
reduction, that will reduce the energy density of the reactant at the increase
of its total energy, or momentum. The opposite are the analytical
(decomposition) reactions, when mobility density of reactant is increased
and consequently its instability and collisions and the force of the binds reduces,
often in terms of oxidation, submitting electrons, thereby increasing the pressure
on the disintegration of the reactant. The same objectives can be achieved in
the first case by lowering the energy density, virutally mobility e.g. by
cooling or by inhibitor (i.e. by the substance with low mobility) and in the
second case by warming or by the catalyst (i.e. by the substance with
substantially higher momentum), which will increase the energy of the reactant.
At the same time common are
the reactions, where at one the substance or the reactant increases energy or
mobility density and the reduction of the total energy or mobility density and for
the second vice versa. Syntetical
(composition) reactions represent the influence of the next dimension of other
mass and other energy to our dimension in the form of coagency. Decomposition
reactions are own to vacuum contraagency.
4.3.1 INTRODUCTORY DEFINITIONS
( performance)
It is the science about
inorganic substances. Inorganic substances are compounds of the chemical
elements with the exception of complex compounds based on carbon and hydrogen.
4.3.2 CHEMICAL ELEMENTS
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
The basic chemical element is hydrogen, which is in the
form of cation without neutron, thus so called hydrogen isotope is basically
the proton. The hydrogen atom is nuclide with one electron, the proton and
neutron and as such it is the basic building unit of all other elements.
For example the carbon 66C
could also be understood as 6H to reach the same proton and nuclide number. Necessary
then is the conversion of 6 cores of hydrogen into a single nucleus of carbon
through nuclear forces, which reach a considerable size. If we assume, that in
the past the Universe was formed by the Big Bang, thus by an enormous energy,
which was created by speeding up of nothing on our dimension of mass and energy
and the next dimension of other energy and other mass, we can imagine, where
this nuclear energy was taken from, which led to the formation of increasingly
complex and artificial elements of matter, virtually antimatter, or other
matter.
This theory responds also to
the nucleogenesis, when the elements in the Universe are formed by nuclear
reactions at high temperatures, 107 to 1010 K. For
example:
41H →4He
+ 2e+
By other nuclear reactions inside
stars other elements with higher proton numbers arise. Hydrogen prevails also
in the composition of the Universe next to helium.
4.3.3 INORGANIC COMPOUNDS
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
They are compounds of most of
the elements with the exception of the complex carbon compounds, which are explored
mainly in inorganic chemistry. Border area the organoc compounds represent,
they are artificial substances, for which a metal-carbon bond is characteristic,
it is necessary to differ them from the coordination compounds of organic
chemistry.
For inorganic compounds is
important an oxidation number, which
equals to the charge number of an element, which is the number of elementary
charges. Whereas, that local balance may be different, but universal (all)
mobility balance is a constant (which is e.g. the sum of the relativistic mass
of our dimension and relativistc other mass of the next dimension), so they are
the elements with supra average universal (all) momentum for positive and
negative charge, but due to the formation of electrons and protons from the
neutron forming local mobility balance, so a proton is the particle with supra
average local mobility density and an electron and its surroundings in atom is
a particle with sub average local mobility density. The elementary charge is
the smallest charge and it has a value of 1,602 * 10-19 C (Coulomb).
Oxidation number or charge is for
most of the elements and compounds 0,
this is so, because the local balance momentum forces make balance movement or
momentum m*v. Therefore the free
electroneutral atoms of the majority of compounds have oxidation number zero
(and even if they are composed of opposite ions). Some of the elements have the
same oxidation number in all compounds as H+ I, O-II, F-I
, the alkali metals have an oxidation number I (eg. Na+1), s2
elements have oxidation number II (eg. Ca+ II), up to some
exceptions.
Using oxidation number we form
the names of compounds, both of cations, as well as of acids and salts.
We distinguish the hydrides, which are ionic and covalent compounds of
hydrogen, there are also metal hydrides. Furthermore there are the oxides with
the oxidation number -II, halides with the oxidation number -I, sulphides
with the oxidation number -II. Furthermore there are hydroxides with the
formula M(OH)a, where a is 1 to 4 and it indicates a positive
oxidation number of metal M.
Without oxid acids are water solutions of some
2-elements compounds of hydrogen. The names of the other acids can be inferred
by the naming of the element, or by the number of hydrogen atoms. If an element
with the same oxidation number forms several oxoacids with different number of
hydrogen atoms in the molecule of acid, we distinguish them with prefix hydrogen- supplemented by a number of hydrogen atom, sometimes is used the prefix
ortho-.
Salts are derived by substitution of
hydrogen ions in acid molecules by ions of metals. Hydrogen salts have
in the name non-substituted hydrogen atoms with the prefix hydrogen- and
numeral prefix indicates their number. Double or triple salts have a name
composed of cations in order according to the increasing oxidation number, that
are separated by hyphens.Mixed salts have the anions listed in
alphabetical order by symbol of element and they are separated by hyphens.
In the nomenclature of crystal
solvents the number of molecules of solvent is characterized by numeral
prefixes (for 1/2 hemi, for 3/2 sesqui).
The nomenclature of coordination
compounds see below.
4.3.4 PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF SUBSTANCES
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
Substances with covalent bonds
(the essence of these bonds is
the sharing of electrons, most often of their pairs between the bound atoms)
have low boiling point due to the low
energy (momentum) of the bonds. While substances with ionic bonds (the
essence of these bonds are electrostatic forces acting between oppositely
charged ions) of atomic or metal type have
due to the higher energy of bonds a high boiling point and low melting point.
Electrically conductive are metals, semimetals are
charcterised with semiconductor conductivity due to the low bond energy
(momentum) of electrons. Compounds with the ionic structure lead
electric current in molten state and in aqueous solution for similar reasons.
Substances with ionic
structure or those, which may dissociate to ions, are soluble in water due to the large momentum
of ions of water.
Coloring of substances is related to the
momentum of the particles in the substances, that absorb the momentum of some photon of wavelength spectrum.
The elements are divided into groups
according to the number of valence electrons, which specifies some of their
properties such as melting point, boiling point, reactivity or stillness in
compounds. Elements such as hydrogen have one valence electron. Elements
marked as p-elements have two electrons within s valence orbital and in orbital
p one to six electrons, these are the elements of the six main groups of the
periodic system of elements (so-called Mendeleev's table of the chemical
elements) from the III.A group to the
group VIII.A (with the exception of
helium), it is always the last six elements in 2nd up to 6th period, p5
elements contain five valence electrons and they are especially
halogens. Atoms of oxygen, one of the p4elements are unstable
and they combine with other oxygen atoms to molecules O2 or with
atoms of the other elements to form compounds, thus they gain more stable
electron configuration, two unpaired electrons in the π*-orbitals explain
the paramagnetism of oxygen. Electron configuration of the valence electrons
is significantly reflected in the behaviour of the respective elements in the
magnetic field. Substances, of which atoms have all valence electrons paired
(e.g., calcium Ca, zinc Zn), are diamagnetic (magnetic field repels them).
A substance containing atoms with unpaired valence electrons (titanium Ti, cobalt Co, nickel Ni, copper Cu, etc.) are paramagnetic,
i.e.. they are involved in magnetic
field. A special subgroup of paramagnetic substances are ferromagnetic substances,
of which unpaired valence electrons have such an arrangement to increase the
external magnetic field. In addition after the disappearance of external
magnetic field the ferromagnetic substances themselves act magnetically on
other substances, that is why they are used as permanent magnets, these include
in particular the various alloys of iron (hence the name ferromagnetic). P2
elements of group of carbon C are elements of IV.A group, their
atoms have four electrons in the valence orbitals. Pure carbon occurs in two
shapes (allotropic) modifications, such as diamond and graphite. In the polymer
structure of the diamond the carbon atoms are bounnd mutually by four hard
covalent bonds, therefore a diamond is the hardest natural substance. In the layered
structure of graphite each of planes of carbon atoms are bound mutually only by
weak bonds, therefore graphite is soft and it conducts the electric current.
The elements of p3 group of nitrogen N contain in valence
orbitals 5 electrons, they are the elements of V.A. group, they can share 3 electron
pairs in 3 covalent bonds. The elements s are elements of I.A and II.A
group, their atoms have in valence orbital one or two electrons. Elements d
are the transition elements, they are placed in the table between s and p
elements, they are all metals, e.g. iron Fe (Ferrum), cobalt Co, nickel Ni,
copper Cu, gold Au, silver Ag, chromium Cr, many of the
transition elements and their compounds are catalysts of chemical and
biochemical reactions.
The number of valence
electronsit is important for the
reactivity of the elements, electrons in the outermost orbitale have
momentum, which is the least affected by the mobility of protons of an element.
If they form the electron octet (i.e. 8 valence electrons, such as rare
gases such as helium, etc. see http://leccos.com/index.php/articles/elektronovy-octet
), then they are stable due to its relatively largely balanced momentum, elements
with less than 4 electrons tend to due to their imbalanced momentum release their electrons and to react as
cations with other elements. Elements, that have more than 4 electrons, have
thanks to their largely balanced momentum the tendency to receive electrons and
they are more stable.
Transitive and also intransitive
metals form coordination (complex) compounds, for example water, H2O,
containing the central atom or ion, where by coordination (donor-acceptor)
bonds the ligands (from the Latin
ligare-to bind) are bound. The name of the ligand may be international, the
name of the anion ligand has the endings -o. Coordination compounds are
used as catalysts, apparently for their average local mobility density of bonds,
that prevents them to enter permanently into inbalanced compounds with other
elements.
Metal cations are from metal
ores obtained by reduction
reactions. For example in blast furnaces using the carbon.
Iron compounds as the cation are formed with
oxidation number (II) or (III), corrosion is the oxidation of the metal, which continues
and it does not stops in the iron at the top corrosion layer.
Elements of copper group such as copper (Cu), silver(Ag)
are elements of I.B group. Based on photochemical reaction on-going in the crystals of silver halides (mainly AgBr, silver
bromide) they react at irradiation by electron, which reduce the nearest silver
cation, around which the other atoms of Ag are gathering in the following
chemical reaction of developing film. Redundant AgBr is then removed from an
emulsion by solvent in the aqueous solution of Sodium Thiosulphate Na2
S2O3.
Elements f also called
internally transitive elements are placed in the 6th and 7th period. They also
include transuranium elements, which were prepared artificially in nuclear
reactions.
4.4.1 INTRODUCTORY DEFINITIONS
( performance)
Organic chemistry deals with organic compounds,
which are the compounds of carbon, which contain in particular oxygen,
nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, hydrogen and halogens, but they can also contain
other element. In all cases these are elements with a subaverage proton number,
they are complex compounds. From the simple elements, by which formation the
energy is consumed for their creation, often the solar energy in order to
increase momentum and thus the reactivity of these elements. The reason for the
low proton number is low absolute momentum of the elements, which are the basic
building element of the complex organic compounds with high absolute mobility.
High momentum is not reached by the weight of the elements but by their number.
The reason, why carbon is the
cornerstone of organic elements, is its low momentum, virtually proton number
associated with its four-binding, which allows to create complex, variable
organic compounds.
Organic compounds have due to
their low proton number of their elements, i.e. to lower absolute balance local
momentum of an element the low melting
and boiling point, theydo not conduct electric current, because the difference
of momentum of their elements is usually lower. They dissolve in organic
solvents, which stems from their non-ionic nature (small difference of momentum
of components), and only those, which contain hydrogen often ionic bonds, are
dissolved in the water.
Organic compounds occupy such a
spatial arrangement of the atoms, at which is their potential (kinetic) energy
as small as possible. This energy is the smaller, the less is number of
collisions of parts of the molecules, the more distant are the mobility fields of
elements of molecules, the smaller is therefore their non-bond interaction. With
this discipline the conformational analysis deals. The reason for the
distance of momentum fields of elements
is the average momentum local mobility density of a compound and the result is
the stability of compounds, low collisions of parts, thus also the reactivity
and the probability of breakage of molecules.
Compounds associated by simple
electron bonds (one electron pair) are called the saturated, by more
electrons of covalent bond are unsaturated. Double bonds separated by
one simple-bound are called conjugated double bonds. If there is between
doubles more single bonds, we call it isolated.
If electrons are shared
between atoms with the same electronegativity (i.e. the rate-relative variable
of extent of the ability of an atom to attract electrons shared with another
atom), the bond electrons are symmetrically between both and it is a non-polar
bond, otherwise it is the polar bond and electrons are closer to the
atom of the element with greater momentum density.
The π electrons in double
or triple bond are placed between a pair of atoms, of which bond they mediate. In the case of certain
cyclic chains of organic compounds there are delocalized electrons, of which electrons π do not belong to any atomic pairs, but
they are distributed throughout the chain.
Aromatic compounds are cyclic compounds with plane
cycle, in which single and double bonds are alternating, mutually convertible by
the shift of electrons π, of which is 4n+2 (n is 0 or a positive integer).
These molecules have less energy, than it would match their resonance
structures, since the collision of atoms is prevented through in cycle moving
electrons, while reducing their mobility density (this energy difference is
called the resonance delocalizing energy).
Hydrocarbons contain only carbon and
hydrogen, derivatives of hydrocarbons also another element. Derivatives
of hydrocarbons we derive by combining of hydrocarbon rest with the functional
group, which grant to the derivative its functional properties.
From the allocation of the
derivatives of hydrocarbons are interesting mainly hydroxyl derivatives with
a group-OH, primary amines -NH2, secondary amines -NH –, tertiary
amines -N--.
From the basic names are
interesting the basic compounds of methane CH4, ethan CH3CH3,
propane CH3CH2CH3, butane CH3 (CH2)2
CH3, CH3 (CH2)3 CH3
pentane, CH3 (CH2)4 CH3 hexane, CH3
(CH2)5 CH3 heptane, CH3 (CH2)6
CH3 octane, CH3 (CH2)7 CH3
nonane, CH3 (CH2)8 CH3 decane, from
which then are deduced their derivatives, they are acyclic, straight-chain,
saturated or cyciic hydrocarbons. From functional groups there are mainly prefix
hydroxy- or endings -ol:-OH and the prefix amino-or endings -amin:-NH2.
Subagencies
(performance)
4.4.2 OVERVIEW OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
4.4.2.1 ALKANES AND CYCLOALKANES
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
Alkanes and cycloalkanes are hydrocarbons containing
only single bonds C-H, C-C. These bonds are non-polar and the reaction of saturated hydrocarbons have therefore a radical nature. In other words they
are hydrocarbons with little difference in the momentum of the atoms. The
polarization of these compounds is possible by atoms with higher or lower
momentum as oxidation, chlorination, sulfochlorination and cracking (i.e.
essentially melting). The most famous representative is ethan CH3CH3.
For example the derivative of single
bond rest of alkanes is alkyl.
4.4.2.2 ALKENES
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
They are unsaturated hydrocarbons
having one double bond C=C . This double bond allows with exception of the
above radical reactions (hydrocarbon rest) the formation of hydrocarbons. The
most important is the ethylene CH2= CH2.
4.4.2.3 ALKADIENES
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
Alkadienes contain two double
bonds, if they are isolated, they behave as, if they are alkenes, if they are
conjugated (i.e. it means the dispersion
of electrons of two multiple bonds in the molecule of organic compound, thereby
it loses its unsaturation), then they interact mutually and addition on them
can be done in two different ways. Either the addition may occur on the
neighboring atoms or on distant carbon atoms of the chain, causing a shift of
the double bond into the middle of the chain.
4.4.2.4 ALKYNES
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
Alkynes are unsaturated
(i.e. with multiple bond) hydrocarbons with one triple bond, where may be
held radical or electrophilic addition. The best known is acetylene
CH≡CH.
4.4.2.5 ARENES
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
The arenes contain at least
one aromatic ring, they react radically and also electrophilic substitutions
of aromatic ring are typical for them. While the radical substitution is
made up at atom with approximately the same mobility density by the formation
of new orbital and by the sharing of electron, so the electrophilic addition
assumes the work of cations with the supra-average mobilitydensity and of anions
with sub-average mobility density while creating balanced compound. The most
famous representatives are benzene C6H6 and toluene
C6H5CH3. For example the derivative of single
bond rest of arenes is aryl.
4.4.2.6 HALOGEN DERIVATES
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
They are derivatives of
hydrocarbons containing one halogen group.
4.4.2.7 AMINES
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
In my opinion amines belong to
the most important organic compounds in terms of the functioning of the life on
the Earth. As I said above, there can be primary RNH2, secondary
RNHR and tertiary RNRR amines, which are derivatives of ammonia,
primarily composed of nitrogen. Thanks to the non-bond electron pair of nitro
groups these compounds have alkaline and nucleophilic nature.
With water they create hydroxides, with acids ammonium salts,
with alkyl they form more complicated hydrocarbon derivative. Tertiary amines
react with alkylhalides to create tetraalkylamonia salts, which convert under
the effect of silver oxide to tetraalkylamoniuhydroxides. By oxidation of
aromatic compounds of amines the compounds with a very complex structure are formed,
for example aniline C6H5NH2, which is a
poisonous yellowish liquid, it turns red on the air and it darkens, in the nature it is located in black-coal
tar, industrially it is produced by reduction of nitrobenzene, it is used in
the manufacture of dyes and pharmaceuticals. At present most inks are made of
aniline colors, arabic gum (formerly phenol was often used instead of it, but
due to its toxicity the adding to the ink was abandoned) and water. These inks
are not too light resistant and due to the possibility of their erasing are not
appropriate for documentary purposes, but thanks to the wide range of colour
shades they are very popular. Their big advantage compared to oak apples
(obtained when killing the insect larvae of Cynips quercusfolii, see http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dub%C4%9Bnky
) inks is the fact, that they are chemically stable and they do not destroy so
writing substances or tools. Also aniline colors are water soluble, therefore
there are no problems with settling colloids in ink tanks or plugging of
filling pens. (see http://is.muni.cz/th/64756/ff_m/Diplomka_PVH_posl_verze.pdf : K výrobě inkoustu a recepturámv
českých zemích do 16. století,
diplomová práce, Brno 2009,
Martina Andryková., http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anilin, http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anilin
)
4.4.2.8 HYDROXYCOMPOUNDS
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
They are derivatives of
water, in which one of the hydrogen atoms is replaced by the hydrocarbon
rest. A typical group is -OH. If this hydrocarbon rest is alkyl, then they are alcohols
ROH, if it is aryl, then they are phenols ArOH, phenol.
4.4.2.9 ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
They are derivatives,
where the -OH group is attached to the carbon atom, that is not part of an
aromatic ring. To their most famous representatives belongs methanol CH3OH
basically toxic residue in the production of ethanol, ethanol CH3CH2OH
commonly called alcohol, or ethyl alcohol, phenol C6H5OH
(obtained from coal tar and it is an important raw material for the production
of many aromatic compounds and plastics) and glycerol (formerly the
glycerin) HOCH2CHOHCH2OH used in cosmetics and also
for its sweet taste in food industry and in pharmacy, as ester with nitric
acid-glyceroltrinitrat e (also incorrectly called nitroglycerin) it is
the explosive used in the manufacture of dynamite and as a medicine for certain
heart diseases as a means for calming heart arrhythmias and blood pressure
reduction (http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nitroglycerin ) .
4.4.2.10 CARBONYL COMPOUNDS
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
They are derivatives with the group
>C=0. This group is polar, which allows the nucleophilic and electrophilic
addition. The most famous representative is formaldehyde or methanal
CH2O, which is used together with phenol at higher temperatures to
produce bakelite as very important kind of plastic (see http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bakelit
) and the solvent acetone or dimethylketone or propanone CH3COCH3.
4.4.2.10 CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
They are derivatives with a
group-COOH. Known representative is formic or methane acid HCOOH used
for the conservation of foodstuffs, ethane or acetic acid CH3COOH,
of which 5%-8% solution is vinegar, butyric or butane acid CH3(CH2)2COOH
contained in sweat and rancid butter, higher fatty acids: Palmitic
acid (e.g. in palm oil, milk products, meat) CH3(CH2)14COOH,
stearic acid (in fats) CH3(CH2)16COOH, oleic
acid (e.g. in the olive and grape oil) CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7COOH
are the acids the most frequently occurring in the form of esters with glycerol
in fats and vegetable oils, oxalic acid (COOH)2, which is
included in virtually all fruits and vegetables and it causes their acidity and
we can find it for example in strawberries, in larger quantities it is
contained in oxalis and sorrel and phthalic acid C6H4(COOH)2,
which is a raw material in the manufacture of plastics. A very important reaction is esterification of carboxylic acids by alcohols in order to form
ester and water, the opposite case is hydrolysis.
R-COOH(carboxylic acid)+R-OH(alcohol)→←R-COOR(ester)+H2O
Literature: http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kyselina_palmitov%C3%A1
, http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kyselina_stearov%C3%A1
, http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kyselina_olejov%C3%A1
, http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kyselina_%C5%A1%C5%A5avelov%C3%A1
,
4.4.2.11 FUNCTIONAL DERIVATIVES OF CARBOXYLIC
ACIDS
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
In them there is modified a
carboxylic group -COOH. The most famous are the amides and nitrides,
which are often mid-products of organic syntheses.
Esters are formed in the reaction of carboxylic acids with alcohols.
4.4.2.12 SUBSTITUTION DERIVATIVES OF CARBOXYLIC
ACIDS
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
Unlike in the functional
derivatives of carboxylic acids here their carbon chain is modified.
In them and among the most
important organic compounds for the formation of life on the Earth amino
acids are included. Amino acids contain alkaline group NH2 (see,
amines) and acid group -COOH (see carboxylic acids). In the isoelectric
point (Isoelectric point is such a
value of pH solution, in which the
molecule or ion, which may act either as an acid or as a alkali, i.e. amfion,
does not move in an electric field; this means, that its free charge is zero
here. Isoelectric point can be specified for each amfion, especially for amino
acids, peptides and proteins , see http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Izoelektrick%C3%BD_bod
, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amphoteric
, http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amf%C3%AD%C3%B3n
), i.e. in the local mobility balance, which is different for different amino
acids, there is an amino acid in an aqueous solution as an inner salt,
so the amino acid and carboxylic group are mutually fully neutralized. By
increasing the Ph the inner salt passes on cation, inversely on anion. Amino
acids, especially with the amino group on the carbon atom α are crucial
for the construction of the proteins and as compounda they are involved in
various metabolic processes.
Among them also belong and the
most famous among them are the lactic acid, tartaric acid and salicylic
acid, which is contained in larger quantities in the willow bark and in
artificial (synthetic) form there is the structural basis of many drugs, e.g.
as acetylsalicylic acid CH3COOC6H4COOH it
is the basic component of acylpyrin (see http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kyselina_salicylov%C3%A1
).
4.4.2.13 DERIVATIVES OF CARBONIC ACID
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
Free carbonic acid cannot be prepared,
yet its derivatives (esters, phosgene, urea) have practical
significance. The best known are phosgene, dichlorid carbonic acid,
which is a highly reactive gas, that is fast hydrolysating to carbon dioxide
and hydrogen chloride, in the first world war it was used as fighting chemical,with
ammonia it forms urea. Urea, diamid of
carbonic acid is produced from carbon dioxide and ammonia, which is used to
manufacture plastics, as an ingredient into cattle feed and fertilizer, it is
also a raw material for the manufacture of certain drugs, it is the waste product
of the metabolism of mammals and it is therefore in their urine.
4.4.3 REACTION MECHANISMS
4.4.3.1 ELECTRON SHIFTS IN MOLECULES
4.4.3.1.1 Inductive effect
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
It is the shift of σ
electrons. The source of the positive inductive effect is atoms or
groups repelling electrons or atoms bearing a negative charge, the source of
the negative inductive effect are atoms or groups attracting electrons
or atoms carrying a positive charge. Inductive effect manifests itself
primarily on the carbon atom, which is in close proximity to the source and
with increasing distance it is getting weak.
4.4.3.1.2 Mesomeric (conjugation) effect
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
It is the shift of π
electrons or of non-bond electron pairs. The positive mesomeric effect manifests
the atoms or groups, which give away their non-bonding electrons. The
negative mesomeric effect have atoms or groups, which attract these
electrons. By delocalization of electrons occurs the reduction of the
different motion of free electrons and hence the reduction of energy of
compound.
4.4.3.2 RADICAL SUBSTITUTIONS
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
They are characteristic for
compounds with non-polar covalent (i.e. based on the sharing of electrons,
most often of their pairs between bound atoms) bonds. Due to the effect of large amount of energy (movement, momentum) the
formation of a chlorine radical ·Cl occurs, i.e. a particle with
unpaired electron, which rips out thanks
to its momentum the molecule of hydrogen
and it produces methyl radical ·CH3 and hydrogen chloride,
methyl radical generates chloromethane again from a molecule of chlorine
Cl2 and the remaining chlorine radical, triggering a chain
reaction, that ends by joining two chlorine radicals and the formation of
chloromethanes from radical. While the non-bonding electron as well as the atom
has a very high momentum.
4.4.3.3 ELECTROPHILIC SUBSTITUTIONS
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
Electrophilic substitution is
a characteristic reaction of arenes. It is essentially an exchange, for
example in nitration of nitronic cation of inorganic substance for
hydrogen cation of organic compound at this organic substance. Similarly at the
arenes occur chlorination of Cl+, bromation Br+, sulphonation SO3 or +SO3H,
methylation +CH3 , etc.
4.4.3.4 NUCLEOPHILIC SUBSTITUTIONS
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
If the carbon atom is bound to
a group with a negative charge with lower mobility density, it may be replaced
by another group e.g. OH- with a negative charge.
4.4.3.5 ELIMINATION
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
By elimination occurs the off- cleaving of low molecular
substances such as water, alcohol or hydrohalogens and a positive charge is
compensated by a duplication of the bond between the carbons and by the
separation of hydrogen.
4.4.3.6 ELECTROPHILIC ADDITION
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
During this reaction the
reaction between π electrons and electrophilic agents occurs, where there
anion and cation and organic compounds form, in this way eg. halogens,
hydrohalogens or sulphuric acid are added. According to the Markovnikov's
rule the nucleophilic part of added molecule attaches to the carbon atom the
multiple bonds, which has fewer hydrogen atoms. Thus with the carbon atom with the
smallest absolute momentum due to the balance forces.
4.4.3.7 NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
Nucleophilic reagent (eg. water, alcohol, ammonia,
nitrogen and sulphur compounds) is added on the carbon atom with the C=O
double bond, which has as a result of the bond to oxid a positive charge,
which the added reagent obtains with a free electron, which balances the mobility
balance. After the elimination of water follows.
4.4.3.8 ESTERIFICATION AND HYDROLYSIS OF ESTERS
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
Furthermore there are
esterifications, by which we understand the reaction of acids with alcohols
usually in the presence of a small quantity of strong inorganic acid. The
first level is the protonation (proton bond, in essence H+) of
carboxylic acid followed by nucleophilic addition of the alcohol.
The reverse order is the hydrolysis of ester.
4.4.3.9 TRANSPOSITIONS
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
Transpositions are
the changes of a compound,
where the rearrangement of the substances in the compound occurs only. The
formation of the isomer occurs, i.e. of chemical compound with the same
molecular formula but different grouping of substances, i.e. also with the different
chemical and physical characteristics.
4.4.3.8 CONCLUSION OF REACTION MECHANISMS
Conclusion
(termination of subagency performance)
In general we can say, that
organic reactions, during which more complex organic compounds arise, in the context of the
formation of life on the Earth require energy, or motion, which changes the mobility
density of a compound in terms of its reactivity . If at the same time there is
not formed such simpler compound, which has a lower mobility density, the
consumption of energy occurs during this reaction, either spontaneously by solar energy or artificially with the help of a man.
4.4.4 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY IN THE MODERN SOCIETY
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
They are mainly natural recent
(current) substances such as wood, potatoes, animal tissues and fossil
(primeval) substances like natural gas, crude oil, coal. Further in
particular of them produced artificial products of man as synthetic polymers
(i.e. in particular plastics or artificial plastics. Plastics, which
soften by heat are called thermoplastics, their molecules form mutually disconnected chains. By contrast the thermosetting
polymerss, e.g. the above mentioned bakelite does not soften while heating,
but it decomposes, their chains are netted. The plastics are hard and
well to shape, easy to cut and they usually have good thermal insulation
properties, compared with metals they are not subject to corrosion, they are
almost permanent, but therefore the waste of plastic is non-ecological,
because it is only slowly decomposed in the wild), gasoline, synthetic
detergents. Drugs as anesthetics, hypnotics and tranquilizers,
antipsychotic medication and chemotherapy agents, antibiotics. Next pesticides
(from English word pest i.e. to exterminate
pests) as insecticides (insects control), herbicides (plant control), DDT, insect
hormones and pheromones. Pheromone (from Greek pherein–to transmit and
hormone- to stimulate) is according to commonly accepted definitions the
substance secreted by one individual and accepted by the second one of the same
type, thus this substance gives rise to a certain reaction. Pheromones are
chemicals produced by the body and spread for the purpose of innerspecies communication.
(see http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Feromon
) Primary explosives such as propellants, secondary explosives
such as glycerolnitrate. Fighting chemical substances as phosgene,
mustard gas, organic arsenic derivatives.
4.4.5 NATURAL SUBSTANCES
4.4.5.1 INTRODUCTORY DEFINITION
(performance)
I understand the natural
substances as chemical compounds or
their mixtures occurring in the nature.
4.4.5.2 LIPIDS
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
Lipids are derivatives of higher
fatty acids and aliphatic, alicyclic, hydroxy- and amino- compounds. They are
insoluble in water, i.e. with strong bonds, they are abundant store of energy, as well
as construction materials of cellular membranes.
Lipids generally on behalf of
the acylglycerols contain derivatives of amino acids or carboxyl group COOH.
Also they contain esters of glycerol and of fatty acids. Fatty acids are
aliphatic monocarboxylic acids obtained by hydrolysis of natural lipids. In
other words we can talk about a common basis of lipids and amino acids.
4.4.5.3 TERPENES
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
Terpenes are natural compounds
contained mostly in plants, they arise by combining five-carbons isoprene units.
They can be oxygen derivatives of alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, or of carbonyl
acids, to which amino acids belong too. Among the substances are vitamin A,
carotenoids, and natural rubber in raw form as latex of an emission of resin of
rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis), which is manufactured similarly as
synthetic rubber to natural rubber, the mixture of terpenes include also essential
oils of mint, camphor, lavender
or turpentine.
4.4.5.4 STEROIDS
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
They are either hydrocarbons
or their oxygen derivatives containing hydroxyl group -OH, so a part of the
carboxylic group. This is a physiologically and pharmacologically significant
substances. Probably the most famous steroids are cholesterol and D-vitamins.
These include for example anabolic steroids – supporting the growth of
bones and muscles, ergosterols - occurring in the mushrooms (Ergocalciferol
is one of the forms of vitamin D, also called vitamin D2. It is manufactured
from viosterol, which is formed in turn by the activation of ergosterol in
fungi by ultraviolet radiation), phytosterols – occurring in plants.
Also steroid hormones are
included, that are divided on sex hormones (male testosterone
and female progesterone affecting
sexual differentiation and reproduction) and corticoid hormones (in
mammals contained in the cortex of the adrenal gland and they control the
metabolism of sugars, economy of water and ions of potassium and sodium). (see http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Steroidy , http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ergokalciferol
)
4.4.5.5 ALCALOIDS
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
They contain in their
molecules at least one nitrogen atom, they are mostly poisonous. Tropin
alkaloids contain a ring of seven members, atropine, which is
contained in the extracts of Atropa belladonna, is used in ophthalmology
and internal medicine, Claviceps purpurea alkaloids are derived from the
lyserg acid and they are in the Sclerotium the product of fungi Claviceps
purpurea, which parasites the rye, it is used in medicine. Synthetically
prepared lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) has a strong hallucinogenic
effects. Opium alkaloids are extracted from the juice of unripened poppy
capsules of poppy seeds, in particular it contains morphine, from
poppy capsules a resin-juice, opium is extracted and out of it the drug heroin
is produced, morphine is used also as pain-reliever in medicine. Other
alkaloids are the nicotine from tobacco and caffeine contained in
coffee and tea. (see http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Morfin
, http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Opium )
4.4.5.6 CARBOHYDRATES OR SUGARS
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
In particular they are the
source of movement, the energy of living
organisms such as gasoline or diesel fuel for motor vehicles. Carbohydrates
have also industrial importance, they are natural raw materials for the
production of paper, textile fibres, ethanol, explosives http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sacharidy.
They form from carbon dioxide and water by effect of sunlight in the presence
of biocatalyst chlorophyll, the green dye in the leaves of green plants through
complex chemical processes referred to cumulatively as photosynthesis.
Carbohydrates are one of the fundamental natural substances in plant and animal
organisms. Other organisms are dependent on their income in food. In the short lack
of them they can synthesis them of amino
acids and glycerol. Simple carbohydrates, so called monosaccharides,
on each atom there is fundamentally one hydroxyl group -OH, and aldehydic
R,H>C=O at hydroxyaldehydes or ketonic group R,R>C=O at hydroxyketones,
monosaccharides are further divided according to the number of carbon atoms
into trioses (C3), tetroses (C4), pentoses (C5)
hexoses (C6), heptoses (C7). The most important are hexoses
representing for the organism direct energy source (glucose, fructose, galactose)
and pentoses, which are part of the nucleotides and nucleic acids, which
are all acyclic structures of monosaccharides with five carbon atoms. Cyclic
monosaccharides creates through connections with a hydroxyl group at the
far end of the molecule so called semiacetal hydroxyl, which is a new chiral
(i.e. the carbon atom with the highest sequence number) carbon center with a
hydroxyl group. By the effect of alcohols in acidic environment the monosaccharides
are changing to the glycosides, in which the hydrogen atom of semiacetal
hydroxyl is replaced by hydroxcarbon rest called aglycone CH3.
By glycosidic bond the oligo-, poly- saccharides are formed. On the cell
surface there are also aminosaccharides (glucosamine, neuraminic acid).
Nitrogen analogue of glycosides are N-Glycosides, in which the aglycone is
bound to anomeric (we distinguish α-anomers, D-monosaccharides
have in cyclical patterns the hydroxyl group -OH to C(1) pointing
downwards and β-anomers, D-monosaccharide have in cyclical
patterns the hydroxyl group -OH to C(1) pointing upwards) carbon atom
via the nitrogen. They are the nucleosides and in the form of phosphate
esters-nucleotides they are the building unit of nucleic acids.
Important Monosaccharides are:
- D-Ribosa and
2-deoxy-D-ribosa, which are the building blocks of nucleic (i.e. of cell
nucleus) acids and of biologically important nucleotides, e.g. ATP.
- D-glucose (normally called
just glucose), which is also known under the name of grape sugar,
for example in the fruits or meat, at mammals it is present in blood, in urine it
is in the case of illness (diabetes). Glucose residues are part of many
oligo-and poly- saccharides. By fermentation can be produced from glucose the ethanol
or ethyl alcohol, acetone and citric acid , etc. Aqueous solutions of glucose
in the form of an infusion are dripped to the ill directly into the blood. By reduction
of glucose is created a sugar alcohol called D-glucitol so called sorbate,
which is used by diabetics to sweetening and from which we can synthesize L
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C). By heating the glucose changes into brown
caramel used as a dye in the food industry. Technically the glucose is produced
by the hydrolysis of starch.
- D-Galactose, which is
contained in milk and it is part of the disaccharide lactose.
- D-Fructose, fruit sugar
is along with the above mentioned glucose a part of disaccharide sucrose,
from which also both of these monosaccharides are formed by hydrolysis, these
glucose and sucrose are in a ratio of 1: 1 the essence of honey.
Oligosaccharides are derived by combining the
two to ten of the same or different monosacharide units by glycosidic bonds.
According to the number of these units they are called di-, tri-, tetra- and
penta- up to decasaccharides. By acid hydrolysis the monosacarides are again
released of them.
The most important
oligosaccharides are the disaccharides:
- Maltose consisting of
two glucose units is obtained by the hydrolysis of starch.
- Lactose, milk sugar
consisting of the above galactose and glucose is present in the milk of
mammals.
- Sucrose, beet and cane
sugar, in their molecules above units of glucose and fructose are combined.
Sucrose is the most common sugar at all and it forms a significant component of
our diet. In mild temperate zone sucrose is obtained from sugar beet, in
tropical zone from sugar cane. By its hydrolysis by acids or enzymes
above glucose and fructose arise, this conversion of the sucrose in the mixture
of two monosaccharides is called inversion of sucrose and the reaction
product is invert sugar (the name has its origin in the word inversion,
i.e. literally upside-down, turn, twist, thus in this, that this mixture turns
due to the strongly negative rotation of the above mentioned fructose a plane
of polarized light to the left). Enzyme hydrolysis
of sucrose occurs in the digestive tract of the bees and its result is a
honey, sucrose hydrolysis can also be done artificially and the result
is a syrup similar to the honey.
Polysaccharides have a similar structure as
the oligosaccharides, except that the number of monosaccharide residues in
their molecules usually reaches many hundreds or thousands. They are mostly macromolecular
compounds. Unlike the above mentioned other sugars they dissolve in the
water only a little, or not at all. They are reserve or construction substances
of plant and animal organisms and some of them even have special biological
functions. Acidic and enzymatic hydrolysis of
polysaccharides form oligo- to monosaccharides. Polysaccharides, by which
hydrolysis it is formed exclusively above said glucose, are called D-glucans
and they have the general formula (C6H10O5)
n
The most important
polysaccharides are:
- Starch is one of the
most important D-glucans. In plants it is in the form of starch
grains in particular in the roots, berries and seeds. Industrial source of
starch are potatoes and cereals. Starch is an important component of the
diet of many animals. By starch degradation through acids or by heating at a
higher temperature the dextrins used for the production of adhesives
are formed.
- Glycogen is the stock
polysaccharide of mammals, in their liver in case of need D-glucose
is formed from it.
- Cellulose is a
polysaccharide, completely insoluble in water. It is also a D-glucan,
but its units of glucose are bound unlike as starch by other type of bond. It is the main building
material of higher plants. In nature it occurs in a very pure form of
cellulose, such as cotton, in wood it is accompanied by other
substances, mainly lignine and hemi (i.e. semi) celluloses. After their
removal from the wood the crude cellulose called wood pulp is produced,
which is used as a raw material for the paper and textile industry. By nitration
of cellulose the nitrates are gained, they are important explosives
and raw materials for the manufacture of cellophane and celluloid.
- Pectins are very
complex polysaccharides presented in particular in young tissues of higher
plants. They are obtained from the fruit peels and they serve for
the production of jams and marmalades. It is a vegetable jelly
(gel), which can partially replace animal jelly (gel), i.e. gelatin.
Note:
Gelatin is very clean and soft glue, which
is obtained long cooking of animal tendons, skin, bones and other
slaughter waste rich for collagen. Through cooking the collagen changes into
glutin, which is a substance, that has the ability to gel up and it is
the most important component of gelatin. Gelatin is used primarily in the food
industry for the manufacture of confections, cakes etc. Its industrial use is significant,
e.g. in the manufacture of photographic emulsions, for negative and positive
materials the gelatin is used as a material, in which the light receiving
elements and compounds are evenly dissolved. In the pharmacy it is used
as tablet binder and in particular for the manufacture of capsules. (see
http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/%C5%BDelatina
)
- Chitin is a
polysaccharide, that contains nitrogen and besides, that it is contained
in mushrooms, it is making up the skeleton of arthropods.
4.5.1 INTRODUCTORY DEFINITION
(performance)
Biochemistry is the discipline about chemical
compounds and their reactions in living organisms in relation to the
biostructures and its features.
In organisms 27 of 90 elements
occur, that are in the wild. All of
these are the elements from the upper half of the table of elements, i.e.
elements with less weight or absolute mobility. Yet relatively large organisms
with quite large absolute mobility are built of them. We can say, that these
organisms are built from small and accurate build stones, not from the heavy elements. Although some of
the elements are in a small quantity, they play an important role.
The basic ingredient is water,
water was formed due to the balanced momentum status, which was achieved at a
relatively low number of atoms with a slightly different charge and with low
atomic mass (or momentum). Water is a compound, that is characterized by a high
degree of balance mobilityand thermal capacity (i.e. richness of content).
The basic biogenic organic
compounds are carbohydrates, amino acids, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids. In my opinion amino acids
have an essential meaning, as their derivatives are included in all other
biogenic organic compounds. In other words the formation of the amino acids had
conditioned and spurred the creation of all other organic biogenic compounds.
Metabolism means all of the chemical
reactions, that are occurring in the body and are catalyzed by enzymes. When
splitting we are talking about catabolism, otherwise about anabolism
during synthesis
reactions. These are different reactions, which tend to be separated even
locally.
Subagencies (performance)
4.5.2 ENZYMES
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
Enzymes are proteins dedicated
to catalysis of chemical reactions in organisms, other enzymes contain
non-protein component cofactor (for example some metal ions or more
complex molecules, which we call the co-enzymes). In most cases, co-enzymes
can be easily separated from proteins, sometimes they are bound by a covalent
bond. Co-enzymes associate with vitamins. Complete functioning enzyme is
called holoenzyme. Holoenzyme consists of apoenzyme (protein) and
coenzyme.
The enzyme as well as another
catalyst is a substance with a supra-average mobilitydensity, which leads to
the speeding of reaction, but due to the higher mobility density of the enzyme
its bond is not permanent, it is realeased at the creation of the product.
The Ph environment affects the activity of the
enzyme, that occurs due to the acidity by the concentrations of the ions H+
further increase in the mobility density.
Similarly it is at a higher
temperature, when the momentum of the particles increases, at the point of
reaching the temperature optimum the upset of enzyme bonds occurs.
Similarly inhibitors and
activators increase or reduce the momentum of the enzymes.
Furthermore there are
so-called regulatory enzymes, on which in addition to the substrate also
modulators bind, that affect its activity. Regulatory enzymes may also
exist in two forms as the active and inactive, the conversion is catalyzed by enzymes.
4.5.3 ENERGETICS OF BIOCHEMICAL PROCESSES
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
Phototrophic organisms obtain energy from light, chemotrophic
by oxidation of macroenergetic substrates – of nutrients. Autotrophic
organisms use carbon dioxide as the sole source, while the heterotrophic
organisms require carbon in the form of complex compounds. Green (chlorophyll) cells of plants in
the light are a representative of
autotroph, while the animals, micro-organisms or plant cells in the dark are the representatives of heterotrophs.
4.5.3.1 PHOTOSYNTHESIS
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
Carbon dioxide is an energetically poor
compound, only organisms with the chlorophyll
(green dye) in cells can convert it into energy-rich compounds.
6CO2+12H2O
(light)→C6H12O6+6O2+6H2O
In the light phase of
photosynthesis is captured the energy of photons and used to create ATP adenosine
triphosphate and decomposition of water into oxygen and hydrogen. Another
product is a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) (see http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NADPH_oxidase
).
In the the dark phase there
are the products of
photosynthesis light phase ATP and NADPH
used for hydrogenation (reduction) of carbon dioxide into glucose C6H12O6.
4.5.3.2 ENERGY OF HETEROTROPHIC CELLS
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
Heterotrophs obtain the energy by required
oxidation of nutrients, carbohydrates, fats and proteins, i.e. transmitting of
electrons and reducing the mobility density or energy density of nutrients. The
energy released by fission is used for the synthesis of energy-rich molecules adenosine
triphosphate (ATP) and adenosine diphosphate (ADP). If the ATP production
is high, the cells multiply and grow.
The process of energy
transfer of nutrients to ATP, assuming that the cell has a sufficient
supply of oxygen, has three phases: in
the first phase the hydrogen from the substrates transfers to coenzyme of dehydrogenases,
NADH (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) and FADH (flavoprotein, reduced
flavin adenine dinucleotide) are formed in the reduced form and the
substrates are oxidized. The way, in which carbohydrates are oxidized anaerobically,
is called glycolysis. Fats are oxidized aerobically through so called β-oxidation.
In the second phase there
is the hydrogen of reducted coenzymes transmited on oxygen and water is formed.
This process is called aerobic respiration (breathing) chain. The
third phase of the formation of ATP is called oxidative (aerobic) phosphorylation.
During the transfer of hydrogen from reduced coenzymes up to oxygen the energy
is released and it is used to the phosphorylation of ADP (adenosine triphosphate)
into the ATP. The transfer of hydrogen from reduced coenzymes on elemental
oxygen is done in cascades by the team of bearers in respiratory (breathing) chain.
The components of this chain are arranged on the mitochondrial membranes of
cells according to increasing affinity to electrons (i.e. the energy released
in the formation of anion from the electroneutral atom in a gaseous state).
Literature: http://answers.yahoo.com/question/index?qid=20100422174148AAIXcpE: What are the full names of NAD, NADH, and FAD?
, http://wiki.answers.com/Q/What_is_FADH2
In other words by splitting the
hydrogen away is released energy or
momentum consumed by the formation of a bond within the compounds, this energy serves
then again to create the bond of energy-rich molecules of ATP.
4.5.4 METABOLISM OF CARBOHYDRATES
Definitions and relations
(performance)
The most important energy
supplier for the heterotrophic organisms is carbohydrates, both mono-, oligo- or
polysaccharides. By their oxidation up to carbon dioxide and water at the
aerobes the energy in the form of ATP is obtained. The complete oxidation of
glucose describes this equation:
C6H12O6+
6O2 → 6CO2+
6 H2O
This leads to the splitting
of sugar molecules in the formatin of ATP and ultimately also CO2
and water. It is a complex process consisting of many reactions. In aerobic
(i.e. capable of life only in the oxid environment) cells these reactions can
be divided into three stages. First in the so-called glykolysis the
six-carbon glucose changes into three-carbon pyruvate (The conjugated, i.e.
with dispersed electrons of two multiple bonds, alkali of pyrogrape acid known
as pyruvate. See http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kyselina_pyrohroznov%C3%A1 , http://www.wikiskripta.eu/index.php/Pyruv%C3%A1t
), which is in the second stage aerobically oxidized to acetylcoenzyme A,
and it is once again in the third stage oxidized up to carbon dioxide and water
in the so called citrate cycle.
Enzymes, that catalyze
reactions of glycolysis, are located in the cytoplasm of cells. Glycolysis
begins with phosphorylation of glucose molecules (polysaccharides break down into
the glucose first). If the cell has enough oxygen, pyruvate transits from the
cytoplasm to mitochondria and it is oxidized to acetylcoenzyme A. Citric cycle (Krebs cycle)
is the designation for a series of reactions, by which acetycoenzyme
(which is formed e.g. from glucose) transforms into carbon dioxide and water.
Enzymes, which catalyze the reactions of the citrate cycle, are located in the
mitochondria.
If the cell does not have
enough oxygen, the final acceptor of electrons the oxygen is missing and the splitting
of oxidation by electron submitting does not occur. The only way, how at a lack
of oxygen the ATP can be produced, is glycolysis, in which glucose
is anaerobically eliminated on pyruvate. Reconstruction of the oxidized NAD+
the reaction of lactic fermentation ensures,
in which glucose breaks down into lactate acid (milk acid):
CH3-COCOO
(pyruvate) +NADH+H+→CH3CHOHCOO-(lactate)
+NAD+, this method of oxidation is greatly ineffective.
Regulation of metabolism is due
to hormones,
hormones affect the process in the entire cell, even if they do not go directly
into it, e.g. by the activation or deactivation of enzymes.
4.5.5 METABOLISM OF LIPIDS
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
Lipids (from Greek lipos i.e. fatty,
see http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lipidy
) are indispensable for the life of the cells, because they are the basic
building units of the cell membranes, but they are also massive source of
energy. According to the function in the body lipids are divided into two groups. Stock
or depositary lipids accumulate
in fatty tissues, but they surround also some of the important organs. In
addition they have a protective function, whether it is a protection against impact,
or against cold. The second group consists of tissue or work lipids, that are building
components of cellular membranes
First carbohyderates break
down, then stock lipids using the enzyme called lipase, that breaks them down to
fatty acids and glycerol. Oxidation, thus removing of electrons increases
the local mobility density of substances, which in consequence break down and
release energy in a few cycles, oxidation takes place in the mitochondria.
4.5.6 SYNTHESIS OF FATTY ACIDS
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
A considerable supply of
energy occurs in the form of ATP, receiving of electrons by reduction, that
reduces the mobility density, but enhances the absolute momentum of the
reactants and so it starts receiving of energy, which allows the synthesis of
fatty acids. Synthesis and splitting of fatty acids are located at
different places in the cell –synthesis in the cytoplasm, fission, i.e. the
oxidation in the mitochondria. Emerging fatty acids are built into the
fats and oils (acetylglycerol)
and stored in the fatty tissues. Lipids are more concentrated, i.e.
denser form of energy storage compared with carbohydrates. (For example one
gram of fat oxidation releases energy of 38kJ from one gram of carbohydrates it
is 17kJ only) In addition lipids are stored almost without water, while
on 1 g of glycogen are bound almost 2 g of water.
4.5.7 RELATIONSHIP OF METABOLISM OF LIPIDS AND
CARBOHYDRATES
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
Lipids and carbohydrates are broken
down to acetylcoenzyme. This can be further metabolized by oxidation, thus by increasing
of the mobility density and splitting into carbon dioxide and water or the reduction
of the mobility density and the increase of overall momentum, virtually of
energy by reduction for the
formation of fatty acids.
Metabolism (substance exchange)
of lipids and carbohydrates are interrelated. Lipids and carbohydrates are broken down to acetylcoenzym
A, that is a key compound in the metabolism of these substances. The
resulting acetylcoenzym A can be further metabolized by several ways. In the
citrate cycle and respiratory chain it can be oxidized into carbon dioxide
and water, and that in a situation, when the cell needs energy. Acetylcoenzym
can also be used as a building unit for the synthesis of fatty acids. As
it can come from carbohydrates too, it means, that the organism may form lipids
from carbohydrates. This conversion takes place, when the body has enough
carbohydrates and energy. Animal organism changes carbohydrates to lipids, but
it cannot convert the lipids to carbohydrates, because its cells do not
have an enzyme catalyzing the conversion of acetylcoenzyme A to pyruvate – the starting
construction component of carbohydrates (see http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acetyl-CoA
).
A certain amount of fat in the
human body is necessary and beneficial. The effort of people with tendency to
obesity to reduce body weight by eliminating fat from food is not entirely
correct, because the organism starts then to miss some vitamins soluble in
natural fats and if the fats in the diet are replaced at the same time by
increased intake of saccharides, an individual can even increase their weight.
4.5.8 NUCLEIC ACIDS AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
Nucleic acids are either
adenine A, thymine (T), guanine (G), cytosine (C). They create a minimum of 20 multiple
compounds in proteins. They are contained in the DNA (Deoxyribonucleic
acid, see http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/DNA
), which is the bearer of genetic
information. In addition to DNA there is also RNA (Ribonucleic acid, see http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/RNA
), DNA is mainly in the nuclei of cells, RNA in the cytoplasm. Building
components of nucleic acids are nucleotides from the nitrogenous base, from
sugar and phosphoric acid. Nucleotides are mutually associated in the polynucleotide
chain. The molecule of DNA consists of 2 polynucleotide chains
twisted into a helix, there are formed pairs A-T, G-C. The molecules of RNA
are single fibred, the cell contains three types of RNA, ribosomal rRNA,
which is part of the ribosome, the information m (messenger) RNA, which
carries the information for protein synthesis, and transmission t (transfer)
RNA, which carries (transports) amino acids into the ribosome, where they
are compiled into polypeptide chains. In my opinion the ribosomal rRNA is
a residue of evolution, when the virus RNA transformed into a rRNA organelle
and their synthesis emerged, the role of the rRNA is not completely clarified,
obviously it is necessary to build a new ribosome (see Harper's Biochemistry,
Murray, R.K. et al., 23. Edition, 4. Czech, in H + H, third edition, 2002, p.
404). In the information mRNA there
are amino acids called codon, against which in the transmission tRNA the coupled amino acid-anticodon
emerges.
The basis of inheritance
are these three processes the replication-copying of DNA molecules in
the reproductive cycle, which happens in the cell nucleus of eukaryotes and in the
cytoplasm of prokaryotes (see DNA replication occurs in the cytoplasm of
prokaryotes and in the nucleus of eukaryotes, http://science.howstuffworks.com/environmental/life/cellular-microscopic/dna3.htm : How DNA Works, BY CRAIG FREUDENRICH, PH.D.
), the transcription, it is transcription of DNA into mRNA, by which the
information transmits from the nucleus of the cell (from DNA), where it is
stored, into the cytoplasm, and the translation, it is the process, in
which the information contained in the molecule mRNA "translates" into
the molecule of protein, it's the process of creating the proteins, which takes
place in the cytoplasm and in addition to the mRNA also ribosomes, activated
tRNA and many enzymes participate in it.
Protein synthesis occurs on
ribosomes, where
there is a couple of codon of informative mRNA, anticodon of transmission tRNA
at two amino acids of future proteins, after the creation of the couple the
transmission tRNA moves, until the whole molecule of protein is formed.
4.5.9 PROTEINS AND THEIR METABOLISM
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
A substantial part of cells
is made up of proteins, that have building and working functions. According
to the composition of the proteins they are divided into simple, consisting
of only amino acid residues and composite (conjugate) containing in the
molecule in addition also non-protein compound. According to the
functions proteins can be divided into enzymes, i.e. catalysts for
chemical reactions, storage proteins (e.g. ovalbumin in egg white),
transporter proteins (e.g. hemoglobin, red transport metalloprotein of red
blood cells of vertebrates and some other animals, which carry oxygen, see http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hemoglobin
), protective proteins (e.g. the substance-immunoglobulin is a protein,
that is capable as a part of the immune system to identify and neutralize
foreign objects (bacteria and viruses) in the body, anti-matters are bearers of
humoral, i.e. of the body juices immunity-defensiveness, see http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Imunoglobulin
), contractile (contract) proteins (e.g., myosin, which is involved in
the muscle contractions), hormones (e.g. insulin, which ensures the
combustion of sugars in the cells of the body), toxic (e.g. snake
poisons), structural proteins (e.g. collagen, which is a water insoluble
protein, which is the basic building material of connective tissues. It covers
up 25-30% of all proteins in the body of mammals. See http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kolagen
).
Amino acids are the building units of
proteins, in proteins there are commonly found 20 proteinogennic amino acids.
By the reaction of two amino acids the dipeptide is formed. Bond,
by which are connected the rests of amino acids, is called peptide bond.
By joining of the rests of three amino acids a tripeptide is formed, by
joining four residues there is tetrapeptide, by combining of many
molecules into the linear chain of amino acids a polypeptide is created.
Chains composed of more than a hundred amino-acid residues are usually
called proteins. Although in proteins only 20 different amino acids are
normally found, the number of possible
variations in the molecule is huge. The properties of each protein are determined
by the order of amino acids in the polypeptide chain-by primary structure.
The bonds of amino acids are
possible by peptide bonds. Peptide bond is a type of covalent chemical
bond containing a grouping of atoms –CO–NH–.
It is typical for example for proteins and polypeptides, in which the -CO-NH–
is created at the connection of the individual amino acids, but also for synthetic
polyamides. (see http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Peptidov%C3%A1_vazba
)
Polypeptide chains of proteins
have specific spatial arrangement-conformation, on which their biological
function depends. The shape of the molecules of the protein is relatively
stable. Fibrous (fibrilar) proteins have a simpler spatial construction,
their polypeptide chains are organized in one direction and they sometimes create
parallel bundles. Fibrilar protein molecules are mechanically very rigid and
very little soluble in water. Fibrilar proteins have in the organism mostly
structural (building) role (such as the proteins of the skin, hair, muscle
fibers). Globular proteins have a very complex structure, their
molecules have more or less compact (i.e.
solid, hard, dense, compressed), spherical shape and most of them is well
soluble in water. In the stabilization of the chain are involved hydrophobic
interactions, disulfide bridges, which are covalent bonds, and hydrogen
bridges and ionic interactions, which are ionic bonds.
In the structure of the
proteins there are found certain regularly arranged sections, also known as the
secondary structure. The arrangement of the entire polypeptide chain in
the area is also known as the tertiary structure. Some globular proteins
are composed of several polypeptide chains, we say, they are oligomeric.
Each chain we call the subunits. The mutual orientation of the subunits in
the molecule of the oligomemic protein is referred to as quaternary
structure. Between the oligomeric proteins for example hemoglobin belongs,
which consists of four subunits.
Native state is
the conformation of the
molecule in the body, denaturing of proteins indicates, that the chain
will be unrolled, because the bonds were interrupted. The denaturing of the
protein may or may not be reversible. Denaturing by heat or by a significant
change in pH is usually non-reversible. A pointer to the pH (in English "the
potential of hydrogen"), also hydrogen exponent is the number, by which we
express in chemistry, whether aqueous solution reacts in acid or alkalic (base)
way. (see http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/PH
) Denaturation by increase of salt content is reversible.
The metabolism of proteins means, that the proteins break
down constantly hydrolytically in the organism (proteolysis) and again they
are formed (proteosysntetis). Hydrolysis of protein from the food on
the components of amino acids (protein digesting) takes place in the
stomach and the small intestine. The hydrolysis is catalyzed by the enzymes
produced by the cells of the gastric wall (pepsin) and the pancreas (trypsin and chymotrypsin), these digestive enzymes (called the
endopeptidases) split proteins on a shorter peptides, total protein
molecules spliting up to amino acids the exopeptidases complete. The
above proteolytic enzymes are placed in cell organelles called the lysosomes.
The enzyme chymosin is present
in the gastric juices of a book and rumen of calves, goats and sheep in
lactation time, it is taken from the stomach of dead pups as rennet to
produce majority of cheeses. (see http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sy%C5%99idlo
)
Amino acids resulting from the
hydrolysis of proteins make up the supply, which a body can make use in several
ways:
-Directly to the body's own
protein synthesis.
-As a source of energy, when
in the citrate cycle there are released electrons, there is increasing
mobility density and the substance disintegrates to carbon dioxide and water.
In this case nitrogen of amino acids is secreted from the body. Some aquatic
animals secrete it, e.g. in the form of ammonia, higher terrestrial
organisms, for which the ammonia is toxic, convert it to urea (theria)
or to uric acid (prototheria). Plants store nitrogen in the form of
specific amino acids and nitrogen bases, e.g. alkaloids.
12 proteinogennics amino acids
a human can synthesize (the so-called nonessential, literally insignificant,
i.e. expendable amino acids), the other 8 must be supplied in the diet (the
so-called essential, i.e. indispensable amino acids.).
4.5.10 IMMUNE SYSTEM
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
There are two types of immune
response: humoral (related to the body juices) immune response-mediated
by soluble proteins-antimatters and cellular immune response-ensured by lymphocytes,
that recognize and destroy cells with foreign structures on the surface. Antimatters
(immunoglobulins) are proteins formed in response to the presence of
foreign substance so called the antigen or immunogen. (see http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Imunoglobulin
) All the immune substances are characterized by their great momentum and by collision
they destroy foreign substances. The proteins, polysaccharides and nucleic
acids act antigenicly. In the
structure of immunoglobulins there are certain patterns, their molecule is
made up of four protein chains, that are held together especially by the disulphide
S-S bonds. The base type of immunoglobulin is immunoglobulin G. In
blood serum there are yet other immunoglobulins. Blood serum is
yellowish, liquid, non-cellular component of the blood ( http://www.example.com,/wiki/S%C3%A9rum
). Immunology has contributed to understanding the essence of a number
of diseases and it enabled the new diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. The
antimatters are a specific search engine of pathogenic (infectious)
microorganisms, tissue damage or the cancer process. Cellular immune system
makes it difficult to adopt a foreign organ at transplantations. The
transplantations were possible only after the development of suppressing
substances partially reducing the immune response of the body. A certain
immunity the organisms must preserve however in order not to be powerless
against infection.
5.3 CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING
ORGANISMS
5.3.1 NON-CELLULAR LIVING
SYSTEMS (VIRUSES AND VIROIDS)
5.3.2 CELL LIVING SYSTEMS (ORGANISMS)
5.4 ESSENCE OF THE EVOLUTION OF
LIVING SYSTEMS
5.5 ESSENCE OF LIFE AND DEATH OR
THE EVILS OF LIVING SYSTEMS
(formation)
The object of biology as a whole (formation
subagencyof formation agency) is particularly internal and external movement
of biological macromolecules (mainly proteins and nucleic acids) or the study
of living systems. Individual disciplines of biology examine this movement
depending on the universality of this movement. As the external movement I
understand the movement of macromolecules as a whole, by internal movement then
the movement of their parts.
By its object the biology differs from the chemistry,
of which object is mainly the movement of electrons in a world of phenomena.
The movement of biological macromolecules is so more special term than the
movement in the context of chemistry. The subject of biology is not the
movement of electrons and nuclei particles, that the chemistry and physics explore, yet the structure of
atoms and molecules is the subject of biology to the extent, to which it specifies
the properties of a living system. Biology is so more special discipline than
chemistry, that is more special than physics and mathematics, which are more special
than the Philosophy of Balance.
Biology as more special science
in relation to the more general chemistry and even more general physics, mathematics
and the Philosophy of Balance is possible to inspect in terms of concepts
of these more general scientific disciplines. This possibility follows from
the nature of the world as an agency, thus a coherent and continuous whole.
This means, that complex concepts of chemistry, physics, mathematics, and Philosophy
of Balance (supraagencies) already include in itself the simpler concepts of
biology (subagencies), from which they are composed. The use of these set concepts
formed from the unification of the elements of the identical properties in the
conceptual (agency) analysis of sentences of biological sciences allows us to
inspect these concepts of biology (the elements of set concepts of chemistry,
physics, and Philosophy of Balance) in the new horizontal (in biology) and
vertical (in the context of chemistry, physics, and Philosophy of Balance)
relations.
Subagencies
(performance)
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
From the standpoint of biology
the concept of the next dimension has the essential meaning. If we use for
Einstein's relationship the basic assumption, that the speed of movement in
the next dimension exceeds by x the speed of light c, we come to the
following relativist relations in the next dimensional space. √[1-(c2+x)/c2)]=√(-x/c2)==i√
(x/ c2), for
x > 0, where i is a complex unit, which is the denominator of the
relativistic relations for time, length, and weight. Under that assumption then
the result of the quotient in our dimension for length and time is ∆t, l =∆t0, l0*i√(x/c2) and for next dimensional mass
m=m0/i√(x/c2). Therefore the non-complex time
and length ∆t0, l0 in our dimension is reflected as
a complex time and length ∆t, l in the next dimension and non-complex
mass m0 in our dimension as a complex mass m in the next dimension.
We get to concepts as other (i.e. different) time, other lenght and other mass
representing the different mass of the next and our dimension. The line between
the next and our dimension between matter and other matter of both dimensions is
the light, i.e. particles moving at the speed of light, and absolute vacuum.
In my opinion the speed of light is the intersection between the next
and our dimension, i.e. the maximum speed achievable in our dimension and
the minimum speed achievable in the next dimension. We come to the following relativist
relations for the light in our and next space. (l-c2/c2)=0, which is the denominator of the relativistic
relations for time, length, and weight. Assuming, that in the numerator of these
relations is ∆t,
1, m0, then the result of this
quotient is -∞≤m,∆t0,l0≥+∞,
as this quotient can be rewritten as (l/+-∞)/(1/+-∞)=x,
-∞≤x≥+∞.
It can be assumed, that in
the distant past the fluctuations between the balance in the next dimension
and our dimension, thus the prevailing of matter and energy and other matter
and other energy were far more extreme. Therefore prevailing of mass in the form of a balance of our
dimension in the form of neutrons and neutral atom substance in this
space-time, that evolved from the electron and the proton chaos according to
the equation 10n =11+0-1e
+00v, developed originally from the slowing of other
mass such as particles moving at a speed greater than the speed of light
onto the speed of light and finally by accelerating the absolute vacuum onto
our mass by light. This slowdown is called the Big Bang, which
caused the initial chaos of our dimension.
As the element with the
smallest mass is hydrogen H, it can be assumed, that hydrogen cation
10H+ as a proton or hydrogen as an element 11H prevailed in the
Universe at the first establishing of a balance at the formation of neutral
atomic substance of elements and by nuclear synthesis of this element in the
gradual deepening of the balance in our dimension, by the formation of neutral atomic
substance of elements the other elements were created at the huge
temperatures as a function of momentum m*v, where m is the mass and v is
a vector of speed corresponding to the action of the other matter, i.e.
particles moving faster than the speed of light.
It can be assumed, that the
Universe emerged in our dimension as the momentum fields characteristic of
different prevailing and average
mobility density m*v. Just as the Earth has set up as a mobility
field characteristic by interval of mobility density. In this momentum
field of the Earth as well as in other momentum fields are nuclear and chemical
reactions characterized by a constitution of heavier elements such as hydrogen
and compounds of these elements. The Philosophy of Balance of chemistry implies,
that each chemical reaction requires environment characterized by a specific
momentum or energy, in other words the mobility field, which enables the
merging of elements. The same applies to nuclear reactions and the
creation of the heavier elements than hydrogen.
Mobility field at synthetic,
composing chemical reaction in chemistry either reduces mobility densitiy of
reactant often caused by the accepting of electron by reduction, that reduces
the momentum of the proton in the nucleus, and thus also the energy density of
the reactant while enhancing its overall energy, or momentum. So this synthesis
reaction, which consumes energy, virtually requiring an increase of the total
momentum, will reduce mobility density of reactants, which causes an
incompatibility of the elements due to the speed of the movement in the next
dimension.
On the Earth as on a unique
momentum field at the prevailing momentum at the value of m*v there was
constitution of water enabled this compound by its own merged momentum. It can be said, that at
a similar value of the mobility density anywhere in the Universe in the
presence of oxygen and hydrogen there would be established the water as the
compound. From the perspective of Philosophy of Balance of physics it can be said,
that it is an internal and external momentum, thus momentum of the atoms or
molecules and all its particles, which are according to the Philosophy of
Balance zero-mass particles at the frequency of ∞.
Water represents the concentration
of hydrogen cations 10H+ and the anion of oxygen
O with a negative charge -II (oxidation number) as a simple (light in terms of
the atomic numbers) stable compound, i.e. the compound of balanced mobility density
of compound as well as of reactants. Also for this reason the water has such a
large thermal capacity (richness of content).
Of the elements arisen from
nuclear syntesis of hydrogen and protons and electrons in the Universe after
the Big Bang the organic substances are emerging in the momentum field of the Earth
thanks to its unique mobility density allowing next to the composite, synthetic
chemical reaction of water also these synthetic chemical reactions of these
organic substances, of which the largest impact the amino acids have, which are
the basis of proteins, nucleotides and their derivatives, lipids,
carbohydrates, and chlorophyll. Mobility field at the value of momentum m*v for
the formation of organic substances is mediated by temperature, pressure, the
presence of the necessary chemicals, etc.
Low molecular weight substance probably originated from
methane, nitrogen, carbon monoxide, ammonia and hydrocyanic acid. The molecules
of these compounds have been demonstrated spectrographically in the clouds of
interstellar gas. The source of energy for their synthesis was heat (from
volcanic activity), ultraviolet radiation (from the sun radiation), thunderbolts.
2CH4+ N2→2HCN+3H2,
CO+NH3→HCN+H2O, CH4+N2+H2O→HCN
(hydrogen cyanide) +R-COH
(aldehyde)
(see http://www.zachranny-kruh.cz/mimoradne_udalosti/amoniak_cpavek_nh3.html : Nejrozšířenější nebezpečné látky - Amoniak – čpavek – NH3, Asociace Záchranný kruh, z.s., Karlovy Vary
)
From aldehyde the imine
was created at exclusion of water, from imine in the presence of hydrocyanic
acid the aminonitrile was created and from aminonitrile in the presence
of water at exclusion of ammonia NH3 an amino acid was created.
From hydrocyanic acid, or aldehyde
the oligomers were formed, which led through condensation by the water
to the adenine and by hydrolysis to uracil. By polymerization of
formaldehyde the ribose was formed as another compound of ribonucleotides.
Prior-biological synthesis of
amino acids and the compounds of nucleic acids do not demonstrate onlyexperiments,
in which were reproduced the conditions on the Earth, but also the presence of
these substances in the meteorites.
At the same time with the
formation of amino acids, nucleotides and other simple organic compounds
were also formed substances with condensation properties, condensing
reagents. These substances have been a necessary condition for the
condensation of amino acids and nucleotide into polymer compounds such as proteins
and nucleic acids. During these condensations covalent bonds between amino acids were formed
at the exclusion of water for forming the
initial proteins (proteinoids) and between the nucleotides for creating initial
nucleic acids (RNA). Effective condensing reagents were polyphosphates,
carbodiimide and montmorillonite.
Furthermore the primary
synthesis of proteins (proteinoids) occured. Polymers, which are similar to
the polypeptides, are formed under conditions, in which the amino acids are heaed
t up and they are exposed to electric discharges or condensing reagents act on
them, for example polyphosphate esters. Such polypeptides are known as
proteinoids. They have a molecular weight of about 20,000, and contain about 18
different amino acids. They are sensitive to proteolytic enzymes and they are
also characterized by the properties, that are characteristic for proteins.
However as I have already said, they did not have a direct relevance to the
formation of life, since they did not indicate capability of replication.
The synthesis of primary nucleic
acids could take place in the
absence of enzymes. In laboratory experiments it was shown, that for
example in the presence of polyphosphate as a condensation reagent at 50 ° to
60 ° C oligonucleotide is formed. On polycytidylic acid as the matrix a chain
consisting of the GMP (guanosine monophosphate, see http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kyselina_chlorn%C3%A1 ) is completely created. The bonds between mononucleotides,
which bind to the matrix at the formation of complementary polynucleotide, are created with the
participation of condensing reagents.
The initial RNA did
not quite correspond to the present one, it is assumed, that the water reservoirs (bays, sea, ponds) were
concentrated solutions of low molecular weight organic compounds amino acids,
nucleotides, perhaps even proteinoids, but especially of the ribonuclease
acids.This water tank is referred to as the primeval broth.
It can be assumed, that RNA
with autocatalytic capability appeared too. The strong support for the
assumption of the existence of autocatalytic RNA is the finding, that from some
of the current organisms, for example from protozoa the intronic RNA has
been isolated, which is characterized by the ability itself as intron between
two exons to extract and ends of exons again by phosphodiester bond to connect
together in the absence of enzymes. It can
sort even on itself as a matrix nucleotides and estericly bind them by
replication.
The status of the primeval
broth, when there the concentration of autoreplicating RNA molecules prevailed,
is referred to as the realm of RNA.
At present the nucleic acid are
adenine, thymine, guanine or cytosine,. They create a minimum of 20 multiple compounds
in proteins. They are contained in the DNA, which is a carrier of
genetic information. In addition to the DNA also RNA exists, DNA is
mainly in the nuclei of cells, RNA in the cytoplasm. Building component of
nucleic acids is nucleotides from the nitrogenous bases, sugar, and phosphoric
acid. Nucleotides are mutually connected in the polynucleotide chain.
The molecule of DNA consists of 2 polynucleotide chains twisted into a helix,
there the pairs A-T, G-C are
created. The molecules of RNA are single fibered, the cell contains the
three types of RNA, ribosomal rRNA, which is part of the ribosome, the
information mRNA, which carries the information for protein synthesis, and transmission
tRNA, which transmits (transports) amino acids into ribosomes, where they
are compiled into polypeptide chains. In my opinion the ribosomal rRNA is a residue
of elvolution, when the virus RNA transformed into a rRNA organelle and their
synthesis occured. In the information mRNA there are amino acids codon, against which in the transmission tRNA
a coupled amino acid-anticodon
is created.
The basis for inheritance
in the present are three processes the replication-copying of DNA molecules in the reproductive cycle, the transcription,
transcription of DNA into mRNA and the translation, the translation from
the speech of bases of the amino acids, it is the process of making proteins.
The current translation is
done only in ribosomes. Of course in the form, as we know them today, in the
realm of the RNA they still did not exist. But there were the beginnings of
their existence. To understand this, let us consider, that in the prehistoric
(i.e. primeval) broth there were also ribonucleotides and amino acids. Here
without the presence of enzymes and by the influence of the condensing reagents
the formation of oligoribonucleotide the predecessors of today's tRNA (further we
use the term primordial tRNA) could be. The primordial tRNA bearing
different amino acids could couple with the replicating molecules of RNA and sort
on them these amino acids, which have been connected then with the use of condensing
reagents by peptide bonds into polypeptide chains. Among the large number of so
created polypeptides could eventually occur even proteins catalyzing the
synthesis of the peptide bonds between amino acids far more efficiently than
condensing reagents. They were probably the first ribosome proteins.
Another protein, that had to
create very soon, was the protein acting as an enzyme, that catalyzed the RNA
replication. This enzyme resembles by its function so called RNA-replicase, which is an enzyme, that
catalyzes the replication of RNA. Autoreplicating activity of RNA ceased to
have then in dependance on this enzyme its original meaning and it is preserved
as a relic in the some of the current introns (Intron is the area of
pre-mRNA, which forms together with exons the basis of gene, see http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intron ).
The initial translational
system therefore we can imagine as a
self-replicating RNA, which was in the system (complex) with the following
proteins: 1. Of initial RNA-replicase, which catalyzed the replication
of this RNA, 2. Of the first ribosome proteins, that catalyzed the
synthesis of the peptide bonds between amino acids. Part of this translational system
was however also its surroundings, that contains solution of amino acids and
ribonucleotides (in prehistoric broth). The complex of the RNA with the initial
RNA-replicase and primary ribosome proteins we can understood as the initial
ribosome. This very simple complex of RNA with proteins capable of
translation began to prevail in the realm of RNA, which gradually changed into the
realm of RNP. As the realm of RNP we understand the state of the
prehistoric broth, in which prevailed the concentration of RNA complexes with
proteins characterized by the translation, which allowed the existence and
reproduction of this complex.
However to enable to maintain and
to reproduce such a complex of RNA with proteins representing the initial
translational system , it had to meet two conditions: 1. To border against its
surroundings, 2. To enable, if possible, the exact translation of the sequence
(order) of RNA into the initial RNA-replicase and initial ribosome proteins. To meet the first condition was not so
difficult, because the initial translational system was in environments with a
high content of phospholipids. These could easily create around it
bimolecular double layer, which gradually formed complexes with proteins and it
changed to the current lipoprotein membrane. This assumption is
currently preferred.
To meet the second condition
is more difficult, because it already assumes the existence of genetic code.
How was the genetic code established and created, according to which certain codons correspond by
their anticodons to certain transfer RNA, is a mystery, on which there is
not yet a satisfactory logical answer. There is not also the answer, why was by
genetic code selected 20 L-amino acids, which are today considered as the
standard ones. The genetic code was created. We do not know when and how.
The initial translational system
was characterized by several features, that characterize the live system. They are: a) reproduction
(multiplication) of translational system by replication of its RNA, b) the
border of the phospholipid (or already lipoprotein?) layer against the
surroundings, c) Transfer of genetic information by RNA replication and by
translation of genetic code d) genetic variability, and hence the ability to
evolve.
Genetic variability
(volatility) of the RNA was however immerse (we see it in the current RNA-viruses).
It was therefore necessary to separate its own replication mechanism from the
translation. This was managed by reverse transcription of RNA into DNA already
in the initial translational system. This transcription was catalyzed by the
reverse transcriptase. Reverse transcriptase is probably one of the
oldest enzymes. It has been detected in prokaryotes and sequences for its
synthesis have been identified in a number of introns. Therefore we can assume,
that it appeared in the times, when the first live system were created. The
formation of DNA moved the living systems development significantly
forward.
This development led to the
so-called urcell, which has already developed in the simple form all the
basic features and functions of living organisms, and they are the simplest
living systems, which are also referred to as progenotes. Their important
character is, that the transmission of genetic information in their
reproduction (multiplication) was already arranged by DNA, so their genome was
made up of DNA. Therefore the realm of RNP has developed in the realm of DNA
characterized by the existence of urcells (progenotes). The development, which
led to the existence of the first living organisms (urcells, progenotes), is
referred to as chemical evolution, since it works purely chemically
through the synthesis of increasingly complex substances up to urcells. We
emphasize however, that no urcells were experimentally (by experiment) proved,
neither they were observed, but however in a number of places we can rely on
the facts (e.g. on the experiments , which imitated the conditions, that have been on
Earth 4 billion years ago, the volcanos, on the presence of organic
compounds in the meteorites etc.). We just guess, that prior to
current simplest cells even simpler ones had to be, which we identify with the
urcells. If they existed, then they started the biological evolution,
which is characterized by a formation of different types of living organisms
from the simplest to the structurally (building) and functionally (agency) more
complex.
The Earth formed about 4.6
billion years ago. In the period prior to 4.2 billion years ago it was an
inhospitable period for the formation of organic compounds. In the period before
3.6 billion years ago there was a prior-biological synthesis of organic
substances and information macromolecules and the formation of urcells
(progenotes), i.e. of the first living organisms. In the period before 3
billion years the formation of eubacteria, archaebacteria and eukaryotes
started, around the time of 2.5 billion years ago the development of the
oxygen phototrophs, i.e. cyanobacteria started. In the period prior to 1.2
billion years ago the creation of oxidized environment and development of
the ozone layer started, before about 1.2 billion years ago the formation of
eukaryotic cells occurred (endosymbiosis is a symbiosis (coexistence) of two
species of organisms, from which one lives inside the body of the other, see
http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endosymbi%C3%B3za ). In the period from 0.8
billion years ago there was the formation of multicellular organisms.
An example is an evolution
diagram from the present time, from the German physics von Weizsacker
(hereinafter referred to as diagram), his diagram contains this sequence:
unicellular → cyclostomata → reptiles → marsupials →
insectivora → monkeys → human (see http://granosalis.cz/ebooks/evolucniteorie.htm
, Evolutionary theory-science or religion, Ing. Josef Potoček, joseph.potocek@mmhk.cz , GRANO SALIS NETWORK, 2004, www.granosalis.cz
), these below used dates of geological periods (determined by geological
layers of certain rocks) do not match the modern geological time, that changes
frequently (see for example. http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/T%C5%99etihory
)
In the precambrian (according
to the diagram in the time since the
creation of the Earth to 520 million
years before the present, it includes Hadean, the following is Archean after
3.8 billion years before the present, when the life started, the following is Proterozoic
after 2.5 billion years before the
present, to the beginning of Cambrian, ice time, orogeny) the unicellulars were formed (among
them predominantly are ranked monera-bacteria, but they also include e.g. mold,
yeast, some algae and protozoa), from them then were formed algae, protozoa, the
simplest animals (metazoa) as the radiata or simplest bilateralia (which are a
large group of the evolutionarily most developed multicellular animals, that
includes vertebrates). From bilateralia it was the simplest protostomia
(protostomes), namely the worms, from them the annelids (ringed worms), and furthermore from
bilateralia the simplest deuterostomes (deuterostomia), from them then acorn
worms (enteropneusta, which are a class of deuterostome animals belonging to
the family of hemichordate, reaching the size of 20 cm to 2 metres, they are very
little explored animals living in the sea up to a depth of 3000 m).
In the Cambrian period (since
1960 the split is into Cambrian and Ordovician, according to the diagram in the
period after 520 million before the present, the oldest period of the Paleozoic
era, which lasted roughly 345 million years) originated the sea sponges and cnidaria from radiata,
from ringed worms formed molluscs and crayfish, from deuterostomes were created
cephalochordata and the simplest cyclostomata, from acorn worms were formed
echinoderms.In the late Silurian (according to the diagram in the time after
the 440 million years before the present) from the molluscs originated the
simplest ammonites (a kind of prehistoric mollusks, i.e. mollusks, i.e. extinct
cephalopod), from crayfish originated spiders and millipedes, from acorn worms,
cephalochordata and cyclostomata were then selachii, the simplest crossopterygia
(lungfish) and dipnoi (also known as salamanderfish). In Devon (according to
the diagram in the time after the 320 million years before the present, the
Caledonian orogeny) the first mainland plants (psilofyta-a group of extinct
ancient plants, that have not differentiated body into leaves, stem and roots,
see http://encyklopedie.vseved.cz/Psilophyta
) were created, from the centipedes (i.e. millipedes) was formed insect, from crossopferygia (coelacanth) were formed stegocephalia and from selachii were
formed paramblypterusu and amblypterusu.In the Carboniferous (according to
the diagram in the time after the 265 million years before the present) were formed equisetaceae
(sometimes horsetail) and lycopodiophyta, leptosporangiate ferns, from
stegocephalia were reptiles.In Permian (according to the diagram in the time
after the 210 million years before the present, the youngest period of the
Paleozoic era, ice time variskov orogeny) were formed coniferous trees. (In Devon and Carboniferous
according to the http://www.gvp.cz/~kuceraj/zemepis/vrasneni.html at the time of 409-290 million years before present the development of
amphibians initiated, in Permian at http://www.gvp.cz/~kuceraj/zemepis/vrasneni.html at the time of 290-245 million years before present the reptiles development
and amphibians decline occurred.)
Towards the end of
the Paleozoic era there was only one "mega-continent" called PANGAEA.
Pangea split then in 2 parts, on the northern part it was LAURASIE and
in the southern part there was GONDWANA. Between these continents there was
the Mediterranean Sea called TETHYS. To Laurasia its name the two large
territories gave, which lay in it: Laurentia (North America, for the first
time, including Florida) and Asia. Among them of course the territory of
today's Europe lays, firstly including the Iberian and Apennine peninsula,
however China and vast areas of Southeast Asia were missing. Furthermore at the
end of the Paleozoic era the sea receded and there was much more massive
termination of organisms than at the end of Cretaceous.
Paleozoic flora: Unlike flora,
which is known from the Proterozoic, era we know from the Paleozoic the vascular
plants. Typical is the presence of vessels and improved reproductive
organs, flowering plants have not developed yet. The oldest Paleozoic do not provide
many fossil material, of which we could make satisfactory conclusions. The
first period, which is more favorable for paleontologists is Devon. Between the
most primitive vascular plants of Devon we include ryniophyta with a very simple
body building. A typical representative was the plant Rhynia major,
which is considered to be the predecessor of today's vascular plants. Relative
genus was Psilophyton. From middle-bohemian Devon there are
supported ancient lycopodiophyta
Drepanophycus and Protolepidodendron,
it is considered to be the ancestor for the lycopodiophyta massively developed in Carboniferous. One of the most
abundant fossils of bohemish Devon is Protopteridium hostinense, it
belongs among the ancestors of ferns. From Carboniferous we know extensive
forests of vascular sporogenous plants (arborescent lycopodiophyta, Equisetaceae (sometimes
horsetail), leptosporangiate ferns). From these plants coal was formed. The late Carboniferous
is the period, when lycopodiophyta developed massively. For the extinct arborescent lycopodiophyta of carbon, we have a common name-Lepidodendrales.
The most famous genus is Lepidodendron (up to 30 m) and Sigillaria. The oldest horsetails
we know already from Devon, a major development occurred however in Carboniferous.
Carboniferous and Permian horsetail
is known especially as a
representative of the genus Calamites, these plants grew in
marshes. We know from carbon a very interesting group of seed ferns,
which represent the evolution link between the development of fern stubs and
gymnosperm plants, they looked like ferns, but the anatomy as Gymnosperms, the
examples are the genera Neuropteris, Alethopteris, and Odontopteris.
The next group of late Carboniferous trees are gymnosperms cordaitales growing up
to height of 10 m. In the upper Carboniferous coniferous wood appeared
for the first time. Vegetation in the Permian was very
similar to Mesozoic era. There was drying of swamps and many genera were
extinct (arborescent forms of lycopodiophyta),
a horsetail arborescent were still surviving.
In Triassic period (according
to the diagram in the time after the 185 million years before the present, the oldest period of the
Mesozoic era) originated
from reptiles big lizards and marsupials (in the Triassic period, from http://www.gvp.cz/~kuceraj/zemepis/vrasneni.html at the time of 245-208 million years before the present, originated the
first dinosaurs and mammals) from paramblypterusu and amblypterusu (fish) were
formed osteichthyes and teleostei
(fish). In Jura (according to the diagram in the time after the 155 million
years before the present) from the insects were butterflies and Hymenoptera
(e.g. ants, bees, wasps), from reptiles were created birds, from Stegocephalia
were salamanders and frogs. In Cretaceous (according to the diagram in the
time after 130 million years before the present, the youngest period of the
Mesozoic era) were formed
flowering plants (anglospermae) and also from the marsupials were formed the simplest
insectivora, of which at that time were formed carnivores, rodents, ungulata
and a monkeys (in the Cretaceous, from http://www.gvp.cz/~kuceraj/zemepis/vrasneni.html
at the time of 145-85 million years before the present, the development of dinosaurs).
In Mesozoic Gondwana lost its glaciations and it began
to break apart. The climate was more balanced than in Permian, overall however it
was warmer. Gondwana was a supercontinent, which included the territory of
today's South America, Africa, Arabia, India, Australia and Antarctica. It was formed
as part of a larger supercontinent Pannotia at about 600 million years
ago. To Laurasia China and the vast areas of Southeast Asia joined at
about 100 million years ago at the time, when it almost fell apart to Eurasia
and North America.
Mesozoic flora: In the earlier Mesozoic era were abundant 2 genera of
horsetails : Equisetites and Neocalamites, they were as tree
so herbal types. Unlike Mesozoic calamites they did not secondly put on weight and if so, so only very little. From ferns are abundant
representatives of family Matoniaceae and Dipteridaceae, today they survive
on a small territory in the Indomalaysian area. In Jura the representatives of
the gymnosperm plant- cycads embarked in the massive extent, flora of Jura
was relatively uneventful. Also Ginkgo species were largely
widespread. In the late
Cretaceous the breakage from the perspective of the evolution of the flora occurs,
the first flowering plants discovered, this is a very progressive
group of plants able to push away other species. The famous is Czech cenomanska
locality-Vyšehořovice by Český Brod. Fossils of Parasitic
fungi (Phacidum species and Cercospora species
) are also known. In Cretaceous gymnosperms were an important part of
flora, among them were: representatives of the family Taxodiaceae-a
genus of Sequoia and similar to it the genus Sequoiadendron.
From the time before the 90 million years ago we know first a pine (Pinus
longifolia) and fir tree, which are not substantially different
from those of today. From flowering plants (angiosperms) these plant
representatives were abundant: genus Araliphyllum.
Cenozoic is the youngest geological
era, it has begun about at 65.5 million years after the big
termination of animal and plant species at the end of Cretaceous (at the end of
the Mesozoic era), during which all the flightless dinosaurs died out, and it
lasts to this day, it includes Tertiary
and Quaternary Period, and it is referred to as the modern history of the
Earth. In Tertiary (according to the
diagram at the time after 60 million years before the present) warmer and
colder climates alternated, many mountain ranges were
formed: the Alps, the Pyrenees, the Carpathian Mountains and the Himalayas, here is the main extension in mammals and birds,
the first primates and the first predecessors of today's man-hominoid (see
below), in Tertiary the flowering plants predominated
and most plants coincided with today's (recent) flora. In Quaternary Period-Antropozoic
era (according to the diagram in the period after 1 million years before
present, ice age) today's man was formed
(see below).
In the time before 25-14
million years ago Dryopithecus evolved, more than 14 million years ago Ramapithecus
split from them, 4 million years ago discovered their two successors
Australopithecus and Homo habilis, from 4 to 1.5 million years the
African continent populated three different forms of Australopithecus: Australopithecus
africanus, Australopithecus robustus (also called Paranthropus robustus)
and Australopithecus boisei (referenced as Paranthropus boisei or
Zinjanthropus). They ate mainly plant food, especially Australopithecus africanus
living in the savannas did not reject possibly also small animals, that he or
she hunted and treated already using simple tools, such as broken animal bones
or jaws with sharp teeth. Brain of australopithecus was not even greater than of
any other ape. Homo habilis lived from 2.7 to 1.5 million years ago
(classification to the genus Homo-human is disputed), he or she was apparently
also a scavenger, he or she already made simple stone tools (that is why Homo
habilis, a skillful man) and his or her skull is surprisingly reminiscent
of a modern man's skull, volume of his or her brain was still significantly
smaller than of Homo sapiens but Homo habilis's brain was already well developed.
Homo erectus lived before 2 million up to 500 or 400 thousand years ago,
when the youngest member of the genus Homo erectus lived, so called Peking
Man (in today's China). The oldest representatives of Homo sapiens (Wise
Man, today's man) link directly to the forms of Homo erectus.
Literature: HARENBEG, B. et al.: Kronika
lidstva. Fortuna Print Praha, spol. s r.o., Praha, 2001, s. 9-12, velký anglicko-český slovník, Karel Hais a Břetislav
Hodek, first edition Acacdemia, nakladatelství ČSAV, 1984, 2nd edition
Acacdemia, nakladatelství ČSAV, 1991, http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/%C4%8Ctvrtohory ,
http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metazoa
, http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Protozoa
, main page , http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bilateralia
, http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Protostomia
, http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/%C5%BDaludovci
, http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kopinatci
, http://geologie.vsb.cz/paleontologie/paleontologie/zoopaleontologie/CHORDATA/Crossipterygii.htm : Podtřída Crossopterygii –
lalokoploutví, Vysoká škola
báňská, Ostrava
, http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blanok%C5%99%C3%ADdl%C3%AD
, http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_habilis
, http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Starohory
, http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/T%C5%99etihory
, http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kenozoikum
, http://www.gvp.cz/~kuceraj/zemepis/vrasneni.html : Geomorfologická modelace Země vnitřními silami,
Studentská práce v rámci
zeměpisného projektu 2003, Gymnázium Na
Vítězné plání, Praha 4 , http://www.gvp.cz/~kuceraj/zemepis/vrasneni.html : Geomorfologická modelace Země vnitřními silami,
Studentská práce v rámci
zeměpisného projektu 2003, Gymnázium Na
Vítězné plání, Praha 4, http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mikroorganismus
, http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geologick%C3%BD_%C4%8Das
, http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Archaikum
, http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/K%C5%99%C3%ADda
, http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gondwana
, http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Laurasie
, http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hadaikum
, http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ordovik
Walking with Cavemen with
Robert Winston, 2DVD-116minut, production of
the series Mike Salisbury, Director and Executive Producer Richard Dale,
co-production of BBC/Discovery Channel 2002, published by Mladá Fronta Dnes, (DVD I: 1st-2nd Part food for human ancestors until Homo ergaster,
2nd part time 24:59 et seq. Homo habilis as a scavenger after the discovery of
production of stone (probably flint) tools, Part 2 time 28:01 et seq. the first
Homo ergaster 2 million years ago, DVD
II: Part 3 time 1:39 et seq. wildebeest hunting by Homo ergaster, 3rd part
time 24:01 et seq. stopping the evolution of Homo ergaster until a million
years ago.
Note:
As a molecular fossil of ribosomal
rRNA I personally consider RNA-viruses or viroids without protein
packaging, which are organisms, for which there is no transcription of DNA, but
only replication of RNA and translation of RNA molecules into proteins of virus
packaging. However fundamentally these transfers may take place only in the
cells never outside. It can be assumed, that in the prehistoric broth occurred the
formation of a large number of these simplest non-cellular organisms with a
very short lifetime outside the cell. So occurred a very quick birth and death
of RNA viruses, which newly mutate by adaptive natural selection in the spirit
of modern evolutionary theory and it occurs the genetic developments thanks to
speciation.
Also we are talking about the
origin of mitochondria and chloroplasts, which are considered to be originally
the eubacterial cells, that have penetrated into the eukaryotic cells and lived
in symbiosis with them. This symbiosis laid in an effective oxidation of
organic substances and the relaxed energy for the cells they used to their
life. Similar is probably the origin of chloroplasts, which were
originally photosynthesis eubacteria cells (cyanobacteria), that could carry
out photosynthesis in the eubacteria cells, with which they lived in symbiosis.
Similarly as in the case of
RNA viruses it could lead according to me to the formation, penetration and symbiosis of DNA viruses mutually
with RNA viruses capable of transcription in the prehistoric broth.
A division of these viruses into prokaryotic nucleus (nucleotide), ribosomes
(in which replication occurs), cytoplasmic membrane and cell wall could give a
rise to a prokaryotic cell.
5.3 CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING
ORGANISMS
5.3.1 NON-CELLULAR LIVING SYSTEMS (VIRUSES AND
VIROIDS)
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
Non-cellular living systems can multiply only in the
cells. These may be the prokaryotic cells or plant or animal ones. They are
divided into viruses and viroids.
Viruses can be broadly
categorized as follows:
1. They are particles
composed of nucleic acids and proteins. Nucleic acid has the same function
as chromosome and it can therefore be considered as chromosome of virus, it is
a bearer of genes of the virus, according to which the proteins are made up, of
which is composed the package of the virus.
2. Nucleic acid of virus
may be deoxyribonucleic or ribonucleic. Therefore according to the contents of
nucleic acids the viruses are DNA viruses and RNA-viruses. At DNA-viruses
the genetic information (genes) of greatly replicated DNA is transcribed into
mRNA, which is translated on ribosomes of host cell into proteins, by which is
then wraped up all copies of nucleic acid of virus, so it creates a complete
viral particles or virion, which are released into the environment, where they
can infect other cells. At RNA-viruses the transcription does not occur,
but only the replication of RNA and translation of RNA molecules to proteins of
viral packaging (i.e. capsid). DNA viruses are thus characterized by the DNA
replication, transcription and translation, whereas RNA-viruses only by RNA
replication and by its translation. However these methods of transmission of
genetic information may take place only in the cells, never outside.
3. Viruses have very tiny
dimensions. They are visible only with help of the electron microscope.
4. Outside the cell the viruses
are not capable of life. Only when they enter the cell, they apply their
main life function, that they have, and it is a reproduction.
Three different types of viruses:
in the left part the virus is infecting bacteria or a Bacteriophage, in the
top right section there is a cross-section of the non-covered virus with
icosahedral symmetry, right below there is the cross-section with the HIV
retrovirus, at which a viral particle is still wrapped by membrane with
surface glycoproteins. Genomic nucleic acid is always shown in blue (see
http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vir ,
the Original uploader was Xmort at cs wikipedia , 26.12.2004).
Viroids differ from the viruses mainly
by their nucleic acid RNA, which is not wrapped by proteins, they are particles
composed only of RNA capable to replicate only in their host cells.
![]() Structure du secondaire supposee PSTVd viroďde
(potato spindle tuber viroid), see http://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Viro%C3%AFde
, Putative secondary structure of the PSTV (potato spindle tuber viroid).
Author: Jakub Friedl (user kyknos) {{GFDL}}, 11.4.2005.
Structure du secondaire supposee PSTVd viroďde
(potato spindle tuber viroid), see http://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Viro%C3%AFde
, Putative secondary structure of the PSTV (potato spindle tuber viroid).
Author: Jakub Friedl (user kyknos) {{GFDL}}, 11.4.2005.
5.3.2 CELL LIVING SYSTEMS (ORGANISMS)
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
Cell living system
(organisms), i.e.
the living system composed of cells, are, as far as the basic structure of cells
is concerned, of procaryotic and eucaryotic type.
Organisms of procaryotic-type
or Monera (apparently literally
forebodies or urbodies) are generally characterized by the following
characteristics and features:
1. They are mostly
single-celled organisms, they do not constitute functionally and
morphologically differentiated tissues. Except to the cytoplasm, which fills completely
the space of a prokaryotic cell, they have four ever present structures: prokaryotic
nucleus (nucleoid), cytoplasmic membrane, ribosomes, and usually also the cell
wall.
2. The nucleus of
prokaryotic cells is not separated from the cytoplasm by membrane. It is
stored in the cytoplasm and it consists only of one large molecule of
deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), which fulfils in the prokaryotic cell the function
of a chromosome and it is double chained and circular (has no loose ends).
3. Dividing of prokaryotic
cells nucleus includes only replication of DNA, never mitosis.
4. Up to a few exceptions
all prokaryotic cells are wrapped up with a rigid membrane, so called cell wall.
The chemical composition of the cell wall of prokaryotic cells is however
different than the cell walls of plant cells. The main component of the cell
wall of prokaryotes is peptidoglycan (murein) or atypical peptidoglycan
(pseudomurein). Since the cell wall of prokaryotes is solid, Monera cells can
maintain their shapes.
5. Prokaryotic cells reproduce by transverse
dividing. First their circle chromosome, i.e. DNA divides and then
the cell splits gradually into two daughter cells. Both cells grow up and they divide
transversely again.
6. Prokaryotic cells do not contain
organelles such as mitochondria and chloroplasts of eukaryotic cells, but as
well as eukaryotic cells they contain ribosomes in the cytoplasm, which are
used to synthesize proteins. Protein synthesis in ribosomes is controlled
by genes, which are stored in the circle chromosome (DNA) of prokaryotic cell. At
prokaryotes there are all ways of transfer of genetic information, i.e. replication
of a circle chromosome, its transcription into mRNA, whose information is overwritten
from the circle chromosome and it is translated into the primary structure of
the proteins.
7. Nutrition of procaryotes
is varied. Some are fed autotrophicly, others heterotrophicly. Basic
nutrient of autotrophic prokaryotes is carbon dioxide (CO2). On the
other side heterotrophic prokaryotes gain carbon from a variety of organic
substances, such as carbohydrates, proteins, salts of organic acids, alcohols,
etc.
8. All organisms of
procaryotic cell type are referred to as bacteria according to
"Bergey´s Manual of
Determinative Bacteriology" from 1994. On the basis of evolutionary lines expressed in universal
phylogenetic tree they are divided into two realms:
I. Eubacteria. The main
chemical constituent of the cell wall of all eubacteria is peptidoglycan (murein),
containing muramic acid as one of its main components. By the influence of
peptidoglycan the surface of the eubacterial cells is hard, for all eubacteria
it is typical the translation, during which on ribosomes the amino acid
formylmethionine is sorted into the
primary structure of polypeptide chain. For example cyanobacteria, green nonsulfur bacteria, purple bacteria,
flavobacteria, gram-positive bacteria, from eubakteria developed
mitochondria and chloroplasts.
II. Archaebacteria.
Procaryotic cell wall is made up either of pseudomurein, which is an atypical
peptidoglycan not containing muramic acid, or it is made up of proteins, some
archaebacteria even do not have a cell wall. Their other hallmark is that during
translation, that occurs on their ribosomes, as the first one into the polypeptide
chain the amino acid metionin is sorted.
Both of the realms diverged
from a common hypothetical ancestor (urcell, progenota) into two different
evolutionary lines (branches), the first branch is eubacteria, and the second
branch is archaebacteria and on them in this second branch following eukaryotes.
The cross section through a prokaryotic
cell (see http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prokaryotick%C3%A1_bu%C5%88ka
, English: diagram of
prokaryotic cells, Mariana Ruiz Villarreal LadyofHats,
translated by Michael Maňas (User: Snek01), Mar 2, 2008,
30.3.2008, translated) from the top capsule, cell wall, a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, , ribosomes, plasmid, pili,
bacterial flagellum, a nucleotide (a circular DNA)
Organisms of eukaryotic type
or the eukaryotes (literally apparently a good
body) are single-celled as well as multi-cellular (e.g. gradually entamoebas, mycetozoa, ciliates, fungi, and
plants and animals). Their cells are referred to as eukaryotic and they are
characterized by these characters and properties:
1. They include a nucleus,
that is distinctly separated from the cytoplasm by nuclear membrane. Mass, by
which is composed a nucleus of eukaryotic cells, is called chromatin. It
consists of DNA and proteins. During mitosis the chromatin condenses in
microscopically visible threads-chromosomes.
Unlike prokaryotic cells each chromosome of eukaryotic cells is composed of protein and a
long double chain thread of DNA, of which both ends are free and they are
therefore not linked to the circle, as it is in the case of prokaryotes.
Therefore DNA, which is located in the chromosomes of eukaryotic cells,
is not circular but linear.
2. Dividing of a nucleus of
eukaryotic cells is miotic. By this division the accurate distribution of
chromosomes among daughter cells is ensured. Mitosis (mitotic division)
is a type of cell division, of which task is to ensure the smooth transmission
of not reduced genetic information to daughter cells. During mitosis a complex
process of the division of cell nuclei precedes
the own division of a cell, during which number of chromosomes remains retained
in the daughter nuclei. (see http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mit%C3%B3za
)
3. All eukaryotic cells contain
mitochondria unlike prokaryotes. Mitochondria contain DNA, which is circular
and in this respect it is similar to DNA, that forms the chromosome of
prokaryotes.
4. Eukaryotic cell contain similarly
as prokaryotic the ribosomes, i.e. organelles, in which takes place a synthesis
of proteins. Unlike prokaryotes the eukaryotic ribosomes are of dual-type
(in the case of plants of three type):
a) cytoplasmatic ribosomes,
which are found in the cytoplasm and by its composition they are in some ways
different from the procaryotic ribosomes.
b) mitochondrial ribosomes,
which are in mitochondria and they have almost the same composition as procaryotic
cells.
5. In all eukaryotic cells there
is the transfer of genetic information in two tracks (three tracks at plants):
a) replication of DNA of nuclear chromosomes by transcription of this
DNA into larger molecules, so called precursor mRNA or pre-mRNA, which breaks
down into smaller molecules having a function of mRNA and translated on the
cytoplasmic ribosomes into primary structure of proteins;
b) replication of DNA of
mitochondria by its transcription into mRNA molecules translated on mitochondria
ribosomes into the primary structure of proteins.
At plants as a third track the
transmission of genetic information in chloroplasts participates (see below).
6. Translation is a
dual-type:
a) translation on
cytoplasmic ribosomes, during which similarly as at eubacteria as the first
amino acid into the primary structure of polypeptide chain the amino acid methionine
is sorted.
b) translation on mitochondrial
ribosomes, during which similarly as at eubacteria as the first amino acid
into the primary structure of the polypeptide chain the amino acid formylmethionine
is sorted.
7. Furthermore in eukaryotic
cells these structures are: endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi system, lysosomes.
For each of these components of eukaryotic cells is characteristic, that it is
separated from the cytoplasm by membrane.
Eukaryotes are divided into
three realms:
I. Plants (Plantae).
Part of their cells are next to mitochondria also chloroplasts. Chloroplasts contain
similarly as mitochondria the circular DNA, on which are located genes, that
control the synthesis of proteins required for the function of chloroplasts.
This synthesis is the same as for prokaryotes. The transmission of genetic
information in the chloroplasts is happening in this way: by the replication of
DNA of chloroplasts and its transcription into mRNA molecules added onto
chloroplast ribosomes into the primary structure of proteins. Similarly as prokaryotic cells the plant
cells are also covered by membrane known as a cell wall. Cell wall of plant
cells is unlike at prokaryotes composed of cellulose. Below the cell wall there
is a cytoplasmic membrane. The plants are mostly photolitotrophic (photoautotrophic)
organisms (trophic means nourishing tissue concerning organisms nutrition), of
which basic nutrient is carbon dioxide, from which in photosynthesis (photo
indicates a relationship to the light) they gain carbon for the synthesis of
starch as the storage subsatance.
II. Fungi (Fungi). The fungi
cells have a cell wall from chitin. They are heterotrophic and they contain mitochondria,
not chloroplasts.
III. Animals (Animalia).
Animal cells do not have a cell wall and they have only cytoplasmic membrane
and they do not contain chloroplasts. Their nutrition is heterotrophic.
Eukaryotes are the product of
a third evolutionary line (branch). All eukaryotes should be included into a
single realm with subrealms Fungi, Plantae and Animalia, which we classify
so far at the level of the realms. A number of groups of eukaryotic organisms (ciliates,
mycetozoa, etc.) derived from the main evolutionary line towards the animals,
fungi and plants and apparently each of them will constitute a separate subrealm.
It is expected that in the nearest future the system of organisms will be
adapted to the universal phylogenetic
tree.
Schematic model of
eukaryotic cells. 1-nucleolus; 2-nucleus; 3-ribosome; 4-vesicle; 5-rough
endoplasmic reticulum; 6-Golgi apparatus; 7-cytoskeleton; 8-smooth endoplasmic
reticulum; 9-mitochondria; 10-vacuole; 11-cytosol; 12-lysosome; 13-centriole
(see http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eukaryotick%C3%A1_bu%C5%88ka
, MesserWoland and Szczepan1990 , 15.10.2008, file: Biological cell. svg)
5.4. ESSENCE OF THE EVOLUTION
OF LIVING SYSTEMS
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
In the context of biological
evolution there is the constant formation of some species, individuals and
virtually the termination of other species and individuals. It is a natural
selection, where only the best individuals, genetically well equipped,
survive and who proliferate also well.
The Universe is from the perspective of
Philosophy of Balance of physics a mobility field characterized by the
existence and by movement of particles
of different weights, or of zero weight. These particles collide with each
other and here I see the essence of all physical, chemical and biological
phenomena in our world.
The object of physics as a whole (formation
subagency of formation agency) is the movement. The object of chemistry as a whole (formation subagency of
formation agency) is the movement of electrons, or chemical reaction. The
object of biology as a whole (formation subagency of formation agency) is
particularly internal and external movement of biological macromolecules
(mainly proteins and nucleic acids) or the study of living systems. It is the
movement, which is the progress from general to specific scientific
disciplines, still more specific and more special phenomenon.
From the above it follows,
that also the subject of biology as the science about living systems is the
movement of particles, namely the movement of biological macromolecules.
It is from the perspective of Philosophy of Balance once again the mobility
field characterized by a certain interval of motion of particles. If we translate this idea to the common
denominator of all atomic structures, we can talk about the momentum of
protons, neutrons and electrons of biological macromolecules, i.e. organic
chemical substances.
It can be concluded, that with
the evolutionary development of advanced organisms more complex living
systems are formed. In my opinion the more complex system is characterized
by a larger number of units, of which it is composed, I mean cell
organelles, cells of tissues, organs and organisms. From the perspective of
Philosophy of Balance of physics the improved organisms are characterized by a
larger movement of biological macromolecules than simpler organisms. In the
above defined meaning we can say, that protons, neutrons and electrons of
improved organisms are characterized by higher mobility density than the
same particles of simpler organisms.
In this context it is
necessary to use a quantity a mobility density, or the amount of
movement or the size of momentum per unit of volume of the living system, as we
do not want to measure the size of organisms, but their evolutionary
perfection. Large organism is characterized by greater absolute momentum of the
above mentioned particles, but greater or lesser mobility density according to
the perfection of an organism.
Most of perfect organisms
consists of the same eukaryotic cells, so we can talk about the same,
or similar mobility density of these cells. Where is the difference of
organisms according to their evolutionary perfection, it is in their outer
movement, the complexity of tissues, organs, that form these cells.
Therefore we can talk about the differences especially in their external
momentum, mainly at similar organisms, which consist of similar quantity and a type
of biological macromolecules.
This mobility expression of
evolutionary perfection of the organism corresponds also to philosophical
teaching, which sees the main difference of living systems in their
movement, which does not come from the outside but from the inside of this
living system.
Each kind of living
organism represents so the mobility field of particles of a certain value
of the momentum. From the standpoint of biology then it represents a system of
electrons, neutrons and protons of biological macromolecules at a certain constant
value of the momentum of particles. Or also
at a specific average momentum
per one electron, proton and neutron of biological macromolecules.
Every living organism as a
mobility field in the momentum field of the Universe is so exposed to collision
with other momentum fields with other particles of different momentum.
The aim of an organism is then to maintain itself during these collisions. Maintaining
itself from the perspective of Philosophy of Balance of physics is then the conservation
of the living system as the movement of biological macromolecules, i.e.
momentum field at the specific value of the momentum of particles, and it's
through collisions with particles outside of the living system at a different
momentum.
This maintenance is done by
the energy or momentum supply (the link between the momentum and
energy was shown in the Philosophy of Balance of Physics) from
photosynthesis or food and liquids. Thus it increases the momentum of
biological macromolecules, which is reduced by collisions of particles of mostly
inorganic and also organic surroundings ofthe system. At the same time the
momentum of particles of living system increases through collisions of
particles, which have a greater momentum than the particles of a living system.
By oxidation we call an agency, in which a
reactant passes its electron, thus it reduces its overall local momentum,
however it increases its mobility density, reduction, in which a
reactant accepts an electron, thus it increases its overall local momentum, but
it reduces its mobility density. Oxidation and reduction occur mostly in one reaction and the resulting charge is then the same
or a zero. An example of a redox reaction is electrolysis. At
secondary batteries it is reversed process, oxidized electrons are reduced and
then they oxidize again.
Reactions in chemistry either
reduce mobility density of a reactant, then they are fundamentally synthesis reactions often caused
by the adoption of the electron through reduction, that will reduce the
momentum of a proton in the nucleus and thus also the energy density of the
reactant at the increase in its total energy, or momentum. The opposite are analytical
(decomposition) reactions, when mobility density of the reactant is
increased and consequently its instability and crashes and the stronghold of
bonds is reduced, often it is oxidation by the handover of electron,
thereby the momentum of the bound neutral protons and the pressure on the
disintegration of the reactant increase. The same targets can be achieved by
lowering energy, mobility density, virtually by cooling or with an inhibitor
(i.e. the substance with low mobility) and by warming or with a catalyst (i.e.
the substance with substantially higher momentum), which will increase the
energy of the reactant.
At the same time the reactions
are common, where at one substance of a
reactant the energy or mobility density increases and the total energy,
virtually momentum reduces and at the second substance vice versa. Analytical
(decomposition) reactions represent the influence of the next dimension of other
mass and other energy to our dimension in the form of contracoagency. Synthesis
(composition) reactions are own to our dimension in the
form of coagency.
In addition to chemical
reactions the interaction of particles
of an organism and particles of surroundings at different momentum occurs also
through the biological and physical movement. An example of a physical
movement is a bullet from a pistol and an example of biological motion e.g. an
attack of a virus.
In the context of biological
evolution only those survive, who can inherently adapt to the fight for life,
i.e. to maintain itself and to find a balance between composition and
decomposition processes in the way to be maintained a living system as the
mobility field of particles at a certain value of the momentum.
Biological evolution presents
the gradual interaction of various organisms as momentum fields with other
organisms as the momentum fields and momentum fields of inorganic surroundings.
It is the competition of momentum fields of the different values for momentum,
where the most stable mobility field survives. Stable mobility field
represents the balance between clashes with particles of greater and lesser
momentum while keeping its own values of momentum of particles.
It is logical, that to
maintain its own momentum are primarily predestined the systems of high
absolute value of momentum as the planets of the planetary system or large
animals, etc. Also the organisms, which are characterized by a high degree of
processing energy or momentum resources, which enables them to maintain a
relatively high mobility density of living organisms. Improved living
system as the mobility field of higher mobility density must be characterized
by improved way of the processing of energy, virtually momentum resources.
The cause of natural selection
in the form of collisions of momentum fields I see in the interaction of our
and the next dimension. In my opinion the next dimension represents mobility
field of particles at a speed greater than the speed of light. The intersection
between the next and our dimension represents then the light as a stream
of particles at zero rest mass-photons at the speed of light and absolute
vacuum. In my opinion the proof of the existence of a next dimension are then
black holes, as I have already stated and tried to prove in the Philosophy
of Balance of physics.
Particles of our and next
dimension increase thereby the momentum of the particles of our dimension by
constant collisions with them, thus this energy or momentum allows the
development of living organisms of higher mobility density or of improved
living systems. Our dimension as our Universe reduces then the momentum of particles
of momentum fields by its lower momentum.
Due to this continuous
increase and decrease in momentum of momentum fields of our and next dimension
occurs then constant creation of new advanced forms of organisms, or life,
which must resist however the struggle for life, the constant process of
formation and termination, creation and destruction caused by the speeding
forces of the other energy and other mass of the next dimension and the mass
and energy of our dimension (see Philosophy of Balance of physics, the
chapter Next dimension).
5.5 ESSENCE OF LIFE AND DEATH,
OR THE EVILS OF LIVING SYSTEMS
Definitions and relationships
(performance)
Living system or organism is, as I have
already said above in terms of the Philosophy of Balance of physics a mobility
field, i.e. the field of particles, possibly particles of zero weight
with certain momentum, which react with other particles of this momentum field
or even with surrounding particles, i.e. of other momentum fields, through
collisions. What distinguishes the momentum field of the living system from momentum
field of inanimate systems, it is its composition of particles, grouped into
biological macromolecules.
The goal of any living system
is to preserve itself, whether in the form of its own existence or in the form
of offsprings.
As I have already stated, the
preservation of itself assumes to find a balance between composition and
decomposition processes in order to maintain a living system as a mobility
field of particles at a certain value of the momentum. Or the maintaince of
a certain value of the momentum own to a living organism or to its
indispensable part or of intervals of momentum, in which organism or its part
can still survive, it is a prerequisite condition for conservation and the
existence of a living system or life of the organism.
It is logical, that to
maintain its own momentum the systems of high absolute value of momentum as large
animals are predestined primarily. Also the organisms, which are
characterized by a high degree of processing energy or momentum resources,
which enables them to maintain a relatively high mobility density of living
organisms. Improved living system as the mobility field at higher mobility density
is characterized by improved way of processing the energy or momentum
resources.
Organisms are constantly
exposed to competitive momentum fields of their surroundings, whether
inanimate or living nature, that through collisions of their particles either
increase or reduce the momentum of the particles of momentum field of living
system and thus they push them outside the value of the momentum, that suits best
to a given organism.
The cause of natural selection
in the form of collisions of momentum fields I see in interaction of the next
and our dimension. In my opinion the next dimension represents mobility
field of particles at a speed greater than the speed of light. The intersection
between the next and our dimension represents then the light as a stream of
particles at zero rest mass - of photons at the speed of light and absolute
vacuum. In my opinion the proof of the existence of a next dimension are black
holes, as I have already stated and tried to prove in the Philosophy of Balance
of physics.
Particles of our and next
dimension increase thereby the momentum of the particles of our dimension by
constant collisions with them, this energy or momentum allows thus the
development of living organisms of higher mobility density or of improved
living systems. Our dimension as our Universe reduces then the momentum of particles
of momentum fields by its lower momentum.
Due to this continuous
increase and decrease in momentum of momentum fields of our and next dimension
occurs then constant creation of new advanced forms of organisms, or life,
which must resist however the struggle for life, the constant process of
formation and termination, creation and destruction caused by the speeding
forces of the other energy and other mass of the next dimension and the slowing
mass and energy of our dimension (see Philosophy of Balance of physics, the
chapter Next dimension).
While keeping its momentum alive
organism uses energy, or momentum accepted in the form of food and liquids,
virtually nutrients from its surroundings. The more improved is the
organism, the better it uses its energy or momentum of accepted nutrients, not
only external momentum, but also internal momentum of the particles of these
nutrients in the form of complex chemical reactions, that, figuratively
speaking, push them to a life.
In addition to these external
sources of momentum coming into an organism from its surroundings the organisms
use apparently also inner energy or momentum of their building elements,
i.e. of biological macromolecules, that are, figuratively speaking, worn out
with the length of life or their internal momentum gets spend.
If there is a reduction or
an increase in momentum outside the existential interval of given living
organism or of its part, then the living organism dies or its part dies,
both as regards its external momentum as a result of lack of food or liquid
intake, virtually nutrients, or also, what concerns its internal momentum in
the form of weakening of the organism, for example by old age. An example of
such a change of momentum can be another organism, that invaded the given
organism and it changed the momentum of its parts, or it separates it from the
momentum field, as well as an inanimate object like a bullet shot from a gun, that
changesthe momentum of the organism by increasing its external momentum.
The influence of competing
momentum fields is manifested also in instincts, or the brain of man
or of other living system, who is also exposed to collisions with particles, that
change the momentum of his or her particles, virtually of chemical reactions in
the way, that it is incompatible with the momentum of other momentum fields
representing their living and nonliving surroundings. Thus a living system is forced
through mostly chemical reactions as chemical movement in the brain, virtually
through instincts to behavior, which is incompatible with a life of other
living systems.
In this sense it is necessary
to see the evil ideas of man as chemical reactions in the brain, as cerebral
partial mobility fields, when these fields are found outside the mobility values,
which are own to a man. In this sense, it is possible to understand also to
harmful mental processes in terms of psychology. Similarly it is in the case of
other living systems except it, that these other living systems are less able
to influence these processes alone by their will now.
Preserving and promoting of
wider application of own values of momentum often leads to incompatibility with
the values of momentum of other living systems, that get so outside the interval of their
existential values, virtually values, in which the living organism is still
able to survive.
At the same time it can be self-destructive
behavior, when a living system changes under the influence of competing
momentum fields its and its surroundings momentum in a way, that does not
correspond to its natural value of momentum, virtually momentum of its organs
and other parts, virtually it can cause a deflection of this momentum beyond
its existential interval, i.e. outside the values, in which this system is still
able to survive and live.
Organisms or their organs and
other parts are constantly exposed to competitive momentum fields of their
surroundings, whether inanimate or living nature, that either increase or
reduce by collisions of their particles the momentum of particles of momentum
field of living system and thus it pushes out the value of the momentum, which
best suits to a given organism.
In this sense the evil of
living systems shoud be seen in their death or in death of their parts, that is caused by
constant colliding with the wholes of lower and higher momentum. Organisms must
constantly fight for life by renewing their natural momentum by their self-regulatory
abilities. The organism, virtually its part suffers also, if this momentum
field gets off a value of their natural momentum.
To the removal of the evil of
living systems is needed for living systems to exist in the outer momentum
field, which is not incompatible with life, virtually outside the existential
mobility interval of any of these momentum fields, or any living system. Or it is
incompatible with them at a minimum possible extent even at the cost,
that these mobility fields will be outside their ideal interval,l at a price,
that they will allow the existence or the value, which is in an existential momentum
interval of all other momentum fields.
Due to the fact, that all mobility
fields, or alive and lifeless world are connected by collisions of their particles, so the disposal of one albeit
seemingly unneeded momentum field for a human may ultimately lead even for him
or her to the very harmful consequences, because there the regrouping of the
total momentum of the total momentum field of live and inanimate world occurrs,
while the total value of the momentum and energy does not change according
to the law of conservation of momentum and energy. Therefore each
intervention into the nature, which is not reversible, one must think throughfully.
Literature: http://www.novinky.cz/veda-skoly/279473-nasa-chce-dohnat-star-trek-a-cestovat-vesmirem-nadsvetelnou-rychlosti.html : pst, Novinky, 2012
POLAK, J.: Přehled
středoškolské matematiky. Prague, SPN, 1977
SVOBODA, et al.: Přehled
středoškolské fyziky. Prometheus, spol. s r.o., Prague, 2001.
VACIK, J. et al.: Přehled
středoškolské chemie. SPN-pedagogické nakladatelství, Inc., 1999.
ROZSYPAL, S.: Přehled biologie. Prague,
Scientia, spol. s r.o., 1998.
LADISLAV REJMAN, Dr., Slovník
cizích slov. Statní pedagogické nakladatelství, n.p., 2nd Edition, Prague,
1971.
Philosophy
of Balance or ORDER OF VICTORIOUS ARMY as biblical paradise in the world for
all living creatures by our own forces as commentary on Bible, Genesis, chapter
1-4
Genesis 1-4:26
King James Version (KJV)
1
1 In the beginning God created the heaven and the earth.
2 And the earth was
without form, and void; and darkness was upon the face of the deep. And the
Spirit of God moved upon the face of the waters.
3 And God said, Let
there be light: and there was light.
4 And God saw the
light, that it was good: and God divided the light from the darkness.
5 And God called the light Day, and the darkness he called Night. And the evening and the morning were the first day.
6 And God said, Let there be a firmament in the midst of the waters, and let it divide the waters from the waters.
7 And God made the firmament, and divided the waters which were under the firmament from the waters which were above the firmament: and it was so.
8 And God called the firmament Heaven. And the evening and the morning were the second day.
9 And God said, Let the waters under the heaven be gathered together unto one place, and let the dry land appear: and it was so.
10 And God called the dry land Earth; and the gathering together of the waters called he Seas: and God saw that it was good.
11 And God said, Let the earth bring forth grass, the herb yielding seed, and the fruit tree yielding fruit after his kind, whose seed is in itself, upon the earth: and it was so.
12 And the earth brought forth grass, and herb yielding seed after his kind, and the tree yielding fruit, whose seed was in itself, after his kind: and God saw that it was good.
13 And the evening and the morning were the third day.
14 And God said, Let there be lights in the firmament of the heaven to divide the day from the night; and let them be for signs, and for seasons, and for days, and years:
15 And let them be for lights in the firmament of the heaven to give light upon the earth: and it was so.
16 And God made two great lights; the greater light to rule the day, and the lesser light to rule the night: he made the stars also.
17 And God set them in the firmament of the heaven to give light upon the earth,
18 And to rule over the day and over the night, and to divide the light from the darkness: and God saw that it was good.
19 And the evening and the morning were the fourth day.
20 And God said, Let the waters bring forth abundantly the moving creature that hath life, and fowl that may fly above the earth in the open firmament of heaven.
21 And God created great whales, and every living creature that moveth, which the waters brought forth abundantly, after their kind, and every winged fowl after his kind: and God saw that it was good.
22 And God blessed them, saying, Be fruitful, and multiply, and fill the waters in the seas, and let fowl multiply in the earth.
23 And the evening and the morning were the fifth day.
24 And God said, Let the earth bring forth the living creature after his kind, cattle, and creeping thing, and beast of the earth after his kind: and it was so.
25 And God made the beast of the earth after his kind, and cattle after their kind, and every thing that creepeth upon the earth after his kind: and God saw that it was good.
26 And God said, Let us
make man in our image, after our likeness: and let them have dominion over
the fish of the sea, and over the fowl of the air, and over the cattle, and
over all the earth, and over every creeping thing that creepeth upon the earth.
27 So God created man in
his own image, in the image of God created he him; male and female created he
them.
28 And God blessed them,
and God said unto them, Be fruitful, and multiply, and replenish the earth, and
subdue it: and have dominion over the fish of the sea, and over the fowl of the
air, and over every living thing that moveth upon the earth.
29 And God said, Behold,
I have given you every herb bearing seed, which is upon the face of all the
earth, and every tree, in the which is the fruit of a tree yielding seed; to
you it shall be for meat.
30 And to every beast of
the earth, and to every fowl of the air, and to every thing that creepeth upon
the earth, wherein there is life, I have given every green herb for meat: and
it was so.
31 And God saw every
thing that he had made, and, behold, it was very good. And the evening and
the morning were the sixth day.
2
1 Thus the heavens and the earth were finished, and all the host
of them.
2 And on the seventh
day God ended his work which he had made; and he rested on the seventh day from
all his work which he had made.
3 And God blessed the seventh day, and sanctified it: because that in it he had rested from all his work which God created and made.
4 These are the generations of the heavens and of the earth when they were created, in the day that the Lord God made the earth and the heavens,
5 And every plant of the field before it was in the earth, and every herb of the field before it grew: for the Lord God had not caused it to rain upon the earth, and there was not a man to till the ground.
6 But there went up a mist from the earth, and watered the whole face of the ground.
7 And the Lord God formed man of the dust of the ground, and breathed into his nostrils the breath of life; and man became a living soul.
8 And the Lord God planted a garden eastward in Eden; and there he put the man whom he had formed.
9 And out of the ground made the Lord God to grow every tree that is pleasant to the sight, and good for food; the tree of life also in the midst of the garden, and the tree of knowledge of good and evil.
10 And a river went out of Eden to water the garden; and from thence it was parted, and became into four heads.
11 The name of the first is Pison: that is it which compasseth the whole land of Havilah, where there is gold;
12 And the gold of that land is good: there is bdellium and the onyx stone.
13 And the name of the second river is Gihon: the same is it that compasseth the whole land of Ethiopia.
14 And the name of the third river is Hiddekel: that is it which goeth toward the east of Assyria. And the fourth river is Euphrates.
15 And the Lord God took the man, and put him
into the garden of Eden to dress it and to keep it.
16 And the Lord God commanded the man, saying,
Of every tree of the garden thou mayest freely eat:
17 But of the tree of
the knowledge of good and evil, thou shalt not eat of it: for in the day that
thou eatest thereof thou shalt surely die.
18 And the Lord God said, It is not good that
the man should be alone; I will make him an help meet for him.
19 And out of the ground
the Lord God formed every beast of the field, and every fowl of
the air; and brought them unto Adam to see what he would call them: and
whatsoever Adam called every living creature, that was the name thereof.
20 And Adam gave names
to all cattle, and to the fowl of the air, and to every beast of the field; but
for Adam there was not found an help meet for him.
21 And the Lord God caused a deep sleep to fall
upon Adam, and he slept: and he took one of his ribs, and closed up the flesh
instead thereof;
22 And the rib, which
the Lord God had taken from man, made he a woman, and brought her
unto the man.
23 And Adam said, This
is now bone of my bones, and flesh of my flesh: she shall be called Woman,
because she was taken out of Man.
24 Therefore shall a man
leave his father and his mother, and shall cleave unto his wife: and they shall
be one flesh.
25 And they were both naked, the man and his wife, and were not ashamed.
3
1 Now the serpent was more subtil
than any beast of the field which the Lord God had made. And he said unto the woman, Yea, hath God said, Ye shall
not eat of every tree of the garden?
2 And the woman said
unto the serpent, We may eat of the fruit of the trees of the garden:
3 But of the fruit of
the tree which is in the midst of the garden, God hath said, Ye shall not eat
of it, neither shall ye touch it, lest ye die.
4 And the serpent said
unto the woman, Ye shall not surely die:
5 For God doth know
that in the day ye eat thereof, then your eyes shall be opened, and ye shall be
as gods, knowing good and evil.
6 And when the woman
saw that the tree was good for food, and that it was pleasant to the eyes, and
a tree to be desired to make one wise, she took of the fruit thereof, and did
eat, and gave also unto her husband with her; and he did eat.
7 And the eyes of them
both were opened, and they knew that they were naked; and they sewed fig leaves
together, and made themselves aprons.
8 And they heard the
voice of the Lord God
walking in the garden in the cool of the day: and Adam and his wife hid
themselves from the presence of the Lord God amongst the trees of the garden.
9 And the Lord God called unto
Adam, and said unto him, Where art thou?
10 And he said, I heard
thy voice in the garden, and I was afraid, because I was naked; and I hid
myself.
11 And he said, Who told
thee that thou wast naked? Hast thou eaten of the tree, whereof I commanded
thee that thou shouldest not eat?
12 And the man said, The
woman whom thou gavest to be with me, she gave me of the tree, and I did eat.
13 And the Lord God said unto the
woman, What is this that thou hast done? And the woman said, The serpent
beguiled me, and I did eat.
14 And the Lord God said unto the serpent,
Because thou hast done this, thou art cursed above all cattle, and above every
beast of the field; upon thy belly shalt thou go, and dust shalt thou eat
all the days of thy life:
15 And I will put enmity between thee and the
woman, and between thy seed and her
seed; it shall bruise thy head, and thou shalt bruise his heel.
16 Unto the woman he
said, I will greatly multiply thy sorrow and thy conception; in sorrow thou
shalt bring forth children; and thy desire shall be to thy husband, and he
shall rule over thee.
17 And unto Adam he
said, Because thou hast hearkened unto the voice of thy wife, and hast eaten of
the tree, of which I commanded thee, saying, Thou shalt not eat of it: cursed
is the ground for thy sake; in sorrow shalt thou eat of it all the days of thy
life;
18 Thorns also and
thistles shall it bring forth to thee; and thou shalt eat the herb of the
field;
19 In the sweat of thy
face shalt thou eat bread, till thou return unto the ground; for out of it wast
thou taken: for dust thou art, and unto dust shalt thou return.
20 And Adam called his
wife's name Eve; because she was the mother of all living.
21 Unto Adam also and to
his wife did the Lord God
make coats of skins, and
clothed them.
22 And the Lord God said, Behold, the man is
become as one of us, to know good and evil: and now, lest he put forth his
hand, and take also of the tree of life, and eat, and live for ever:
23 Therefore the Lord God sent him forth
from the garden of Eden, to till the ground from whence he was taken.
24 So he drove out the man; and he placed at the east of the garden of Eden Cherubims, and a flaming sword which turned every way, to keep the way of the tree of life.
4
1 And Adam knew Eve his wife; and she conceived, and bare Cain, and said, I have gotten a man
from the Lord.
2 And she again bare
his brother Abel. And Abel was a keeper (of sheep), but Cain was a tiller of
the ground.
3 And in process of time it came to pass, that Cain brought of the fruit of the ground an offering unto the Lord.
4 And Abel, he also brought of the firstlings of his flock and of the fat thereof. And the Lord had respect unto Abel and to his offering:
5 But unto Cain and to his offering he had not respect. And Cain was very wroth, and his countenance fell.
6 And the Lord said unto Cain, Why art thou wroth? and why is thy countenance fallen?
7 If thou doest well, shalt thou not be accepted? and if thou doest not well, sin lieth at the door. And unto thee shall be his desire, and thou shalt rule over him.
8 And Cain talked with
Abel his brother: and it came to pass, when they were in the field, that Cain rose up against Abel his brother, and slew him.
9 And the Lord said unto Cain,
Where is Abel thy brother? And he said, I know not: Am I my brother's keeper?
10 And he said, What
hast thou done? the voice of thy brother's blood crieth unto me from the
ground.
11 And now art thou
cursed from the earth, which hath opened her mouth to receive thy brother's
blood from thy hand;
12 When thou tillest the
ground, it shall not henceforth yield unto thee her strength; a fugitive and a
vagabond shalt thou be in the earth.
13 And Cain said unto
the Lord, My
punishment is greater than I can bear.
14 Behold, thou hast
driven me out this day from the face of the earth; and from thy face shall I be
hid; and I shall be a fugitive and a vagabond in the earth; and it shall come
to pass, that every one that findeth me shall slay me.
15 And the Lord said unto him,
Therefore whosoever slayeth Cain, vengeance shall be taken on him sevenfold.
And the Lord set
a mark upon Cain, lest any finding him should kill him.
16 And Cain went out
from the presence of the Lord,
and dwelt in the land of Nod, on the east of Eden.
17 And Cain knew his
wife;
and she conceived, and bare Enoch: and he builded a city, and called the name
of the city, after the name of his son, Enoch.
18 And unto Enoch was born Irad: and Irad begat Mehujael: and Mehujael begat Methusael: and Methusael begat Lamech.
19 And Lamech took unto him two wives: the name of the one was Adah, and the name of the other Zillah.
20 And Adah bare Jabal: he was the father of such as dwell in tents, and of such as have cattle.
21 And his brother's name was Jubal: he was the father of all such as handle the harp and organ.
22 And Zillah, she also bare Tubalcain, an instructer of every artificer in brass and iron: and the sister of Tubalcain was Naamah.
23 And Lamech said unto his wives, Adah and Zillah, Hear my voice; ye wives of Lamech, hearken unto my speech: for I have slain a man to my wounding, and a young man to my hurt.
24 If Cain shall be avenged sevenfold, truly Lamech seventy and sevenfold.
25 And Adam knew his wife again; and she bare a son, and called his name Seth: For God, said she, hath appointed me another seed instead of Abel, whom Cain slew.
26 And to Seth, to him also there was born a son; and he called his name Enos: then began men to call upon the name of the Lord.
http://www.biblegateway.com/passage/?search=Genesis%201:1-4:26&version=KJV